Preparation of PLGA/MWCNT Composite Nanofibers by Airflow Bubble-Spinning and Their Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. The Apparatus of Airflow Bubble-Spinning
2.3. The Process of Airflow Bubble-Spinning
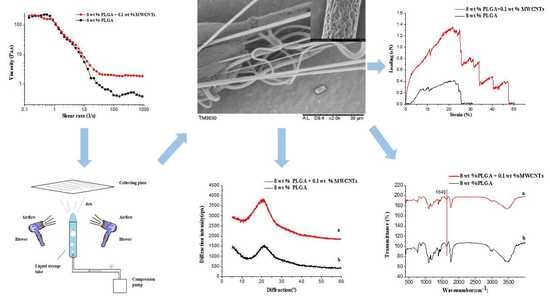
2.4. Measurement and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Spinning Concentration on the Morphology of PLGA Fibers
3.2. Effect of Relative Humidity on the Morphology of PLGA Fibers
3.3. Effect of MWCNTs on the Structure and Properties of PLGA Nanofiber Bundles Prepared by Airflow Bubble-Spinning
3.3.1. Rheological Properties
3.3.2. Morphology of the PLGA/MWCNT Composite Nanofibers
3.3.3. Thermo Gravimetric Analyzer (TGA)
3.3.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.3.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.3.6. Mechanical Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, S.Y.; Park, C.K.; Jeong, Y.H.; Cho, J.H.; Paik, J.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Hwang, K.R. The fabrication and characterization of piezoelectric PZT/PVDF electrospun nanofiber composites. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Ding, J.; Wei, G. Cheminform abstract: Electrospinning: A facile technique for fabricating polymeric nanofibers doped with carbon nanotubes and metallic nanoparticles for sensor applications. Cheminform 2015, 46, 52598–52610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, J.J.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y.W.; Shi, N.; Chen, S.; Xie, L.; Qian, Y.; Huang, W. A highly sensitive fluorescent sensor based on small molecule doped in electrospun nanofibers: Detection of explosives as well as color modulation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8193–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Lv, D.; Yao, J.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Electrospun soy-protein-based nanofibrous membranes for effective antimicrobial air filtration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailek, N.; Daranarong, D.; Punyodom, W.; Molloy, R.; Worajittiphon, P. Crosslinking assisted fabrication of ultrafine poly(vinyl alcohol)/functionalized graphene electrospun nanofibers for crystal violet adsorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Kai, D.; Annamalai, S.K.; Arunachalam, K.D.; Ramakrishna, S. Tissue engineered plant extracts as nanofibrous wound dressing. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enayati, M.S.; Behzad, T.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Rafienia, M.; Bagheri, R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Kolbuk, D.; Pahlevanneshan, Z.; Bonakdar, S.H. Development of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)-based bionanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 106, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.K.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.K. Investigation of the lamination of electrospun graphene-poly(vinyl alcohol) composite onto an electrode of bio-electro-fenton microbial fuel cell. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosunmu, O.O.; Chase, G.G.; Kataphinan, W.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibres from multiple jets on a porous tubular surface. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.Y.; Sun, G. BioMimic fabrication of electrospun nanofibers with high-throughput. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2008, 37, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.H.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.Y. The principle of bubble electrospinning and its experimental verification. J. Polym. Eng. 2008, 28, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, P.; He, J.H. A Belt-Like Superfine Film Fabricated by the Bubble-Electrospinning. Therm. Sci. 2013, 17, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, L. Formation mechanism of highly aligned nanofibers by a modified bubble-electrospinning. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Kong, H.Y.; Yang, R.R.; Dou, H.; Faraz, N.; Wang, L.; Feng, C. Review on fiber morphology obtained by bubble electrospinning and blown bubble spinning. Therm. Sci. 2012, 16, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, X.; Zhao, J.H.; Hua, L. Numerical simulation for the single-bubble electrospinning process. Therm. Sci. 2015, 19, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Xu, L.; Liu, Q. Effect of ethanol post-treatment on the bubble-electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofiber. Therm. Sci. 2015, 19, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienek, D.R.; Hoffman, K.M.; Tutak, W. Blow-spun chitosan/PEG/PLGA nanofibers as a novel tissue engineering scaffold with antibacterial properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, S.