Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Single Fiber Tensile Test
2.3. Single Fiber Pull-Out Test
2.4. Mechanical Properties
2.4.1. Fabrication of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites
2.4.2. Flexural Testing
2.4.3. Quasi-Static Fracture Toughness Test
2.5. TGA/DTG
2.6. FTIR
2.7. SEM
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. SEM Images of Alkali-Treated Bamboo Fibers
3.2. FT-IR Analysis
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Single Bamboo Fiber
3.4. Interfacial Shear Strength Measurement
3.5. Thermal Properties
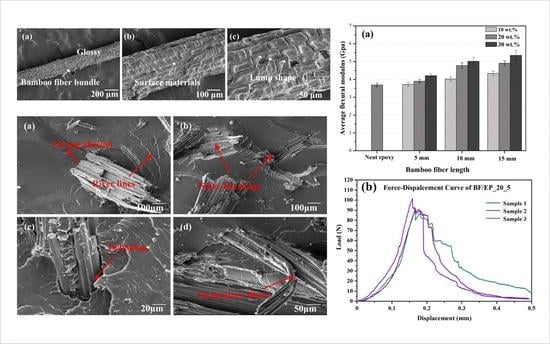
3.6. Flexural Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites
3.7. Fracture Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy
3.8. Fracture Surface Morphology of Fracture Toughness Test Samples
4. Conclusions
- After 6 wt.% NaOH treatment, the tensile properties of bamboo fibers were improved, and bamboo fibers showed strong bonding with the epoxy matrix.
- When compared to neat epoxy, the flexural modulus of composites are always higher, and monotonically increase with fiber length and content. However, for all samples, composites showed negligible difference on the flexural strength.
- Compared to neat epoxy, there was a 39%, 159%, and 224% increase in fracture toughness values for BF/EP_20_5, BF/EP_20_10, and BF/EP_20_15, respectively.
- Bamboo fibers treated with 6 wt.% NaOH solutions had better thermal stability than untreated fibers. Bamboo-fiber composites, therefore, have potential for engineering applications.
- Fiber breakage, matrix cracking, debonding, and fiber pull out were major failure types, but the predominant failure mode was hard to quantify.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Progress report on natural fiber reinforced composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeencham, R.; Suppakarn, N.; Jarukumjorn, K. Effect of flame retardants on flame retardant, mechanical, and thermal properties of sisal fiber/polypropylene composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. The effect of alkaline treatment on mechanical properties of Kenaf fibers and their epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavudeen, A.; Rajini, N.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thiruchitrambalam, M.; Venkateshwaren, N. Mechanical properties of Banana/Kenaf fiber-reinforced hybrid polyester composites: Effect of woven fabric and random orientation. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Majid, M.A.; Afendi, M.; Mazlee, M.N.; Gibson, A.G. Thermal behavior and dynamic mechanical analysis of Pennisetum purpureum/glass-reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Compos. Struct. 2016, 152, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalo, A.C.; Wani, E.; Zukarnain, N.A.; Karunasena, W.; Lau, K.T. Effects of alkali treatment and elevated temperature on the mechanical properties of bamboo fibre-polyester composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 80, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.V.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Arora, S. Are natural fiber composites environmentally superior to glass fiber reinforced composites? Compos. Part A 2004, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.V.R.; Rao, K.M. Mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced polyester composites: Jowar, sisal and bamboo. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4658–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Booth, T.; He, X. Changes of carbon stocks in bamboo stands in China during 100 years. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Xu, J.K.; Huang, P.L.; Sun, R.C. Effect of alkaline pretreatment on the preparation of regenerated lignocellulose fibers from bamboo stem. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2727–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Gonzalez, A.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Olayo, R.J.I.P.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Effect of fiber surface treatment on the fiber-matrix bond strength of natural fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 1999, 30, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Pickering, K.L.; Foreman, N.J. Influence of alkali fiber treatment and fiber processing on the mechanical properties of hemp/epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 3696–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Lin, N.; Chang, P.R.; Huang, J. Reinforcement and nucleation of acetylated cellulose nanocrystals in foamed polyester composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deka, H.; Varghese, T.O.; Nayak, S.K. Recent development and future trends in coir fiber-reinforced green polymer composites: Review and evaluation. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 3296–3309. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Hui, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Effect of surface modification of bamboo cellulose fibers on mechanical properties of cellulose/epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 51, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Takagi, H.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Li, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I. Effect of alkali treatment on interfacial bonding in abaca fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Part A 2016, 90, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Sato, N.; Tölle, F.; Mülhaupt, R.; Fiedler, B.; Schulte, K. Fracture toughness and failure mechanism of graphene based epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 97, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojny, F.H.; Wichmann, M.H.G.; Köpke, U.; Fiedler, B.; Schulte, K. Carbon nanotube-reinforced epoxy-composites: Enhanced stiffness and fracture toughness at low nanotube content. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushvaha, V.; Tippur, H. Effect of filler shape, volume fraction and loading rate on dynamic fracture behavior of glass-filled epoxy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 64, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, K.L.; Timoshkin, I.A.; Gutnikov, S.I.; Zhukovskaya, E.S.; Lipatov, Y.V.; Lazoryak, B.I. Effect of silane/nano-silica on the mechanical properties of basalt fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Interfaces 2017, 24, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; van Hoa, S. Mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy/clay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Yousif, B.F.; Islam, M. Fracture behaviour of bamboo fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 116, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, I.M.; Santulli, C.; Sarasini, F. Mechanical and thermal characterization of epoxy composites reinforced with random and quasi-unidirectional untreated Phormium tenax leaf fibers. