Innovative Method for the Mass Preparation of α″-Fe16N2 Powders via Gas Atomization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
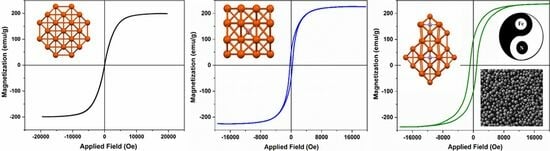
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCallum, R.; Lewis, L.; Skomski, R.; Kramer, M.; Anderson, I. Practical Aspects of Modern and Future Permanent Magnets. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2014, 44, 451–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Perspective and Prospects for Rare Earth Permanent Magnets. Engineering 2020, 6, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, G.; Barucca, G.; Kaidatzis, A.; Psycharis, V.; Salikhov, R.; Farle, M.; Koutsoufakis, E.; Niarchos, D.; Mehta, A.; Scuderi, M.; et al. L10-FeNi flms on Au-Cu-Ni bufer-layer: A high-throughput combinatorial study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Suh, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Choi-Yim, H. Properties of a rare earth free L10-FeNi hard magnet developed through annealing of FeNiPC amorphous ribbons. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2019, 19, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.A.; Tang, W.; Liu, X.; Nolte, A.I.; Ouyang, G.; Dennis, K.W.; Cui, J. Optimizing composition in MnBi permanent magnet alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 181, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Choi, J.P.; Li, G.; Polikarpov, E.; Darsell, J.; Overman, N.; Olszta, M.; Schreiber, D.; Bowden, M.; Droubay, T.; et al. Thermal stability of MnBi magnetic materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 064212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, T.; Murgulescu, I.-I.; Ababei, G.; Stoian, G.; Lostun, M.; Porcescu, M.; Grigoras, M.; Lupu, N. Facile method of raising the LTP content in Mn-Bi alloys by using sequential separation techniques for Bi and Mn. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odkhuu, D.; Hong, S.C. Simultaneous tuning of the magnetic anisotropy and thermal stability of α″-phase Fe16N2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochirkhuyag, T.; Hong, S.C.; Odkhuu, D. First-Principles Prediction of Enhanced Magnetic Anisotropy of α″-Phase Fe16N2 with B and C Impurities. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 7000103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Allard, L.F.; Lara-Curzio, E.; Wang, J.-P. N site ordering effect on partially ordered Fe16N2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 092506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, M.; Jamali, M.; Shi, F.; Kang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Okatov, S.; Faleev, S.; et al. Heavy-Metal-Free, Low-Damping, and Non-Interface Perpendicular Fe16N2 Thin Film and Magnetoresistance Device. Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 1900089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, B.; Lauter, V.; Wang, J.-P. Epitaxial Fe16N2 thin film on nonmagnetic seed layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 192402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Nomura, K.; Wang, J.-P. New insight on the Mössbauer spectra for Fe16N2 thin films with high saturation magnetization. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, 120907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Mehedi, M.A.; Fu, E.; Wang, Y.; Allard, L.F.; Wang, J.-P. Synthesis of Fe16N2 compound Free-Standing Foils with 20 MGOe Magnetic Energy Product by Nitrogen Ion-Implantation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.-P. Synthesis of α″-Fe16N2 foils with an ultralow temperature coefficient of coercivity for rare-earth-free magnets. Acta Mater. 2020, 184, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dabade, V.; Allard, L.F.; Lara-Curzio, E.; James, R.; Wang, J.-P. Synthesis of α′′−Fe16N2 Compound Anisotropic Magnet by the Strained-Wire Method. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 6, 024013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.-P. Synthesis of α″-Fe16N2 ribbons with a porous structure. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kuang, Q.; Men, X.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Choi, C.; Zhang, Z. Anisotropic Growth and Magnetic Properties of α″-Fe16N2@C Nanocones. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirba, I.; Schwöbel, C.A.; Diop, L.V.B.; Duerrschnabel, M.; Molina-Luna, L.; Hofmann, K.; Komissinskiy, P.; Kleebe, H.-J.; Gutfleisch, O. Synthesis, morphology, thermal stability and magnetic properties of α″-Fe16N2 nanoparticles obtained by hydrogen reduction of γ-Fe2O3 and subsequent nitrogenation. Acta Mater. 