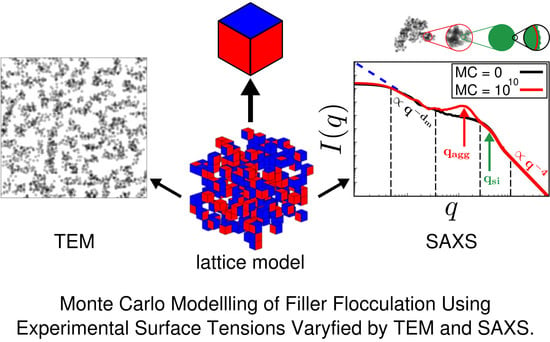
Modelling Filler Dispersion in Elastomers: Relating Filler Morphology to Interface Free Energies via SAXS and TEM Simulation Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monte Carlo Flocculation
2.2. Surface Tensions
2.3. Calculation of TEM Pictures and SAXS Intensities
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SA(X)S | small angle (X-ray) scattering |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| BR | polybutadiene rubber |
| CR | polychloroprene rubber |
| NR | natural rubber |
| SBR | styrene-butadiene rubber |
| XNBR | carboxylated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber |
| PI | polyisoprene |
| TESPT | Bis[3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl]tetrasulfide |
References
- Kumar, S.K.; Benicewicz, B.C.; Vaia, R.A.; Winey, K.I. 50th Anniversary Perspective: Are Polymer Nanocomposites Practical for Applications? Macromolecules 2017, 50, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, J.L. Filled Polymers: Science and Industrial Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, C.M. Reinforcement of Elastomers. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiel, L.; Gerspacher, M.; Yang, H.; O’Farrell, C.P. Filler dispersion, network density, and tire rolling resistance. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2001, 74, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacayo-Pineda, J. Filler dispersion and filler networks. In Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgis, T.A.; Heinrich, G.; Klüppel, M. Reinforcement of Polymer Nano-Composites; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, G.G.A.; Nguyen, M.N. Flocculation of carbon black in filled rubber compounds. 1. Flocculation occurring in unvulcanized compounds during annealing at elevated temperatures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 55, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Hergenrother, W.L.; Alexanian, E.; Böhm, G.G.A. On the filler flocculation in silica-filled rubbers part I. Quantifying and tracking the filler flocculation and polymer-filler interactions in the unvulcanized rubber compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2002, 75, 865–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, S.; Datta, R.N.; Noordermeer, J. Flocculation in silica reinforced rubber compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2009, 82, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunnicliffe, L.; Kadlcak, J.; Morris, M.D.; Shi, Y.; Thomas, A.G.; Busfield, J.J.C. Flocculation and viscoelastic behaviour in carbon black-filled natural rubber. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.G. Flocculation in elastomeric polymers containing nanoparticles: Jamming and the new concept of fictive dynamic strain. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2015, 88, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hyun, K.; Ahn, B.S.K.H.; Clasen, C. Structural development of nanoparticle dispersion during drying in polymer nanocomposite films. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9068–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G.J. Analyse der Struktur von Aktiven Füllstoffen Mittels Streumethoden. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, D.W.; Justice, R.S. How nano are nanocomposites? Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8501–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls, D.J.; Schaefer, D.W.; Kosso, R.; Feinblum, E. Silica fillers for elastomer reinforcement. In Current Topics in Elastomer Research; Bhowmick, A.K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Takenaka, M.; Aizawa, K.; Amino, N.; Nakamura, M.; Yamaguchi, D.; Koizumi, S. Nonlinear and plastic behavior of soft thermoplastic and filled elastomers studied by dissipative particle dynamicsew insight into hierarchical structures of carbon black dispersed in polymer matrices: A combined small-angle scattering study. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouault, N.; Vallat, P.; Dalmas, F.; Said, S.; Jestin, J.; Boue, F. Well-dispersed fractal aggregates as filler in polymer-silica nanocomposites: Long-range effects in rheology. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberdisse, J.; Pyckhout-Hintzen, W.; Straube, E. Structure determination of polymer nanocomposites by small angle scattering. In Recent Advances in Polymer Nanocomposites; Thomas, S., Zaikov, G.E., Valsaraj, S.V., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 397–438. [Google Scholar]
- Baeza, G.P.; Genix, A.C.; Degrandcourt, C.; Petitjean, L.; Gummel, J.; Couty, M.; Oberdisse, J. Multiscale filler structure in simplified industrial nanocomposite silica/SBR systems studied by SAXS and TEM. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, S.; Datta, N.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M.; Amino, N.; Ishikawa, Y.; Nishitsuji, S.; Takenaka, M. Ultra small-angle X-ray scattering study of flocculation in silica-filled rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2014, 87, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odo, E.A.; Britton, D.T.; Gonfa, G.G.; Harting, M. SAXS study of silicon nanocomposites. Int. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 5, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Baeza, G.P.; Genix, A.C.; Paupy-Peyronnet, N.; Degrandcourt, C.; Couty, M.; Oberdisse, J. Revealing nanocomposite filler structures by swelling and small-angle X-ray scattering. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 186, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yin, Y. Small-angle X-ray scattering study on nanostructures of MgO/LDPE nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Electrical Materials and Power Equipment (ICEMPE), Xi’an, China, 14–17 May 2017; pp. 