PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels with Excellent Swelling Behavior and Enhanced Mechanical Performance: Preparation and Drug Release of 5-Fluorouracil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Swelling Equilibrium of the PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels
2.5. Mechanical Performance Test
2.6. Drug Release Behavior of 5-Fluorouracil
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.2. Interior Morphology
3.3. Volume Phase Transition Behavior
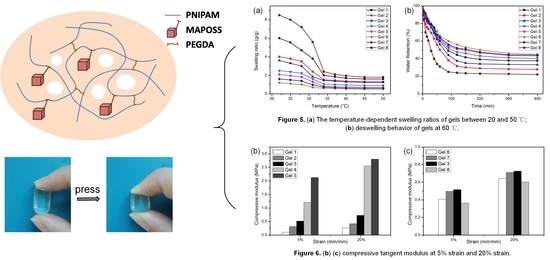
3.4. Swelling and Deswelling Behavior
3.5. Mechanical Performance
3.6. Drug Release of 5-Fluorouracil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, N.N.; Ravindra, S.; Reddy, N.M.; Rajinikanth, V.; Raju, K.M.; Vallabhapurapu, V.S. Temperature responsive hydrogel magnetic nanocomposites for hyperthermia and metal extraction applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 394, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio, O.G.; Pizarro, G.D.C.; Jeria-Orell, M.; Geckeler, K.E. Swelling behavior and metal ion retention from aqueous solution of hydrogels based onN-1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone andn-hydroxymethylacrylamide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, O.; Gidon, D.; Kizilel, S. Visible-light-induced synthesis of pH-responsive composite hydrogels for controlled delivery of the anticonvulsant drug pregabalin. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhu, J. Full-color photonic hydrogels for pH and ionic strength sensing. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 83, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Song, J. Electroresponsive behavior of a sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel and its application to electrodriven artificial fish. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Temperature and magnetism bi-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers: Preparation, adsorption mechanism and properties as drug delivery system for sustained release of 5-fluorouracil. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 61, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; He, T.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, L.; Ma, S. Adsorption dynamics, diffusion and isotherm models of poly(NIPAM/LMSH) nanocomposite hydrogels for the removal of anionic dye amaranth from an aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124–125, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JagadeeshBabu, P.E.; Suresh Kumar, R.; Maheswari, B. Synthesis and characterization of temperature sensitive P-NIPAM macro/micro hydrogels. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.; Sarker, P.; Rimmer, S.; Swanson, L.; MacNeil, S.; Douglas, I. Hyperbranched poly(NIPAM) polymers modified with antibiotics for the reduction of bacterial burden in infected human tissue engineered skin. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, R.; Baby, D.K.; Kumar, D.S. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel: Effect of hydrophilicity on controlled release of ibuprofen at different pH. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 5079–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.K.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, J.-C. Release property of microgels formed by electrostatic interaction between poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-dimethylaminoethylmethacrylate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.-C. Release behavior of freeze-dried alginate beads containing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, L.; Dan, Y. Preparation and thermal response behavior of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-a crylic acid) microgels via soap-free emulsion polymerization based on aibn initiator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 3322–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, V.V.A.; Tepale, N.; Sánchez-Díaz, J.C.; Mendizábal, E.; Puig, J.E.; Soltero, J.F.A. Thermoresponsive nanostructured poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels made via inverse microemulsion polymerization. Coll. Polym. Sci. 2005, 284, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.A.D.; Pinto, V.D.; Costa, R.A.S.; Dias, R.C.S.; Hernándes-Ortiz, J.C.; Costa, M.R.P.F.N. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels synthesis using free radical and RAFT polymerization. Macromol. Symp. 2013, 333, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Lyon, A.L. Tunable swelling kinetics in core-shell hydrogel nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7511–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kim, N.H.; Hui, D.; Rhee, K.Y.; Lee, J.H. Improved mechanical and swelling behavior of the composite hydrogels prepared by ionic monomer and acid-activated Laponite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Du, X.; Deng, J.; Yang, W. Synthesis of optically active macroporous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with helical poly(N-propargylamide) for chiral recognition of amino acids. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennerfeldt, D.A.; Renth, A.N.; Talata, Z.; Gehrke, S.H.; Detamore, M.S. Tuning mechanical performance of poly(ethylene glycol) and agarose interpenetrating network hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8241–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.; Clay, N.E.; Qin, E.C.; Sullivan, K.M.; Kim, D.H.; Kong, H. In situ assembly of the collagen–polyacrylamide interpenetrating network hydrogel: Enabling decoupled control of stiffness and degree of swelling. