Responsive Protein Hydrogels Assembled from Spider Silk Carboxyl-Terminal Domain and Resilin Copolymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Materials
2.2. Construction of Protein Expression Plasmids
2.3. Protein Expression, Purification, and Identification
2.4. Characterization of Phase Transition
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.6. Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formation
2.7. Rheological Measurements
2.8. pH-Responsive Drug Release Assay
2.9. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. Design and Biosynthesis of Spider Silk CT and Resilin Copolymers
3.2. Thermally Responsive Behavior of Copolymer Solutions
3.3. Thermo- and Salt-Sensitive Gelation of Copolymers
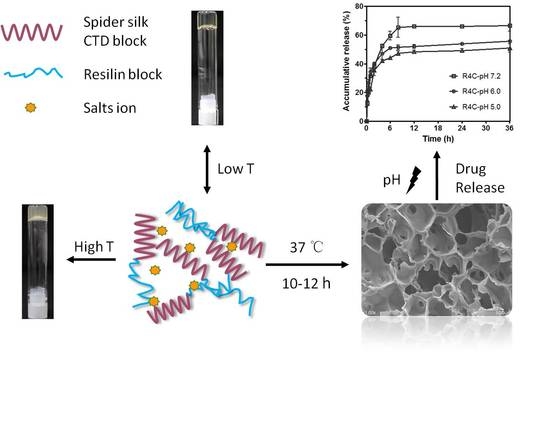
3.4. Time-Dependent Gelation at 37 °C for pH-Responsive Drug Release
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopeček, J.; Yang, J. Smart self-assembled hybrid hydrogel biomaterials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 7396–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, D.; Wu, F.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Xing, T.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Silk fibroin/polyvinyl pyrrolidone interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. Polymers 2018, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, D.; Nunalee, M.L.; Lim, D.W.; Simnick, A.J.; Chilkoti, A. Peptide-based biopolymers in biomedicine and biotechnology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2008, 62, 125–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Tirrell, D.A. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature 2004, 428, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xia, X.; Huang, W.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. High throughput screening of dynamic silk-elastin-like protein biomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.L.; Qian, Z.G.; Chen, L.; Kaplan, D.L.; Xia, X.X. Rationally designed redox-sensitive protein hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3508–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Stewart, R.J.; Kopeček, J. Hybrid hydrogels assembled from synthetic polymers and coiled-coil protein domains. Nature 1999, 397, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.P.; Pochan, D.J.; Ozbas, B.; Rajagopal, K.; Pakstis, L.; Kretsinger, J. Responsive hydrogels from the intramolecular folding and self-assembly of a designed peptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 15030–15037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrick, J.D.; Deo, S.K.; Browning, T.W.; Bachas, L.G.; Madou, M.J.; Daunert, S. Genetically engineered protein in hydrogels tailors stimuli-responsive characteristics. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.W.; Tarakanova, A.; Dinjaski, N.; Wang, Q.; Xia, X.X.; Chen, Y.; Wong, J.Y.; Buehler, M.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Design of multistimuli responsive hydrogels using integrated modeling and genetically engineered silk-elastin-like Proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4113–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogsgaard, M.; Behrens, M.A.; Pedersen, J.S.; Birkedal, H. Self-healing mussel-inspired multi-pH-responsive hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Li, J.; Tan, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y. Photodegradable supramolecular hydrogels with fluorescence turn-on reporter for photomodulation of cellular microenvironments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18718–18721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Teller, S.; Clifton, R.J.; Jia, X.; Kiick, K.L. Tunable mechanical stability and deformation response of a resilin-based elastomer. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2302–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stile, R.A.; Healy, K.E. Thermo-responsive peptide-modified hydrogels for tissue regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.T.; Xue, F.; Hong, Z.; Punihaole, D.; Asher, S.A. 2D photonic crystal protein hydrogel coulometer for sensing serum albumin ligand binding. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4840–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.P.; Konst, S. Novel hydrogel actuator inspired by reversible mussel adhesive protein chemistry. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3415–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.G.; Zhou, M.L.; Song, W.W.; Xia, X.X. Dual thermosensitive hydrogels assembled from the conserved C-terminal domain of spider dragline silk. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, R.E.; Nairn, K.M.; Huson, M.G.; Kim, M.; Dumsday, G.; Elvin, C.M. Comparisons of recombinant resilin-like proteins: Repetitive domains are sufficient to confer resilin-like properties. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3009–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvin, C.M.; Carr, A.G.; Huson, M.G.; Maxwell, J.M.; Pearson, R.D.; Vuocolo, T.; Liyou, N.E.; Wong, D.C.; Merritt, D.J.; Dixon, N.E. Synthesis and properties of crosslinked recombinant pro-resilin. Nature 2005, 437, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, N.K.; Truong, M.Y.; Mayavan, S.; Roy Choudhury, N.; Elvin, C.M.; Kim, M.; Knott, R.; Nairn, K.M.; Hill, A.J. A genetically engineered protein responsive to multiple stimuli. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 4428–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, R.; Whittaker, J.; Dutta, N.K.; Elvin, C.M.; Choudhury, N.R. Multi-responsive biomaterials and nanobioconjugates from resilin-like protein polymers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5936–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, M.Y.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R.; Kim, M.; Elvin, C.M.; Hill, A.J.; Thierry, B.; Vasilev, K. A pH-responsive interface derived from resilin-mimetic protein Rec1-resilin. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.K.; Rivkin, A.; Lapidot, S.; Hu, X.; Preis, I.; Arinus, S.B.; Dgany, O.; Shoseyov, O.; Kaplan, D.L. Recombinant exon-encoded resilins for elastomeric biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9231–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renner, J.N.; Cherry, K.M.; Su, R.S.; Liu, J.C. Characterization of resilin-based materials for tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3678–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Dudek, D.M.; Cao, Y.; Balamurali, M.M.; Gosline, J.; Li, H. Designed biomaterials to mimic the mechanical properties of muscles. Nature 2010, 465, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charati, M.B.; Ifkovits, J.L.; Burdick, J.A.; Linhardt, J.G.; Kiick, K.L. Hydrophilic elastomeric biomaterials based on resilin-like polypeptides. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.C.; Qian, Z.G.; Dan, A.H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, M.L.; Xia, X.X. Rational design and hierarchical assembly of a genetically engineered resilin-silk copolymer results in stiff hydrogels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Qian, Z.G.; Zhong, J.J.; Xia, X.X. Hyper-production of large proteins of spider dragline silk MaSp2 by Escherichia coli via synthetic biology approach. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, R.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R.; Elvin, C.M.; Lyons, R.E.; Knott, R.; Hill, A.J. An16-resilin: An advanced multi-stimuli-responsive resilin-mimetic protein polymer. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, F.; Qian, Z.-G.; Xia, X.-X. Responsive Protein Hydrogels Assembled from Spider Silk Carboxyl-Terminal Domain and Resilin Copolymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080915
Luo F, Qian Z-G, Xia X-X. Responsive Protein Hydrogels Assembled from Spider Silk Carboxyl-Terminal Domain and Resilin Copolymers. Polymers. 2018; 10(8):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080915
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Fang, Zhi-Gang Qian, and Xiao-Xia Xia. 2018. "Responsive Protein Hydrogels Assembled from Spider Silk Carboxyl-Terminal Domain and Resilin Copolymers" Polymers 10, no. 8: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080915
APA StyleLuo, F., Qian, Z. -G., & Xia, X. -X. (2018). Responsive Protein Hydrogels Assembled from Spider Silk Carboxyl-Terminal Domain and Resilin Copolymers. Polymers, 10(8), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080915