Effect of Sn and Mo on Microstructure and Electrochemical Property of TiZrTaNb High Entropy Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- The microstructure of TiZrTaNb, TiZrTaNbMo and TiZrTaNbSn alloys is dendrite with single BCC structures. The addition of Mo and Sn elements promotes dendrite growth and interdendritic segregation.
- The Ta, Mo elements are mainly enriched in dendrite and Zr, Ti, Nb, Sn elements are mainly distributed in the interdendritic in high entropy alloys, which is attributed to the different equilibrium distribution coefficients.
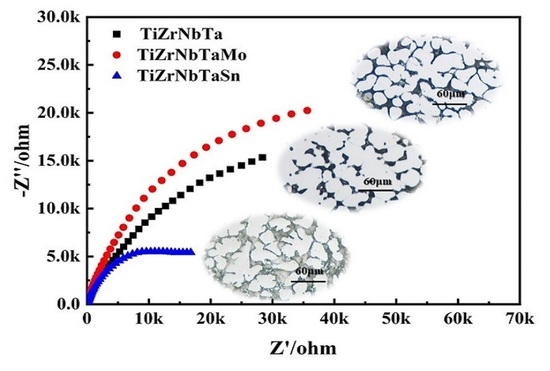
- The TiZrTaNiMo alloy shows excellent corrosion property according to the corrosion parameters Icorr, φcorr, Ipass. The corrosion property of the TiZrTaNb alloy deteriorated after the addition of Sn element and this is attributed to the interdendritic segregation of Sn element.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Y.; Shen, Y.F.; Jia, N.; Liaw, P.K. C and N doping in high-entropy alloys: A pathway to achieve desired strength-ductility synergy. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 25, 101162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, Y.V.; Jaiswal, U.K.; Rahul, M.R. Machine learning approach to predict new multiphase high entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2021, 197, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.X.; Jiang, S.C.; Huang, T.; Qin, M.D.; Hu, T.; Luo, J. Single-phase high-entropy intermetallic compounds (HEICs): Bridging high-entropy alloys and ceramics. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, Y.; Li, G.Q.; Liang, X.B.; Peng, H.Y. Fine-grained FeCoNi(CuAl)(x) high entropy alloys: Phase transformation, microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 537812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.S.; Schweidler, S.; Botros, M.; Fu, T.T.; Hahn, H.; Brezesinski, T.; Breitung, B. High-entropy energy materials: Challenges and new opportunities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2883–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, W.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.S.; Li, D.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Yu, H.L.; Lai, Z.H. Effect of aluminum content on microstructure and wear resistance of CuCrFeMnTiAlx high-entropy alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2011, 40, 550–554. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.K.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Martini, A.; Zhang, C. Effect of carbon content on microstructure, hardness and wear resistance of CoCrFeMnNiCx high-entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 847, 156533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.L.; Curtin, W.A. Origin of high strength in the CoCrFeNiPd high-entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2020, 8, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, C.Y.; Axinte, E.; Ge, W.J.; Zhang, Z.T.; Wang, Y. High-entropy alloy coatings with excellent mechanical, corrosion resistance and magnetic properties prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing sintering. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Xu, J. (TiZrNbTa)-Mo high-entropy alloys: Dependence of microstructure and mechanical properties on Mo concentration and modeling of solid solution strengthening. Intermetallics 2018, 95, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletia, R.R.; Stepanova, N.; Yurchenko, N.; Zherebtsov, S.; Marescab, F. Cross-kink unpinning controls the medium- to high-temperature strength of body-centered cubic NbTiZr medium-entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2021, 209, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleti, R.R.; Stepanov, N.; Yurchenko, N.; Klimenko, D.; Zherebtsov, S. Plastic deformation of solid-solution strengthened Hf-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr body-centered cubic medium/high-entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2021, 200, 113927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Qian, M.; Shi, Z.; Song, T.; Huang, L.; Zou, J. A novel quaternary equiatomic Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta medium entropy alloy (MEA). Intermetallics 2018, 101, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.Q.; Liu, Y.; Min, L.J.; Lai, Z.H.; Han, T.Y.; Yang, D.N.; Zhu, J.C. Alloying effect on phase stability, elastic and thermodynamic properties of Nb-Ti-V-Zr high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 101, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todai, M. Novel TiNbTaZrMo high-entropy alloys for metallic biomaterials. Scr. Mater. 2017, 129, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C.; Springer, H.; Bausch, M. From high-entropy alloys to high-entropy steels. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Abdulahad, S.; Kang, B.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Corrosion resistance of weight reduced AlxCrFeMoV high entropy alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.Y.; Axinte, E.; Sun, J.; Li, X.T.; Li, P.; Du, J.W.; Qiao, P.C.; Wang, Y. CoCrFeNi(W1-xMox) high-entropy alloy coatings with excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hu, L.N.; Ma, L.Q.; Shen, X.D. Electrochemical properties of Co-S/x wt.% AB(5) composite materials. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2015, 58, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Alloy | Icorr/A·cm−2 | φcorr/V | Ipass/A·cm−2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiZrTaNb | 7.08 × 10−7 | −0.87 | 4.12 × 10−2 |
| TiZrTaNbMo | 5.5 × 10−7 | −0.499 | 1.02 × 10−3 |
| TiZrTaNbSn | 7.87 × 10−7 | −0.828 | 5.2 × 10−2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Ma, T.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Zhu, D. Effect of Sn and Mo on Microstructure and Electrochemical Property of TiZrTaNb High Entropy Alloys. Crystals 2021, 11, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121527
Li Q, Ma T, Jin Y, Wang X, Dong D, Zhu D. Effect of Sn and Mo on Microstructure and Electrochemical Property of TiZrTaNb High Entropy Alloys. Crystals. 2021; 11(12):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121527
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiaoyu, Tengfei Ma, Yuliang Jin, Xiaohong Wang, Duo Dong, and Dongdong Zhu. 2021. "Effect of Sn and Mo on Microstructure and Electrochemical Property of TiZrTaNb High Entropy Alloys" Crystals 11, no. 12: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121527
APA StyleLi, Q., Ma, T., Jin, Y., Wang, X., Dong, D., & Zhu, D. (2021). Effect of Sn and Mo on Microstructure and Electrochemical Property of TiZrTaNb High Entropy Alloys. Crystals, 11(12), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121527