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, P.R.; Mantravadi, R.; Jimenez, J.C.; Dikin, D.A.; Wunder, S.L. Lamellar, micro-phase separated blends of methyl cellulose and dendritic polyethylene glycol, POSS-PEG. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.; Sachan, A.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Feller, J.F. Spray layer-by-layer assembly of POSS functionalized CNT quantum chemo-resistive sensors with tuneable selectivity and ppm resolution to VOC biomarkers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fredericks, P.M.; Haddad, A.; Hill, D.J.T.; Rasoul, F.; Whittaker, A.K. Hydrolytic degradation of POSS–PEG–lactide hybrid hydrogels. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, K.; Zheng, S. Hepta(3,3,3-trifluoropropyl) polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-capped poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) telechelics: Synthesis and behavior of physical hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.K.; Varanasi, S.; Strounina, E.; Hill, D.J.; Symons, A.L.; Whittaker, A.K.; Rasoul, F. Synthesis and characterization of a POSS-PEG macromonomer and POSS-PEG-PLA hydrogels for periodontal applications. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Yang, W.; Li, A.; Hou, J.; Zhang, C. Effects of incorporating acrylolsobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane on the properties of p(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate) hybrid hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2016, 74, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Chen, L. Nanocomposite hydrogels with rapid thermal-responsibility by using surfactant detergent as template. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 58, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, S. Organic-inorganic hybrid hydrogels involving poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane: Preparation and rapid thermoresponsive properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiong, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, X. Swelling, mechanical and friction properties of PVA/PVP hydrogels after swelling in osmotic pressure solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 65, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hongyan, W. Synthesis of chitosan-based nanohydrogels for loading and release of 5-fluorouracil. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 490, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.D.; Guerrero, S.; Benito, M.; Fernández, A.; Teijón, C.; Olmo, R.; Katime, I.; Teijón, J.M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a folate-targeted copolymeric submicrohydrogel based on N-isopropylacrylamide as 5-fluorouracil delivery system. Polymers 2011, 3, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.L.; Lin, K.M.; Hsiue, G.H. Preparation and characterization of intelligent core-shell nanoparticles based on poly(d,l-lactide)-g-poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide-co-methacrylic acid). J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.; Gomes, C.P.; Dias, R.C.S.; Costa, M.R.P.F.N. Molecular imprinting of 5-fluorouracil in particles with surface RAFT grafted functional brushes. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 107, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, Y.; Nakano, M.; Juni, K.; Arita, T. Physical properties of pyrimidine and purine antimetabolites. I. The effects of salts and temperature on the solubility of 5-fluorouracil, 1-(2-tetrahydrofuryl)-5-fluorouracil, 6-mercaptopurine, and thioinosine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 1654–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sample | Gels Formulation (g) 1 | MAPOSS (wt %) | LCST (°C) 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPOSS | PEG | |||
| Gel 1 | 0 | 0.10 | 0 | 31.1 |
| Gel 2 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 4.35 | 31.1 |
| Gel 3 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 8.33 | 31.1 |
| Gel 4 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 15.38 | 29.4 |
| Gel 5 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 21.43 | 28.5 |
| Gel 6 | 0.10 | 0 | 8.33 | 31.1 |
| Gel 7 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 8.33 | 31.1 |
| Gel 8 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 8.33 | 31.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Hou, X.; Qu, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, C. PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels with Excellent Swelling Behavior and Enhanced Mechanical Performance: Preparation and Drug Release of 5-Fluorouracil. Polymers 2018, 10, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020137
Li P, Hou X, Qu L, Dai X, Zhang C. PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels with Excellent Swelling Behavior and Enhanced Mechanical Performance: Preparation and Drug Release of 5-Fluorouracil. Polymers. 2018; 10(2):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020137
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peihong, Xiaoman Hou, Lijie Qu, Xueyan Dai, and Chunling Zhang. 2018. "PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels with Excellent Swelling Behavior and Enhanced Mechanical Performance: Preparation and Drug Release of 5-Fluorouracil" Polymers 10, no. 2: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020137
APA StyleLi, P., Hou, X., Qu, L., Dai, X., & Zhang, C. (2018). PNIPAM-MAPOSS Hybrid Hydrogels with Excellent Swelling Behavior and Enhanced Mechanical Performance: Preparation and Drug Release of 5-Fluorouracil. Polymers, 10(2), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020137