Characterization of Highly Filled PP/Graphite Composites for Adhesive Joining in Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Materials Processing
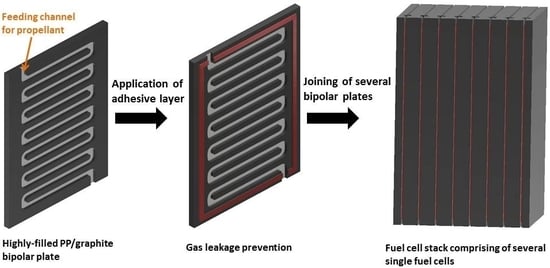
2.3. Joining of the Samples
2.4. Surface Pre-Treatment
2.5. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties of Graphite Composites
3.2. Thermal Conductivity of Graphite Composites
3.3. Electrical Conductivity of Graphite Composites
3.4. Contact Angle and Surface Tension
3.5. Mechanical Properties of Adhesive Joint (Lap-Shear Test)
3.6. Surface Roughness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scherer, G.G. Fuel cells I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yeetsorn, R. Development of Electrically Conductive Thermoplastic Composites for Bipolar Plate Application in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Conductive Thermoplastic Composite Blends for Flow Field Plates for Use in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.-H.; Yen, C.-Y.; Weng, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-F.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Yang, C.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Yen, M.-Y.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Lee, S.-J.; et al. Preparation and properties of carbon nanotube/polypropylene nanocomposite bipolar plates for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, J.L.A. Fuel Cell Systems Explained; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dweiri, R.; Sahari, J. Electrical properties of carbon-based polypropylene composites for bipolar plates in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Pötschke, P.; Hickmann, T. Improvement of Electrical Resistivity of Highly Filled Graphite/pp Composite Based Bipolar Plates for Fuel Cells by Addition of Carbon Black; AIP Conference Proceedings: Melville, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Derieth, T.; Bandlamudi, G.; Beckhaus, P.; Kreuz, C.; Mahlendorf, F.; Heinzel, A. Development of highly filled graphite compounds as bipolar plate materials for low and high temperature PEM fuel cells. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2008, 11, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Grundler, M.; Reich, T.; Derieth, T.; Heinzel, A. Proceedings of the Entwicklung von Hochwärmeleitfähigen Polymer-Compounds, Polymermischungen–Polymerblends & Nanocomposites, Halle/Saale, Germany, 5–6 March 2014.
- Johnson, B.A. Thermally and Electrically Conductive Polypropylene Based Resins for Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-B.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, K.-M.; Lim, D.-S. Preparation and properties on the graphite/polypropylene composite bipolar plates with a 304 stainless steel by compression molding for PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 7621–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, W.; Chai, S.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Largely enhanced thermal and electrical conductivity via constructing double percolated filler network in polypropylene/expanded graphite—Multi-wall carbon nanotubes ternary composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 130, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ni, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, W. Facile method to fabricate highly thermally conductive graphite/PP composite with network structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19732–19738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinci, A. Mechanical and structural properties of polypropylene composites filled with graphite flakes. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 35, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Planes, E.; Flandin, L.; Alberola, N. Polymer composites bipolar plates for PEMFCs. Energy Procedia 2012, 20, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.A.; de Oliveira, M.C.L.; Ett, G.; Ett, V. Carbon materials in composite bipolar plates for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: A review of the main challenges to improve electrical performance. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2945–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermann, A.; Chaudhuri, T.; Spagnol, P. Bipolar plates for PEM fuel cells: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-G.; Guo, Q.-G.; Liu, L.; Song, J.-R. Study on the microstructural evolution of high temperature adhesives for graphite bonding. Carbon 2002, 40, 2447–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, N.; Guo, Q.; Liu, L.; Song, J. Study on the structural evolution of modified phenol–formaldehyde resin adhesive for the high-temperature bonding of graphite. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 348, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Gebauer, K. Graphite Adhesive and Process for Producing Bonded Joints Between Graphite Particles. Patent EP 0388666A1, 27 February 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Farrington, S. Assembling Bipolar Plates for Fuel Cells Using Microencapsulated Adhesive. Patent US 9105883, 11 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Lee, D.G. Development of the anode bipolar plate/membrane assembly unit for air breathing pemfc stack using silicone adhesive bonding. J. Power Sources 2016, 315, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeczkowski, P.; Lucia, M.; Müller, A.; Facklam, M.; Cohnen, A.; Schäfer, P.; Hopmann, C.; Hickmann, T.; Pötschke, P.; Krause, B. Development of Joining Methods for Highly Filled Graphite/PP Composite Based Bipolar Plates for Fuel Cells: Adhesive Joining and Welding; AIP Conference Proceedings: Melville, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Potente, H. Fügen von Kunststoffen: Grundlagen, Verfahren, Anwendung; Carl Hanser Verlag: München, Germany; Wien, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M. Klebstoffe Benetzbarkeit—Bestimmung der Messung des Kontaktwinkels und der freien Oberflächenenergie fester Oberflächen; Deutsche Fassung; DIN EN 828: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bensalah, H.; Gueraoui, K.; Essabir, H.; Rodrigue, D.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.E.k. Mechanical, thermal, and rheological properties of polypropylene hybrid composites based clay and graphite. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 3563–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, M. Handbuch Klebtechnik; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Munich, Germany; Wien, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Ahn, S.H. Evaluation of graphite composite bipolar plate for PEM (proton exchange membrane) fuel cell: Electrical, mechanical, and molding properties. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 187–188, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürmann, H. Konstruieren mit Faser-Kunststoff-Verbunden, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht, G. Kleben: Grundlagen, Technologien, Anwendungen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, M. Oberflächentechnik in der Kunststoffverarbeitung; Carl Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]









| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | >100 S/cm |
| Thermal conductivity | >10 W/m·K |
| Tensile strength | >41 MPa |
| Flexural strength | >25 MPa |
| Description | Graphite Content in Composite (Set Values) [wt %] | Graphite Content in Composite (TGA Values) [wt %] | Rotation Speed [rpm] | Torque [%] | Pressure at the Nozzle [bar] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 0 | - | 200 | 51 | 0 |
| PP/10 | 10 | 10.6 | 200 | 50 | 0 |
| PP/20 | 20 | 20.8 | 200 | 51 | 1 |
| PP/40 | 40 | 40.1 | 200 | 57 | 9 |
| PP/60 | 60 | 59.6 | 300 | 53 | 29 |
| PP/80 | 80 | 78.7 | 300 | 74 | 119 |
| Measuring Liquid | Total Surface Tension [mN/m] | Dispersive Part [mN/m] | Polar Part [mN/m] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distilled water | 72.8 | 21.8 | 51.0 |
| 1,5-pentanediol | 43.3 | 27.6 | 15.7 |
| Diiodmethane | 50.8 | 50.8 | 0 |
| Material | Surface Treatment | Profile | 3D-Surface |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ra [µm] | Sdr [%] | ||
| Pure PP | Milling | 0.8 | 15.3 |
| PP/10 | Milling | 0.7 | 7.3 |
| PP/20 | Milling | 1.1 | 12.8 |
| PP/40 | Milling | 0.5 | 2.7 |
| PP/60 | Milling | 0.5 | 5.0 |
| PP/80 | Milling | 0.5 | 10.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rzeczkowski, P.; Krause, B.; Pötschke, P. Characterization of Highly Filled PP/Graphite Composites for Adhesive Joining in Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030462
Rzeczkowski P, Krause B, Pötschke P. Characterization of Highly Filled PP/Graphite Composites for Adhesive Joining in Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030462
Chicago/Turabian StyleRzeczkowski, Piotr, Beate Krause, and Petra Pötschke. 2019. "Characterization of Highly Filled PP/Graphite Composites for Adhesive Joining in Fuel Cell Applications" Polymers 11, no. 3: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030462
APA StyleRzeczkowski, P., Krause, B., & Pötschke, P. (2019). Characterization of Highly Filled PP/Graphite Composites for Adhesive Joining in Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers, 11(3), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030462