Sequential Recovery of Heavy and Noble Metals by Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine-Polyethyleneimine Conjugated Polyurethane Composite Bearing Dithiocarbamate Moieties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
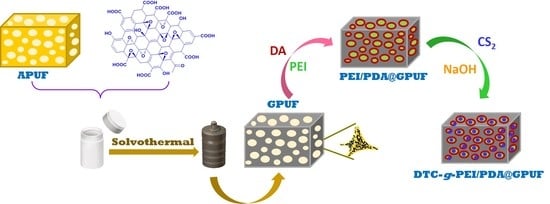
2.3. Synthesis of PE-DA@GB@PU and DTC-g-PE-DA@GB@PU
2.4. Static Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of PE-DA@GB@PU and DTC-g-PE-DA@GB@PU
3.2. pH Effect
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
3.6. Regeneration of DTC-g-PE-DA@GB@PU and PE-DA@GB@PU
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Song, Q.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P.C. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil–vegetable system: A multi-medium analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieszynska, A.; Wieczorek, D. Extraction and separation of palladium(II), platinum(IV), gold(III) and rhodium(III) using piperidine-based extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawed, E.A.; Ishaq, I.; Abdul-Rahman, A.; El-Shahat, M.F. Synthesis, characterization of carbon polyurethane powder and its application for separation and spectrophotometric determination of platinum in pharmaceutical and ore samples. Talanta 2014, 121, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. Key technology research on the efficient exploitation and comprehensive utilization of resources in the deep Jinchuan nickel deposit. Engineering 2017, 3, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Varma, A.J. Functional nanoparticles obtained from cellulose: Engineering the shape and size of 6-carboxycellulose. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8818–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Hsiao, B.S. Efficient removal of UO22+ from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by the nitro-oxidation method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13885–13893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Joshi, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Hsiao, B.S. A simple approach to prepare carboxycellulose nanofibers from untreated biomass. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da̧browski, A.; Hubicki, Z.; Podkościelny, P.; Robens, E. Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoloski, A.N.; Ang, K.-L.; Li, D. Recovery of platinum, palladium and rhodium from acidic chloride leach solution using ion exchange resins. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arabian J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhandare, A.A.; Argekar, A.P. Separation and recovery of platinum and rhodium by supported liquid membranes using bis (2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid (HDEHP) as a mobile carrier. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 201, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.E.D.; Paiva, A.P.; Soares, D.; Labrincha, A.; Castro, F. Solvent extraction applied to the recovery of heavy metals from galvanic sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 120, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, L. Solvent extraction and separation of palladium(II) and platinum(IV) from hydrochloric acid medium with dibutyl sulfoxide. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, H. Novel 2D nanosheets with potential applications in heavy metal purification: A review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1801094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeh, C.C.; Bubacz, M. Current trends in nanocomposite foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2008, 44, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, B. Mussel-inspired modification of carbon fiber via polyethyleneimine/polydopamine co-deposition for the improved interfacial adhesion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 151, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, R.; Shen, F.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, N. Construction of mussel-inspired coating via the direct reaction of catechol and polyethyleneimine for efficient heparin immobilization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 328, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jing, S.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Tan, Y. Preparation of dithiocarbamate polymer brush grafted nanocomposites for rapid and enhanced capture of heavy metal ions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 13112–13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Xiao, D.; Li, Z.; Cui, X. Dithiocarbamate functionalized lignin for efficient removal of metallic ions and the usage of the metal-loaded bio-sorbents as potential free radical scavengers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2136–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hao, G.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L. One-pot synthesis of robust superhydrophobic, functionalized graphene/polyurethane sponge for effective continuous oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Qian, R.; Jiang, P. Mechanically flexible and multifunctional polymer-based graphene foams for elastic conductors and oil-water separators. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5658–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClain, A.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Synthesis of polystyrene-supported dithiocarbamates and their complexation with metal ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.-Y.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.-J.; Shin, D.M.; Lee, J.-C. Cross-linked graphene oxide membrane having high ion selectivity and antibacterial activity prepared using tannic acid-functionalized graphene oxide and polyethyleneimine. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 521, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, M.-Q.; Chen, T.-T.; Zhang, H.; Hu, D.-F.; Wu, B.-H.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Dopamine-triggered one-step polymerization and codeposition of acrylate monomers for functional coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 34356–34366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Shen, P.; Sun, J. Cytosine-functionalized polyurethane foam and its use as a sorbent for the determination of gold in geological samples. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Ramesh, A.; Maki, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Ueda, K. Adsorption of platinum (IV), palladium (II) and gold (III) from aqueous solutions onto L-lysine modified crosslinked chitosan resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Hu, H.; Fu, W.; Wan, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhuge, L.; Xiong, L.; Chen, Q. Synthesis of a novel silica-supported dithiocarbamate adsorbent and its properties for the removal of heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, Z. Hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous manganese dioxide: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, H.; Yu, J.; Lin, S. Study on the competitive adsorption and correlational mechanism for heavy metal ions using the carboxylated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs-COOH) as efficient adsorbents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.A.; Park, H.N.; Won, S.W. A reusable adsorbent polyethylenimine/polyvinyl chloride crosslinked fiber for Pd(II) recovery from acidic solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.N.; Choi, H.A.; Won, S.W. Fibrous polyethylenimine/polyvinyl chloride crosslinked adsorbent for the recovery of Pt(IV) from acidic solution: Adsorption, desorption and reuse performances. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Zhan, C.; Sharma, S.K.; Geng, L.; Hsiao, B.S. Lead removal from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by nitro-oxidation method. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Geng, L.; Amiralian, N.; Martin, D.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose from spinifex as an effective adsorbent to remove cadmium(II) from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Chen, Y. Recycle and reusable melamine sponge coated by graphene for highly efficient oil-absorption. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 488, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Li, G.; Meng, Y. Graphene oxides cross-linked with hyperbranched polyethylenimines: Preparation, characterization and their potential as recyclable and highly efficient adsorption materials for lead(II) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parajuli, D.; Kawakita, H.; Inoue, K.; Funaoka, M. Recovery of gold(III), palladium(II), and platinum(IV) by aminated lignin derivatives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 6405–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elci, L.; Soylak, M.; Buyuksekerci, E.B. Separation of gold, palladium and platinum from metallurgical samples using an amberlite XAD-7 resin column prior to their atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. Anal. Sci. 2003, 19, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Isotherms | Isotherm Constants | Heavy Metal Ions | Noble Metal Ions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pd2+ | Pt4+ | Au3+ | ||
| Langmuir | Fmax (mg g−1) | 41.2 | 113.9 | 57.1 | 285.7 | 185.2 | 384.6 |
| K (L mg−1) | 0.02915 | 0.3776 | 0.1726 | 0.0986 | 0.1192 | 0.2524 | |
| R2 | 0.9164 | 0.9935 | 0.9971 | 0.9985 | 0.9988 | 0.9997 | |
| RL | 0.2554–0.6317 | 0.0145–0.1169 | 0.0461–0.2246 | 0.0125–0.9103 | 0.0138–0.8935 | 0.0049–0.7985 | |
| Freundlich | Kf (mg g−1) (L mg−1)1/n | 2.816 | 44.17 | 15.57 | 37.025 | 32.946 | 58.844 |
| n | 1.823 | 4.200 | 3.207 | 2.682 | 3.095 | 2.597 | |
| R2 | 0.9431 | 0.9891 | 0.9635 | 0.9653 | 0.9614 | 0.9102 | |
| Dubinin–Radushkevich | FD-R (mg g−1) | 30.6 | 98.2 | 45.6 | 128.14 | 101.64 | 195.43 |
| E | 0.082 | 0.780 | 0.728 | 2.946 | 3.402 | 2.884 | |
| R2 | 0.9832 | 0.7024 | 0.8152 | 0.6336 | 0.7531 | 0.7947 | |
| Model | Parameters | Heavy Metal Ions | Noble Metal Ions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pd2+ | Pt4+ | Au3+ | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | k1 (min−1) R2 | 0.1020 0.9440 | 0.1105 0.9649 | 0.1021 0.9657 | 0.1951 0.9456 | 0.2077 0.9240 | 0.1967 0.6513 |
| Pseudo-second-order | k2 (g mg−1min−1) R2 | 0.6965 0.9988 | 2.2519 0.9995 | 1.1523 0.9993 | 5.1564 0.9997 | 1.1750 0.9838 | 26.8477 0.9998 |
| Intraparticle diffusion | Ki (mg g−1 min−0.5) R2 | 0.02166 0.8860 | 0.01451 0.7155 | 0.01773 0.8487 | 0.0247 0.6995 | 0.0369 0.7628 | 0.0118 0.3221 |
| Sample | Analytes | Added (μg g−1) | Found a (μg g−1) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial effluents | Cu | — | 112.6 ± 5.8 | — |
| 100 | 209.2 ± 7.6 | 96.6 | ||
| Pb | — | 12.7 ± 2.0 | — | |
| 10 | 22.6 ± 2.6 | 96.0 | ||
| Cd | — | 5.4 ± 0.4 | — | |
| 10 | 14.6 ± 1.8 | 92.0 | ||
| Copper leaching residue | Pd | — | 13.2 ± 1.8 | — |
| 20 | 32.1 ± 3.4 | 94.5 | ||
| Pt | — | 20.0 ± 3.7 | — | |
| 20 | 40.7 ± 4.0 | 104 | ||
| Au | — | 25.3 ± 2.4 | — | |
| 20 | 46.5 ± 3.0 | 106 | ||
| Anode slime | Pd | — | 33.4 ± 2.8 | — |
| 30 | 62.1 ± 2.4 | 95.7 | ||
| Pt | — | 8.3 ± 1.6 | — | |
| 10 | 17.7 ± 2.2 | 94.0 | ||
| Au | — | 179.8 ± 3.5 | — | |
| 100 | 285.1 ± 2.2 | 105 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, D.; Li, T.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Q.; Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Su, B.; et al. Sequential Recovery of Heavy and Noble Metals by Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine-Polyethyleneimine Conjugated Polyurethane Composite Bearing Dithiocarbamate Moieties. Polymers 2019, 11, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071125
Xue D, Li T, Chen G, Liu Y, Zhang D, Guo Q, Guo J, Yang Y, Sun J, Su B, et al. Sequential Recovery of Heavy and Noble Metals by Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine-Polyethyleneimine Conjugated Polyurethane Composite Bearing Dithiocarbamate Moieties. Polymers. 2019; 11(7):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071125
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Dingshuai, Ting Li, Guoju Chen, Yanhong Liu, Danping Zhang, Qian Guo, Jujie Guo, Yueheng Yang, Jiefang Sun, Benxun Su, and et al. 2019. "Sequential Recovery of Heavy and Noble Metals by Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine-Polyethyleneimine Conjugated Polyurethane Composite Bearing Dithiocarbamate Moieties" Polymers 11, no. 7: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071125
APA StyleXue, D., Li, T., Chen, G., Liu, Y., Zhang, D., Guo, Q., Guo, J., Yang, Y., Sun, J., Su, B., Sun, L., & Shao, B. (2019). Sequential Recovery of Heavy and Noble Metals by Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine-Polyethyleneimine Conjugated Polyurethane Composite Bearing Dithiocarbamate Moieties. Polymers, 11(7), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071125