Microstructure and Mechanical/Hydrophilic Features of Agar-Based Films Incorporated with Konjac Glucomannan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
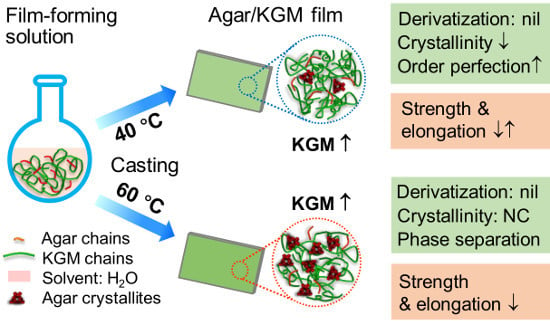
2.2. Preparation of Agar/KGM Films
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
2.5. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.6. X-ray Diffraction
2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.8. Contact Angle Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fracture Surface Morphology
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. Nanoscale Structural Features
3.4. Crystalline Structure
3.5. Mechanical Properties
3.6. Contact Angle Features
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, C.J.; Haugaard, V.; Festersen, R.; Bertelsen, G. Production and applications of biobased packaging materials for the food industry. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, V.; Rocculi, P.; Romani, S.; Rosa, M.D. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, F.; Chen, L. Supramolecular structure of A- and B-type granules of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Dean, K.; Li, L. Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 576–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Mohanty, K.A.; Singh, S.P.; Ng, P.K.W. Preparation and Properties of Biodegradable Multilayer Films Based on Soy Protein Isolate and Poly (lactide). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jiménez, A.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures, active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K.; Drzal, L.T.; Palsingh, R. Recent Advances in Biodegradable Nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Rochas, C. Chemical Structure and Physico-Chemical Properties of Agar; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation and application of agar/alginate/collagen ternary blend functional food packaging films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Reddy, J.P.; Rhim, J.W. Effect of lignin on water vapor barrier, mechanical, and structural properties of agar/lignin composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszalek, P.E.; Oberhauser, A.F.; Pang, Y.P.; Fernandez, J.M. Polysaccharide elasticity governed by chair-boat transitions of the glucopyranose ring. Nature 1998, 396, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuraya, K.; Okuyama, K.; Hatanaka, K.; Oshima, R.; Sato, T.; Matsuzaki, K. Constitution of konjac glucomannan: Chemical analysis and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.A.; Ahmed, J.; Jacob, H. Preparation and characterization of agar-based nanocomposite films reinforced with bimetallic (Ag-Cu) alloy nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsuwan, A.; Shankar, S.; Wang, L.F.; Sothornvit, R.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation of antimicrobial agar/banana powder blend films reinforced with silver nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.W.; Park, H.M.; Ha, C.S. Bio-nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1629–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.W. Physical-Mechanical Properties of Agar/κ-Carrageenan Blend Film and Derived Clay Nanocomposite Film. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, N66–N73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation of nanocellulose from micro-crystalline cellulose: The effect on the performance and properties of agar-based composite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.P.; Rhim, J.W. Characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with agar and paper-mulberry pulp nanocellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cai, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, T.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Q.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; et al. Hierarchical structure and slowly digestible features of rice starch following microwave cooking with storage. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, W.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Xie, F. Changes in Nanoscale Chain Assembly in Sweet Potato Starch Lamellae by Downregulation of Biosynthesis Enzymes. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 6302–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Tu, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Li, N.; Nishinari, K.; Riffat, S.; Jiang, F. Understanding the multi-scale structure and digestion rate of water chestnut starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Xie, F.; Zhang, B.; Zou, W.; Zhao, S.; Niu, M.; Lv, R.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J. A further understanding of the multi-scale supramolecular structure and digestion rate of waxy starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B.; Simon, G.; Jiang, F. Effect of alkanol surface grafting on the hydrophobicity of starch-based films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.W. Antimicrobial and physical-mechanical properties of agar-based films incorporated with grapefruit seed extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Geng, F.; Chang, P.R.; Yu, J.; Ma, X. Effect of agar on the microstructure and performance of potato starch film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, F.; Ni, X.; Yan, W.; Fang, Y.; Corke, H.; Xiao, M. Preparation and characterization of konjac glucomannan and ethyl cellulose blend films. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rubio, A.; Htoon, A.; Gilbert, E.P. Influence of extrusion and digestion on the nanostructure of high-amylose maize starch. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeson, A. Food Stabilisers, Thickners and Gelling Agents; Willey-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Gilbert, E.P.; Qiao, D.; Xie, F.; Wang, D.K.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, F. A further study on supramolecular structure changes of waxy maize starch subjected to alkaline treatment by extended-q small-angle neutron scattering. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, C.; Nascimento, V.; Hernandez-Montelongo, J.; Machado, D.; Lancellotti, M.; Beppu, M. Synthesis and properties of silk fibroin/konjac glucomannan blend beads. Polymers 2018, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Majeed, H.; Antoniou, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yokoyama, W.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Tailoring physical properties of transglutaminase-modified gelatin films by varying drying temperature. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Samples | 40 °C | 60 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | CH2I2 | γs (mJ/m2) | H2O | CH2I2 | γs (mJ/m2) | |
| a100/K0 | 69 ± 2 d | 44 ± 1 A,B | 41 | 70 ± 2 d,e | 43 ± 1 A | 41 |
| a94/K6 | 67 ± 1 c,d | 45 ± 2 A,B,C | 41 | 73 ± 1 e | 44 ± 1 A,B,C | 40 |
| a88/K12 | 67 ± 3 c,d | 45 ± 1 A,B,C | 42 | 68 ± 1 d | 45 ± 1 A,B,C | 41 |
| a82/K18 | 60 ± 1 a,b | 47 ± 1 C | 42 | 63 ± 0 b,c | 46 ± 1 A,B,C | 43 |
| a76/K24 | 58 ± 2 a | 52 ± 1 D | 45 | 62 ± 1 a,b | 46 ± 0 B,C | 44 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, D.; Tu, W.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, F. Microstructure and Mechanical/Hydrophilic Features of Agar-Based Films Incorporated with Konjac Glucomannan. Polymers 2019, 11, 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121952
Qiao D, Tu W, Zhong L, Wang Z, Zhang B, Jiang F. Microstructure and Mechanical/Hydrophilic Features of Agar-Based Films Incorporated with Konjac Glucomannan. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121952
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Dongling, Wenyao Tu, Lei Zhong, Zhong Wang, Binjia Zhang, and Fatang Jiang. 2019. "Microstructure and Mechanical/Hydrophilic Features of Agar-Based Films Incorporated with Konjac Glucomannan" Polymers 11, no. 12: 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121952
APA StyleQiao, D., Tu, W., Zhong, L., Wang, Z., Zhang, B., & Jiang, F. (2019). Microstructure and Mechanical/Hydrophilic Features of Agar-Based Films Incorporated with Konjac Glucomannan. Polymers, 11(12), 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121952