2017, 123, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, W.; Peng, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Hong, B.; Jin, H.; Jin, D.; Ge, H. Synthesis of fine a α″-Fe16N2 powders by low-temperature nitridation of α-Fe from magnetite nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Lauter, V.; Zhang, X.; Ambaye, H.; Wang, J.-P. Strain induced giant magnetism in epitaxial Fe16N2 thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 072411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Suri, P.K.; Kennedy, G.; Thadhani, N.N.; Flannigan, D.J.; Wang, J.-P. Preparation of an α″-Fe16N2 Magnet via a Ball Milling and Shock Compaction Approach. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, J.; Yi, S. Iron nitride based magnetic powder synthesized by mechanical alloying of Fe-based glassy powders and solid nitrogen compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 539, 168329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobise, M.; Saito, S. Synthesis of α″-(Fe,M)16N2 Nanoparticles Obtained by Hydrogen Reduction and Subsequent Nitridation Starting From α-(Fe,M)OOH (M = Co, Al). IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, T.; Li, Q.; Horie, S.; Tameka, A.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. High-purity core-shell α″-Fe16N2/Al2O3 nanoparticles synthesized from α-hematite for rare-earth-free magnet applications. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhijah, R.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Okuyama, K. Effect of oxidation on α″-Fe16N2 phase formation from plasma-synthesized spherical core–shell α-Fe/Al2O3 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhijah, R.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Okuyama, K. Gas phase preparation of spherical core–shell α′′-Fe16N2/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6467–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antipas, G.S.E. Review of gas atomisation and spray forming phenomenology. Powder Met. 2013, 56, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassym, K.; Perveen, A. Atomization processes of metal powders for 3D printing. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Fang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y. Review of the Methods for Production of Spherical Ti and Ti Alloy Powder. JOM 2017, 69, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarriegui, G.; Martín, J.; Burgos, N.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukov, A.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of particle size on grain growth of Nd-Fe-B powders produced by gas atomization. Mater. Charact. 2022, 187, 111824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, M.; Lostun, M.; Stoian, G.; Ababei, G.; Porcescu, M.; Lupu, N. The Influence of Preparation Parameters on the Morphology and Magnetic Properties of Fe-N Powders Obtained by the Gas Atomization Method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, K.H. The occurrence and the crystal structure of α″-iron nitride; a new type of interstitial alloy formed during the tempering of nitrogen-martensite. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1951, 208, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, K. The synthesis and characterization of bulk α″-Fe16N2. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 222, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieverts, A.; Zapf, G. Eisen und Stickstoff. Z. Phys. Chem. 1935, 172, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Kameoka, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; Takanashi, K.; Tsai, A.-P. FeNi and Fe16N2 Magnets Prepared Using Leaching. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoras, M.; Lostun, M.; Porcescu, M.; Stoian, G.; Ababei, G.; Lupu, N. Innovative Method for the Mass Preparation of α″-Fe16N2 Powders via Gas Atomization. Crystals 2023, 13, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13111578
Grigoras M, Lostun M, Porcescu M, Stoian G, Ababei G, Lupu N. Innovative Method for the Mass Preparation of α″-Fe16N2 Powders via Gas Atomization. Crystals. 2023; 13(11):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13111578
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoras, Marian, Mihaela Lostun, Marieta Porcescu, George Stoian, Gabriel Ababei, and Nicoleta Lupu. 2023. "Innovative Method for the Mass Preparation of α″-Fe16N2 Powders via Gas Atomization" Crystals 13, no. 11: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13111578
APA StyleGrigoras, M., Lostun, M., Porcescu, M., Stoian, G., Ababei, G., & Lupu, N. (2023). Innovative Method for the Mass Preparation of α″-Fe16N2 Powders via Gas Atomization. Crystals, 13(11), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13111578