Enhanced Dissolution Efficiency of Tamoxifen Combined with Methacrylate Copolymers in Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solid Dispersions by Solvent Cast
2.3. Solid-State Characterizations
2.3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. TMX Equilibrium Solubility
2.5. Dissolution Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solid-State Characterizations
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared
3.3. TMX Equilibrium Solubility
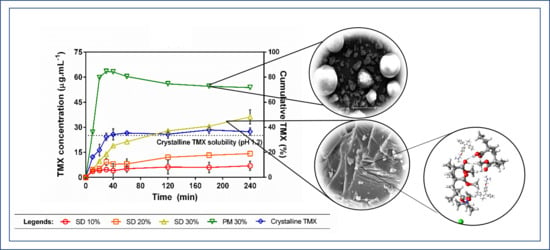
3.4. Dissolution Study under Non-Sink Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huh, W.J.; Khurana, S.S.; Geahlen, J.H.; Kohli, K.; Waller, R.A.; Mills, J.C. Tamoxifen Induces Rapid, Reversible Atrophy, and Metaplasia in Mouse Stomach. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 21–24.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendonsa, N.; Almutairy, B.; Kallakunta, V.R.; Sarabu, S.; Thipsay, P.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Manufacturing strategies to develop amorphous solid dispersions: An overview. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-W.; Baek, S.-H.; Lee, B.-J.; Jin, H.-E. Orodispersible Polymer Films with the Poorly Water-Soluble Drug, Olanzapine: Hot-Melt Pneumatic Extrusion for Single-Process 3D Printing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordhan, D.; Swainson, S.M.; Pearce, A.K.; Styliari, I.D.; Lovato, T.; Burley, J.C.; Garnett, M.C.; Taresco, V. Poly (Glycerol Adipate): From a Functionalized Nanocarrier to a Polymeric-Prodrug Matrix to Create Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Taylor, L.S. Dissolution Performance of High Drug Loading Celecoxib Amorphous Solid Dispersions Formulated with Polymer Combinations. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, W.M.; Obeidat, S.M.; Al-Zoubi, N. Investigations on the Physical Structure and the Mechanism of Drug Release from an Enteric Matrix Microspheres with a Near-Zero-Order Release Kinetics Using SEM and Quantitative FTIR. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.D.; Lee, P.I. Haste Makes Waste: The Interplay Between Dissolution and Precipitation of Supersaturating Formulations. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawar, J.; Tayade, A.; Gangurde, A.; Moravkar, K.; Amin, P.D. Solubility and dissolution enhancement of efavirenz hot melt extruded amorphous solid dispersions using combination of polymeric blends: A QbD approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 88, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, M.; Parvez, K.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Revuri, V.; Khan, H.A.; Feng, X.; Lee, Y.-K. Bioapplication of graphene oxide derivatives: Drug/gene delivery, imaging, polymeric modification, toxicology, therapeutics and challenges. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 42141–42161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdair, A.; Hamad, I.; Alkhatib, H.; Bustanji, Y.; Mohammad, M.; Tayem, R.; Aiedeh, K. Modified-chitosan nanoparticles: Novel drug delivery systems improve oral bioavailability of doxorubicin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Leung, A.W.; Hua, H.; Xu, C.S. pH-responsive polymer–drug conjugates: Design and progress. J. Control. Release 2016, 222, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louage, B.; Nuhn, L.; Risseeuw, M.D.; Vanparijs, N.; De Coen, R.; Karalic, I.; Van Calenbergh, S.; De Geest, B.G. Well-Defined Polymer-Paclitaxel Prodrugs by a Grafting-from-Drug Approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11791–11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Deeba, F.; Priyadarshi, R.; Bano, S.; Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.S. Development of novel cross-linked carboxymethyl cellulose/poly(potassium 1-hydroxy acrylate): Synthesis, characterization and properties. Polym. Bull. 2019, 77, 4555–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séon-Lutz, M.; Couffin, A.-C.; Vignoud, S.; Schlatter, G.; Hébraud, A. Electrospinning in water and in situ crosslinking of hyaluronic acid / cyclodextrin nanofibers: Towards wound dressing with controlled drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Caves, J.M.; Ravi, S.; Li, W.; Chaikof, E.L. Effects of crosslinking on the mechanical properties, drug release and cytocompatibility of protein polymers. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falde, E.J.; Freedman, J.D.; Herrera, V.L.; Yohe, S.T.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Layered superhydrophobic meshes for controlled drug release. J. Control. Release 2015, 214, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhijjaj, M.; Belton, P.; Qi, S. An investigation into the use of polymer blends to improve the printability of and regulate drug release from pharmaceutical solid dispersions prepared via fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustafin, R.I. Interpolymer combinations of chemically complementary grades of Eudragit copolymers: A new direction in the design of peroral solid dosage forms of drug delivery systems with controlled release (review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, J.; Walther, M.; Macrae, R.; Bodmeier, R. Polymer blends for controlled release coatings. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, R.; Leopold, C. Coatings from blends of Eudragit® RL and L55: A novel approach in pH-controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, B.J.; Bergström, C.A.; Vinarov, Z.; Kuentz, M.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P.; Brandl, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; et al. Successful oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs both depends on the intraluminal behavior of drugs and of appropriate advanced drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Rigo, M.V.; Olivera, M.E.; Rubio, M.; Manzo, R.H. Enhanced intestinal permeability and oral bioavailability of enalapril maleate upon complexation with the cationic polymethacrylate Eudragit E100. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nollenberger, K.; Albers, J. Poly(meth)acrylate-based coatings. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Da Da Ana, R.; Souto, S.B.; Zielinska, A.; Marques, C.; Andrade, L.N.; Horbańczuk, O.K.; Atanasov, A.G.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; et al. In Vitro Characterization, Modelling, and Antioxidant Properties of Polyphenon-60 from Green Tea in Eudragit S100-2 Chitosan Microspheres. Nutrients 2020, 12, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tambosi, G.; Coelho, P.F.; Luciano, S.; Lenschow, I.C.S.; Zétola, M.; Stulzer, H.K.; Pezzini, B.R. Challenges to improve the biopharmaceutical properties of poorly water-soluble drugs and the application of the solid dispersion technology. Matéria 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Javed, F.; Othman, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Star-shaped self-assembled micelles of block copolymer [chitosan-co-poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate] hydrogel for hydrophobic drug delivery. Polym. Bull. 2017, 75, 2243–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Domokos, A.; Farkas, A.; Démuth, B.; Borbás, E.; Nagy, B.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Controlled-release solid dispersions of Eudragit® FS 100 and poorly soluble spironolactone prepared by electrospinning and melt extrusion. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Tran, P.H.-L. Controlled Release Film Forming Systems in Drug Delivery: The Potential for Efficient Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehghani, F.; Farhadian, N.; Golmohammadzadeh, S.; Biriaee, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Karimi, M. Preparation, characterization and in-vivo evaluation of microemulsions containing tamoxifen citrate anti-cancer drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.D.; Ju, T.-C.R.; Lee, P.I. Enhanced kinetic solubility profiles of indomethacin amorphous solid dispersions in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueirêdo, C.B.M.; Nadvorny, D.; Vieira, A.C.Q.D.M.; Soares-Sobrinho, J.L.; Neto, P.J.R.; Lee, P.I.; Soares, M.F.D.L.R. Enhancement of dissolution rate through eutectic mixture and solid solution of posaconazole and benznidazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamberini, M.C.; Baraldi, C.; Tinti, A.; Palazzoli, F.; Ferioli, V. Vibrational study of tamoxifen citrate polymorphism. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 840, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Singh, D.; Sirkar, K.K.; Pfeffer, R. Continuous preparation of polymer coated drug crystals by solid hollow fiber membrane-based cooling crystallization. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dereymaker, A.; Cinghia, G.; Mooter, G.V.D. Eudragit® RL as a stabilizer for supersaturation and a substrate for nanocrystal formation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altmeyer, C.; Karam, T.K.; Khalil, N.M.; Mainardes, R.M. Tamoxifen-loaded poly(L-lactide) nanoparticles: Development, characterization and in vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, T.; Gupta, S.S.; Meena, A.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Investigation of thermal and viscoelastic properties of polymers relevant to hot melt extrusion—III: Polymethacrylates and polymethacrylic acid based polymers. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2014, 5, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Indulkar, A.S.; Lou, X.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Insights into the Dissolution Mechanism of Ritonavir–Copovidone Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Importance of Congruent Release for Enhanced Performance. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Su, L.; Li, N.; Hu, Y.; Tang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Z. Understanding the mechanism of dissolution enhancement for poorly water-soluble drugs by solid dispersions containing Eudragit® E PO. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.R.; Lee, P.I. Effect of Extent of Supersaturation on the Evolution of Kinetic Solubility Profiles. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 14, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| System | pH 1.2 | pH 7.4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (µg·mL−1) | AUC | DE (%) * | Cmax (µg·mL−1) | AUC | DE (%) * | |
| SD 10% | 6.9 | 1328 | 7.38 | 57.9 | 13,600 | 4.72 |
| SD 20% | 14.2 | 2572 | 14.29 | 321 | 68,209 | 23.68 |
| SD 30% | 36.2 | 6014 | 33.41 | 345.5 | 86,764 | 30.13 |
| PM 30% | 63.4 | 13,106 | 72.81 | 369.3 | 118,962 | 41.31 |
| TMX | 28.4 | 6051 | 33.62 | 216.9 | 54,718 | 19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
T. C. da Silva, D.; Nadvorny, D.; Danda, L.J.d.A.; Vieira, A.C.Q.d.M.; Severino, P.; Soares, M.F.L.R.; Soares-Sobrinho, J.L.; Souto, E.B. Enhanced Dissolution Efficiency of Tamoxifen Combined with Methacrylate Copolymers in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Crystals 2020, 10, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111046
T. C. da Silva D, Nadvorny D, Danda LJdA, Vieira ACQdM, Severino P, Soares MFLR, Soares-Sobrinho JL, Souto EB. Enhanced Dissolution Efficiency of Tamoxifen Combined with Methacrylate Copolymers in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Crystals. 2020; 10(11):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111046
Chicago/Turabian StyleT. C. da Silva, Dayanne, Daniela Nadvorny, Lucas J. de A. Danda, Amanda C. Q. de M. Vieira, Patricia Severino, Monica F. La R. Soares, José L. Soares-Sobrinho, and Eliana B. Souto. 2020. "Enhanced Dissolution Efficiency of Tamoxifen Combined with Methacrylate Copolymers in Amorphous Solid Dispersions" Crystals 10, no. 11: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111046
APA StyleT. C. da Silva, D., Nadvorny, D., Danda, L. J. d. A., Vieira, A. C. Q. d. M., Severino, P., Soares, M. F. L. R., Soares-Sobrinho, J. L., & Souto, E. B. (2020). Enhanced Dissolution Efficiency of Tamoxifen Combined with Methacrylate Copolymers in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Crystals, 10(11), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111046