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2397–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, L.; Trujillo, E.; Van Vuure, A.W.; Verpoest, I. Morphological aspects and mechanical properties of single bamboo fibers and flexural characterization of bamboo/epoxy composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2011, 30, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Thomason, J.L. Development and application of micromechanical techniques for characterising interfacial shear strength in fibre-thermoplastic composites. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM Inernational. Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials; ASTM D790; ASTM Inernational: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Botsis, J. Experimental and numerical studies in model composites Part I: Experimental results. Int. J. Fract. 1996, 82, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Inernational. Standard Test Methods for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness and Strain Energy Release Rate of Plastic Materials; ASTM D5045-99; ASTM Inernational: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, T.; Fei, B. Effect of alkali treatment on wettability and thermal stability of individual bamboo fibers. J. Wood Sci. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Oudiani, A.; Chaabouni, Y.; Msahli, S.; Sakli, F. Crystal transition from cellulose I to cellulose II in NaOH treated Agave americana L. fibre. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.F. Mechanical and thermal properties of waste water bamboo husk fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 445, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Shin, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Youk, J.H. Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Pan, G.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y. Cellulosic fibers with high aspect ratio from cornhusks via controlled swelling and alkaline penetration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayo, A.Q.; Gao, B.C.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.B.; Derradji, M.; Shah, A.H.; Babar, A.A. Natural hemp fiber reinforced polybenzoxazine composites: Curing behavior, mechanical and thermal properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 144, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Das, S.K.; Mondal, S.; Ramachandrarao, P. Microstructural characterization of bamboo. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydenstricker, T.H.; Mochnaz, S.; Amico, S.C. Pull-out and other evaluations in sisal-reinforced polyester biocomposites. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Sarkar, B.K.; Rana, A.K.; Bose, N.R. The mechanical properties of vinylester resin matrix composites reinforced with alkali-treated jute fibres. Compos. Part A 2001, 32, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhong, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Fei, B. Effect of alkali treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of individual bamboo fibers. Cellulose 2017, 24, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, S.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Ran, S. Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Polylactide Composites Reinforced with Alkali-Treated Bamboo Fibers. Polymers 2018, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarukumjorn, K.; Suppakarn, N. Effect of glass fiber hybridization on properties of sisal fiber-polypropylene composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2009, 40, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylsamy, K.; Rajendran, I. Influence of alkali treatment and fibre length on mechanical properties of short Agave fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4629–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Cho, K.; Woo, T.; Lee, B.H.; Choe, S. Blends of ethylene 1-octene copolymer synthesized by Ziegler-Natta and metallocene catalysts. I. Thermal and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, K.; Lee, B.H.; Choe, S. Thermal and mechanical properties for binary blends of metallocene polyethylene with conventional polyolefins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 69, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; Spinelli, D.; Bose Filho, W.W.; Neto, S.C.; Chierice, G.O.; Tarpani, J.R. Fracture toughness of natural fibers/castor oil polyurethane composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Hayes, S.A.; Jones, F.R. The role of matrix cracks and fiber/matrix debonding on the stress transfer between fiber and matrix in a single fiber fragmentation test. Compos. Part A 2012, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| NAOH Concentration (wt.%) | Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Young’s Modulus (Gpa) | Strain at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| untreated | 262 ± 75 | 9.8± 1.6 | 2.7 ± 0.7 |
| 2 | 283 ± 71 | 9.2 ± 1.3 | 3.1 ± 0.8 |
| 6 | 363 ± 103 | 11.2 ± 2.4 | 3.3 ± 0.5 |
| 10 | 235 ± 67 | 6.1 ± 0.9 | 3.9 ± 1.1 |
| Samples | (°C) 1 | (°C) 1 | (°C) 2 | (%) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBF | 236 | 289 | 368 | 16.7 |
| TBF | 264 | 299 | 374 | 13.1 |
| P(epoxy) | 363 | 372 | 392 | 6.0 |
| P(epoxy)/UBF | 330 | 356 | 386 | 9.7 |
| P(epoxy)/TBF | 334 | 358 | 387 | 8.9 |
| Samples | Flexural Modulus (Gpa) | Flexural Strength (Mpa) | Fracture Toughness KIC (Mpa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat epoxy | 3.69 ± 0.10 | 83.3 ± 1.5 | 1.17 ± 0.04 |
| BF/EP_10_5 | 3.72 ± 0.10 | 82.6 ± 3.3 | -- |
| BF/EP_10_10 | 4.03 ± 0.13 | 80.2 ± 2.9 | -- |
| BF/EP_10_15 | 4.34 ± 0.12 | 75.9 ± 4.3 | -- |
| BF/EP_20_5 | 3.90 ± 0.10 | 85.6 ± 4.9 | 1.63 ± 0.11 |
| BF/EP_20_10 | 4.78 ± 0.16 | 87.2 ± 3.5 | 3.03 ± 0.07 |
| BF/EP_20_15 | 4.91 ± 0.13 | 84.3 ± 4.6 | 3.79 ± 0.27 |
| BF/EP_30_5 | 4.21 ± 0.11 | 77.5 ± 2.8 | -- |
| BF/EP_30_10 | 5.02 ± 0.21 | 72.4 ± 3.7 | -- |
| BF/EP_30_15 | 5.35 ± 0.29 | 70.6 ± 2.5 | -- |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, W.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Yang, B. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060608
Zhang K, Wang F, Liang W, Wang Z, Duan Z, Yang B. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers. 2018; 10(6):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060608
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kai, Fangxin Wang, Wenyan Liang, Zhenqing Wang, Zhiwei Duan, and Bin Yang. 2018. "Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites" Polymers 10, no. 6: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060608
APA StyleZhang, K., Wang, F., Liang, W., Wang, Z., Duan, Z., & Yang, B. (2018). Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers, 10(6), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060608