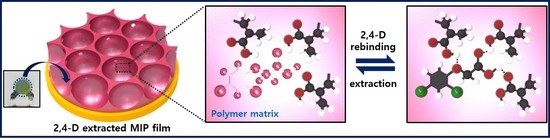
Replicated Pattern Formation and Recognition Properties of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-Imprinted Polymers Using Colloidal Silica Array Molds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Monodispersed Silica Particles
2.3. Fabrication of p-MIP Films
2.4. Characteristics
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abigail, M.E.A.; Samuel, S.M.; Needhidasan, S.; Ramalingam, C. Stratagems employed for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid removal from polluted water sources. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Behbahani, M.; Najafi, F.; Bagheri, S.; Bojdi, M.K.; Hassanlou, P.G.; Bagheri, A. Coupling of solvent-based de-emulsification dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with high performance liquid chromatography for simultaneous simple and rapid trace monitoring of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Yamini, Y.; Seidi, S.; Tahmasebi, E.; Rezaei, F. Electromembrane surrounded solid phase microextraction followed by injection port derivatization and gas chromatography–flame ionization detector analysis for determination of acidic herbicides in plant tissue. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3134–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloschik, E.; Mörtl, M.; Székács, A. Novel derivatisation technique for the determination of chlorophenoxy acid type herbicides by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z. Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Chimuka, L. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics from environmental waters and biological samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Row, K.H. Characteristic and synthetic approach of molecularly imprinted polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubulikasimu, M.; Muhammad, T.; Imerhasan, M.; Hudaberdi, N.; Yang, W.; Zhao, J.; Peng, X. Synthesis of fluorescent drug molecules for competitive binding assay based on molecularly imprinted polymers. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6779–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, E.; Ramström, O.; Möller, P.; Sanchez, D.; Mosbach, K. A facile method for preparing molecularly imprinted polymer spheres using spherical silica templates. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1577–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, T.; Kettisen, K.; Ye, L.; Bülow, L. Chromatographic separation of hemoglobin variants using robust molecularly imprinted polymers. Talanta 2019, 199, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Ou, G.; Gao, Z. Rapid and multiple detections of staphylococcal enterotoxins by two-dimensional molecularly imprinted film-coated QCM Sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 191, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.Z.; Zhao, L.X.; Chu, B.L.; Yan, W.; Lin, J.M. Synthesis and binding site characteristics of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol-imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Wu, X.; Fu, J.; Kang, Q.; Shen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, L. A molecular imprinting-based turn-on ratiometric fluorescence sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.S.; Yang, D.S.; Cho, S.H. Synthesis and characterization of high selective molecularly imprinted polymers for bisphenol A and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by using supercritical fluid technology. Polymer 2013, 54, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, F.; Behbahani, M.; Abandansari, H.S.; Sedighi, A.; Shahtaheri, S.J. Application of molecular imprinted polymer nanoparticles as a selective solid phase extraction for preconcentration and trace determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in the human urine and different water samples. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Kapua, A. Fabrication of molecularly imprinted polymer microstructures. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Surface-relief-gratings based on molecularly imprinted polymer for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid detection. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 220, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Milosevic, B.; Frenot, A.; Ye, L. Generation of molecular recognition sites in electrospun polymer nanofibers via molecular imprinting. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Dabrowski, M.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Surface development of molecularly imprinted polymer films to enhance sensing signals. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y. Effect of lithographically designed structures on the caffeine sensing properties of surface imprinted films. Analyst 2016, 141, 5709–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Shin, H.K.; Hong, S.W.; Park, J.Y. Lithographically patterned molecularly imprinted polymer for gravimetric detection of trace atrazine. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 216, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Yang, J.C.; Park, J.Y. Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) gravimetric sensing of theophylline via molecularly imprinted microporous polypyrrole copolymers. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 206, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Park, J.Y. Polymeric colloidal nanostructures fabricated via highly controlled convective assembly and their use for molecular imprinting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7381–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Yang, J.C.; Park, J.Y. Caffeine-imprinted conducting polymeric films with 2D hierarchical pore arrays prepared via colloidal mask-assisted electrochemical polymerization. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 260, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, N.N.; Yoon, K.B. Facile organization of colloidal particles into large, perfect one- and two-dimensional arrays by dry manual assembly on patterned substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14228–14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, T.; Xia, Y.; Shin, T.J.; Myoung, J.; Jeong, U. Quick, large-area assembly of a single-crystal monolayer of spherical particles by unidirectional rubbing. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4633–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, T.; Grasset, F.; Mornet, S.; Duguet, E.; Cador, O.; Cordier, S.; Molard, Y.; Demange, V.; Mortier, M.; Haneda, H. Functional silica nanoparticles synthesized by water-in-oil microemulsion processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 34, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swihart, M.T. Vapor-phase synthesis of nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, G.H.; Zukoski, C.F., IV. Studies of the kinetics of the precipitation of uniform silica particles through the hydrolysis and condensation of silicon alkoxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 142, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lu, Z.; Teng, Z.; Liang, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Han, M.Y.; Yang, W. Unraveling the growth mechanism of silica particles in the Stöber method: In situ seeded growth model. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5879–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flater, E.E.; Zacharakis-Jutz, G.E.; Dumba, B.G.; White, I.A.; Clifford, C.A. Towards easy and reliable AFM tip shape determination using blind tip reconstruction. Ultramicroscopy 2014, 146, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donjuan-Medrano, A.L.; Montes-Rojas, A. Comparison of sensitivity constants of an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance determined by potentiostatic deposition of Tl, Pb, Ag and Cu films. Curr. Top. Electrochem. 2012, 17, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbrey, G. Use of quartz vibration for weighing thin films on a microbalance. Z. Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohna, J.E.S.; Cooper, M.A. Does the Sauerbrey equation hold true for binding of peptides and globular proteins to a QCM? A systematic study of mass dependence of peptide and protein binding with a piezoelectric sensor. Sens. Bio Sens. Res. 2016, 11, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryshchenko, A.O.; Bottaro, C.S. Development of molecularly imprinted polymer in porous film format for binding of phenol and alkylphenols from water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1338–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aya, G.A.; Yang, J.C.; Hong, S.W.; Park, J.Y. Replicated Pattern Formation and Recognition Properties of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-Imprinted Polymers Using Colloidal Silica Array Molds. Polymers 2019, 11, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081332
Aya GA, Yang JC, Hong SW, Park JY. Replicated Pattern Formation and Recognition Properties of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-Imprinted Polymers Using Colloidal Silica Array Molds. Polymers. 2019; 11(8):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081332
Chicago/Turabian StyleAya, Gita Amiria, Jin Chul Yang, Suck Won Hong, and Jin Young Park. 2019. "Replicated Pattern Formation and Recognition Properties of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-Imprinted Polymers Using Colloidal Silica Array Molds" Polymers 11, no. 8: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081332
APA StyleAya, G. A., Yang, J. C., Hong, S. W., & Park, J. Y. (2019). Replicated Pattern Formation and Recognition Properties of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-Imprinted Polymers Using Colloidal Silica Array Molds. Polymers, 11(8), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081332