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Li, J.; He, J. Fabrication of highly oriented nanoporous fibers via airflow bubble-spinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 421, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Han, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, T. Hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan functionalized-PLGA electrospun fibrous membranes as antibacterial wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Polymers 2017, 9, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Bai, H.; Zhu, J.; Niu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Bai, Y. Enhanced cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in electrospun PLGA/hydroxyapatite nanofibre scaffolds incorporated with graphene oxide. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.E.; Ko, Y.-G.; Kim, W.I.; Kwon, O.K.; Kwon, O.H. Nanofiber mats composed of a chitosan-poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-poly(ethylene oxide) blend as a postoperative anti-adhesion agent. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2016, 105, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, C.; Wang, F.; Pang, M.; Sun, L.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y. Suspended, shrinkage-free, electrospun PLGA nanofibrous scaffold for skin tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Tian, X.; Rui, G.; Luo, Y.; Shen, M.W.; Yu, J.Y.; Shi, X.Y. Controlled release of doxorubicin from electrospun MWCNTs/PLGA hybrid nanofibers. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Tian, L.; Mo, X. The Effect of Plasma Treated PLGA/MWCNTs-COOH Composite Nanofibers on Nerve Cell Behavior. Polymers 2017, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Guo, R.; Shen, M.; Cao, X.; Mo, X.; Wang, S.; Shi, X. Effect of the Porous Microstructures of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/Carbon Nanotube Composites on the Growth of Fibroblast Cells. Soft Mater. 2010, 8, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Min, B.H.; Shin, J.H.; Bae, D.H. Strengthening in nanostructured 2024 aluminum alloy and its composites containing carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, W.J. Strength and strain hardening of aluminum matrix composites with randomly dispersed nanometer-length fragmented carbon nanotubes. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, K.; Esawi, A.M.K.; Lanka, S.; Sayed, A.; Taher, M. Spark plasma extrusion (SPE) of ball-milled aluminum and carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composite powders. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Guo, R.; Shen, M.; Wang, S.; Shi, X. Effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun poly[(lactic acid)-co-(glycolic acid)] nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2009, 294, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, W.A.; Kong, J.H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.X.; Kotaki, M.; Lu, X.H. Polymorphism of electrospun polyvinylidene difluoride/carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites: Synergistic effects of CNT surface chemistry, extensional force and supercritical carbon dioxide treatment. Polymer 2012, 53, 5097–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budun, S.; İşgören, E.; Erdem, R.; Yüksek, M. Morphological and Mechanical Analysis of Electrospun Shape Memory Polymer Fibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 380, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, L. Electrochemical properties of Mg3 MnNi2-x% polymethyl methacrylate-multiwalled carbon nanotubes (PMMA-MWCNTs) (x = 25, 50, 75, 100). J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 6033–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debasis, M.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Ramasamy, T.R.K. Polyvinyl alcohol wrapped multiwall carbon nanotube (MWCNTs) network on fabrics for wearable room temperature ethanol sensor. Rajavel Krishnamoorthy 2018, 261, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wu, J.K.; Zhan, Y.H.; Xia, H.S. Carbon nanotubes/carbon black synergistic reinforced natural rubber composites. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2009, 38, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Sample | Breaking Strength (cN) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA/MWCNTs | 1.36 ± 0.32 | 43.18 ± 6.22 |
| PLGA | 0.42 ± 0.17 | 22.35 ± 4.56 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Y.; Liu, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, P.; He, J. Preparation of PLGA/MWCNT Composite Nanofibers by Airflow Bubble-Spinning and Their Characterization. Polymers 2018, 10, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050481
Fang Y, Liu F, Xu L, Wang P, He J. Preparation of PLGA/MWCNT Composite Nanofibers by Airflow Bubble-Spinning and Their Characterization. Polymers. 2018; 10(5):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050481
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Yue, Fujuan Liu, Lan Xu, Ping Wang, and Jihuan He. 2018. "Preparation of PLGA/MWCNT Composite Nanofibers by Airflow Bubble-Spinning and Their Characterization" Polymers 10, no. 5: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050481
APA StyleFang, Y., Liu, F., Xu, L., Wang, P., & He, J. (2018). Preparation of PLGA/MWCNT Composite Nanofibers by Airflow Bubble-Spinning and Their Characterization. Polymers, 10(5), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050481