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagita, K.; Morita, H.; Doi, M.; Takano, H. Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulation of filled polymer nanocomposites under uniaxial elongation. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1972–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.B. Entropic and Enthalpic Driving Forces on Morphology in Polymer Grafted Particle Filled Nanocomposites. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, A.; Willot, F.; Cantournet, S.; Forest, S.; Jeulin, D. Large-scale computations of effective elastic properties of rubber with carbon black fillers. Intl. J. Multiscale Comput. Eng. 2011, 9, 271–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legters, G.; Kuppa, V.; Beaucage, G.; University of Dayton Collaboration; University of Cincinnati Collaboration. Coarse-Grained Simulation of Polymer-Filler Blends; APS March Meeting Abstracts; American Physical Society: College Park, MD, USA, 2017; p. M1.083. [Google Scholar]
- Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Wießner, S.; Das, A.; Heinrich, G. Filler flocculation in polymers—A simplified model derived from thermodynamics and game theory. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.; Hentschke, R.; Hager, J.; Hojdis, N.W.; Karimi-Varzaneh, H.A. A nano-mechnical instability as primary contribution to rolling resistance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.; Hentschke, R.; Hager, J.; Hojdis, N.W.; Karimi-Varzaneh, H.A. Molecular simulation of viscous dissipation due to cyclic deformation of silica-silica contact in filled rubber. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 6679–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschke, R. The Payne effect revisited. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glandorff, P.; Prigogine, I. Thermodynamic Theory of Structure, Stability and Fluctuations; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Das, A.; Jurk, R.; Heinrich, G. Contribution of physico-chemical properties of interfaces on dispersibility, adhesion and flocculation of filler particles in rubber. Polymer 2010, 51, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.C.; Desobry, S.; Pons, M.N.; Hardy, J. Adhesion of edible oils to food contact surfaces. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Svistkov, A.S.; Pelevin, A.G.; Heinrich, G. Impact of filler surface modification on large scale mechanics of styrene butadiene/silica rubber composites. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4366–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, B.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Brinson, L.C.; Schadler, L.S. Effect of interfacial energetics on dispersion and glass transition temperature in polyer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.; Wendt, R. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. Attractive forces at interfaces. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, A.W. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J. Effect of polymer-filler and filler-filler interactions on dynamic properties of filled vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1998, 71, 520–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatter, O.; Kratky, O. (Eds.) Small Angle X-ray Scattering; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bale, H.D.; Schmidt, P. Small-angle X-ray-scattering investigation of submicroscopic with fractal properties. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucage, G. Approximations leading to a unified exponential/power-law approach to small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Cryst. 1995, 28, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Sotta, P. Nonlinear and plastic behavior of soft thermoplastic and filled elastomers studied by dissipative particle dynamics. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6282–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabia, S.; Sotta, P.; Long, D.R. A microscopic model for the reinforcement and the nonlinear behavior of filled elastomers and thermoplastic elastomers (Payne and Mullins effects). Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8252–8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Hentschke, R. Dynamic moduli of filled elastomers—A coarse-grained computer model. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Hentschke, R. The influence of structure on mechanical properties of filler networks via coarse-grained modeling. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2014, 23, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gundlach, N.; Hentschke, R. Modelling Filler Dispersion in Elastomers: Relating Filler Morphology to Interface Free Energies via SAXS and TEM Simulation Studies. Polymers 2018, 10, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040446
Gundlach N, Hentschke R. Modelling Filler Dispersion in Elastomers: Relating Filler Morphology to Interface Free Energies via SAXS and TEM Simulation Studies. Polymers. 2018; 10(4):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040446
Chicago/Turabian StyleGundlach, Norman, and Reinhard Hentschke. 2018. "Modelling Filler Dispersion in Elastomers: Relating Filler Morphology to Interface Free Energies via SAXS and TEM Simulation Studies" Polymers 10, no. 4: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040446
APA StyleGundlach, N., & Hentschke, R. (2018). Modelling Filler Dispersion in Elastomers: Relating Filler Morphology to Interface Free Energies via SAXS and TEM Simulation Studies. Polymers, 10(4), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040446