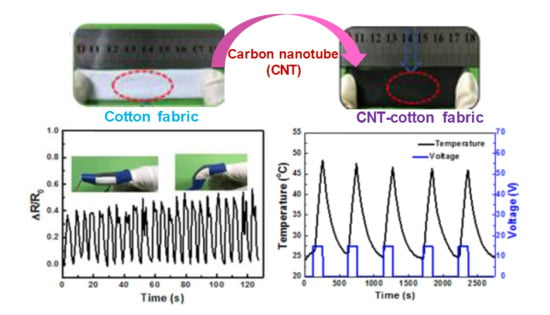
Conductive Cotton Fabrics for Motion Sensing and Heating Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CNT-Cotton Fabric
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Durability Test to Washing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of CNT-Cotton Fabric
3.2. Electrical Conductivity of CNT-Cotton Fabric
3.3. Durability of the CNT-Cotton Fabric to Washing
3.4. Mechanical Properties of CNT-Cotton Fabric
3.5. Electromechanical Performance of the CNT-Cotton Fabric
3.6. Strain Sensing Performance of the CNT-Cotton Fabric
3.7. Electric Heating Performance of the CNT-Cotton Fabric
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, W.; Chen, P.N.; He, S.S.; Sun, X.M.; Peng, H.S. Smart Electronic Textiles. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6140–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.M. Fiber-Based Wearable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Fabrication, Devices, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K.U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, Skin-Mountable, and Wearable Strain Sensors and Their Potential Applications: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1678–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.T.; Zhang, X.H.; Yong, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, D.; Li, R.; Li, Q.W. Carbon-nanotube fibers for wearable devices and smart textiles. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10529–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Yao, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, T. Wearable fiber-shaped energy conversion and storage devices based on aligned carbon nanotubes. Nano Today 2016, 11, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.T.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lou, H.Q.; Shi, X.; Cheng, X.L.; Peng, H.S. A smart, stretchable resistive heater textile. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.R. ; Sun, J; Gao, L. A Stretchable and highly sensitive graphene-based fiber for sensing tensile strain, bending, and torsion. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7365–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Z.M.; Liu, L. Cu-Ag core-shell nanowires for electronic skin with a petal molded microstructure. J. Mater Chem. C 2015, 3, 9594–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Jing, H.Y.; Wei, J.; Han, Y.D. Ag-graphene hybrid conductive ink for writing electronics. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 055201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Sharma, B.K.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.H. Graphene-based transparent strain sensor. Carbon 2013, 51, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, R.R.; Espinosa, N.; Jorgensen, M.; Krebs, F.C. Efficient decommissioning and recycling of polymer solar cells: justification for use of silver. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia-Vladu, M.; Glowacki, E.D.; Voss, G.; Bauer, S.; Sariciftci, N.S. Green and biodegradable electronics. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, Y. Highly conductive and stretchable silver nanowire conductors. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.T.; Li, X.; Zang, X.B.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.L.; Wu, D.H.; Zhu, H.W. Wearable and highly sensitive graphene strain sensors for human motion monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Lai, D.T.H.; Su, B.; Si, K.J.; Ma, Z.; Yap, L.W.; Guo, P.Z.; Cheng, W.L. Highly Stretchy black gold E-skin nanopatches as highly sensitive wearable biomedical sensors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1400063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Jiang, N.; Su, J.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.S.; Lin, H.B.; Moura, F.A.; Yuan, N.Y.; Roth, S.; et al. A bi-sheath fiber sensor for giant tensile and torsional displacements. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.H.; Li, P.C.; Ouyang, J.Y. Graphen coated nonwoven fabrics as wearable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 3224–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Bumgardner, C.; Song, N.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, J.J.; Li, X.D. Cotton-textile-enabled flexible self-sustaining power packs via roll-to-roll fabrication. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Song, N.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, X.D. Cotton-textile-enabled, flexible lithium-ion batteries with enhanced capacity and extended lifespan. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8194–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.S.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, X.; Carey, T.; Chen, K.L.; Yin, Y.J.; Torrisi, F. Environmentally-friendly conductive cotton fabric as flexible strain sensor based on hot press reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 2017, 111, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. From cotton to wearable pressure sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.J.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Li, Y.R. Shi, G.Q. Small and light strain sensors based on graphene coated human hairs. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16361–16365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Pan, Z.J.; Yao, M.; Chen, J.G.; Zhang, Y.X. A large-strain weft-knitted sensor fabricated by conductive UHMWPE/PANI composite yarns. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2016, 238, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, N.; Thilagavathi, G.; Kannaian, T. Polyaniline-coated nylon lycra fabrics for strain sensor and electromagnetic interference shielding applications. High Perform. Polym. 2015, 27, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Long, H.R.; Miao, M.H. High sensitivity knitted fabric strain sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.G.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, M.X.; Xu, J.; Bai, Z.K.; Liang, G.J.; Liu, L.; Fang, D.; Xu, W.L. Cotton fabrics coated with lignosulfonate-doped polypyrrole for flexible supercapacitor electrodes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6261–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tanaka, T.; Yasuhara, T.; Higuchi, E.; Inoue, H. Preparation and characterization of conductive fabrics coated uniformly with polypyrrole nanoparticles. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Jian, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y. Sheath-core graphite/silk fiber made by dry-meyer-rod-coating for wearable strain sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20894–20899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, L. Silver nanowires coated on cotton for flexible pressure sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, Y.A.; Komatsu, K.; Yamashita, D.; Li, Y.Q.; Zheng, L.X.; Alhassan, S.M.; Nakano, Y.; Liao, K. From sewing thread to sensor: Nylon® fiber strain and pressure sensors. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2017, 240, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kwon, H.; Seo, J.; Shin, S.; Koo, J.H.; Pang, C.; Son, S.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, D.E.; et al. Conductive fiber-based ultrasensitive textile pressure sensor for wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Wen, Y.W.; Hong, T.; Xie, Z.S.; Yuan, G.L.; Ji, Q.M.; Jia, H.B. Highly stretchable, ultrasensitive, and wearable strain sensors based on facilely prepared reduced graphene oxide woven fabrics in an ethanol flame. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32054–32064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Li, X.; Gao, E.L.; Jian, M.Q.; Xia, K.L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.P.; Ren, T.L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Carbonized silk fabric for ultrastretchable, highly sensitive, and wearable strain sensors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6640–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Jian, M.Q.; Hao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y. Carbonized cotton fabric for high-performance wearable strain sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Xia, K.L.; Jian, M.Q.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, M.C.; Zhang, Y.Y. Carbonized silk georgette as an ultrasensitive wearable strain sensor for full-range human activity monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7604–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Cai, Z.S.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhao, H.; Ge, F.Y. Potentiostatically synthesized flexible polypyrrole/multi-wall carbon nanotube/cotton fabric electrodes for supercapacitors. Cellulose 2016, 23, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowski, T.; Kowalczyk, D.; Fortuniak, W.; Jeziorska, D.; Brzezinski, S.; Tracz, A. Superhydrophobic properties of cotton woven fabrics with conducting 3D networks of multiwall carbon nanotubes, MWCNTs. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4659–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Q.; Fan, T.; Hu, R.M.; Liu, Y.P.; Lu, M. Surface micro-dissolution process for embedding carbon nanotubes on cotton fabric as a conductive textile. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.Y.; Zheng, G.Q.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.T.; Yan, X.R.; Shen, C.Y.; Guo, Z.H. Carbon Nanotubes-Adsorbed Electrospun PA66 Nanofiber Bundles with Improved Conductivity and Robust Flexibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14150–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroughi, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Aziz, S. Mirabedini, A.; Jeiranikhameneh, A.; Wallace, G.G.; Kozlov, M.E.; Baughman, R.H. Knitted carbon-nanotube-sheath/spandex-core elastomeric yarns for artificial muscles and strain sensing. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9129–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.I.; Lou, C.W.; Pan, Y.J.; Hsieh, C.T.; Huang, C.H.; Huang, C.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Lin, J.H. Conductive fabrics made of polypropylene/multi-walled carbon nanotube coated polyester yarns: Mechanical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 141, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qi, K.; Xin, J.H. Functionalization of cotton with carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3454–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, B.S.; Chen, W.; Doty, C.; Xu, C.; Kotov, N.A. Smart electronic yarns and wearable fabrics for human biomonitoring made by carbon nanotube coating with polyelectrolytes. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.J.; Choi, A.; Kim, D.H.; Jin, K.; Seo, D.K.; Jeong, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Electromechanical properties of CNT-coated cotton yarn for electronic textile applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 20, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilanchezhiyan, P.; Zakirov, A.S.; Kumar, G.M.; Yuldashev, S.U.; Cho, H.D.; Kang, T.W.; Mamadalimov, A.T. Highly efficient CNT functionalized cotton fabrics for flexible/wearable heating applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10697–10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.F.; Huang, Y.; Fu, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, M.S.; Zhi, C.Y.; Hu, H. High-performance stretchable yarn supercapacitor based on PPy@CNTs@urethane elastic fiber core spun yarn. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.F.; Huang, Y.; Hu, H.; Jiang, R.J.; Gai, W.M.; Li, G.M.; Zhi, C.Y. Polyurethane/cotton/carbon nanotubes core-spun yarn as high reliability stretchable strain sensor for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24837–24843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anoshkin, I.V.; Nefedova, I.I.; Lioubtchenko, D.V.; Nefedov, I.S.; Raisanen, A.V. Single walled carbon nanotube quantification method employing the Raman signal intensity. Carbon 2017, 116, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Hofmann, M. The big picture of Raman scattering in carbon nanotubes. Vib. Spectrosc. 2007, 45, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Saito, R.; Jorio, A. Raman spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rep. 2005, 409, 47–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorio, A.; Pimenta, M.A.; Souza, A.G.; Saito, R.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Characterizing carbon nanotube samples with resonance Raman scattering. New J. Phys. 2003, 5, 139.1–139.17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.M.; Yang, M.Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Liu, J.G.; Tang, B.; Wang, X.G. Flexible and wearable strain sensing fabrics. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Pan, J.; Xu, A.; Luo, L.; Cheng, D.; Cai, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, X. Conductive Cotton Fabrics for Motion Sensing and Heating Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060568
Yang M, Pan J, Xu A, Luo L, Cheng D, Cai G, Wang J, Tang B, Wang X. Conductive Cotton Fabrics for Motion Sensing and Heating Applications. Polymers. 2018; 10(6):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060568
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Mengyun, Junjie Pan, Anchang Xu, Lei Luo, Deshan Cheng, Guangming Cai, Jinfeng Wang, Bin Tang, and Xungai Wang. 2018. "Conductive Cotton Fabrics for Motion Sensing and Heating Applications" Polymers 10, no. 6: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060568
APA StyleYang, M., Pan, J., Xu, A., Luo, L., Cheng, D., Cai, G., Wang, J., Tang, B., & Wang, X. (2018). Conductive Cotton Fabrics for Motion Sensing and Heating Applications. Polymers, 10(6), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060568