Three-Step Synthesis of a Redox-Responsive Blend of PEG–block–PLA and PLA and Application to the Nanoencapsulation of Retinol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Redox-Responsive (PEG–block–PLA)-Blend-(PLA)
2.2.1. Step 1: Synthesis of Ethanol, 2-[(5-Nitro-2-pyridinyl)dithio]-(Abbreviated as Compound 1)
2.2.2. Step 2: Synthesis of Disulfide PEG (Abbreviated as P1)
2.2.3. Step 3: Synthesis of Redox-Responsive Copolymer (Abbreviated as P2)
2.2.4. Characterizations
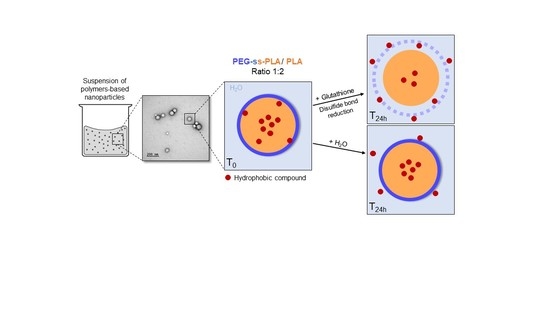
2.3. Preparation of Polymer Nanocarriers
2.4. Characterization of Copolymer-Based Nanocarriers
2.5. Redox-Responsivity of Copolymer-Based Nanocarriers
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies of Retinol-Loaded Nanocarriers
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Redox-Responsive PEG–block–PLA
3.2. Nanocarriers Characteristics
3.3. Nanocarriers Behaviour in a Reductive Medium
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies of Retinol-Loaded Nanocarriers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joglekar, M.; Trewyn, B.G. Polymer-based stimuli-responsive nanosystems for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Ding, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Li, L. Co-delivery of paclitaxel and doxorubicin using mixed micelles based on the redox sensitive prodrugs. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balendiran, G.K.; Dabur, R.; Fraser, D. The role of glutathione in cancer. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2004, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Révész, L.; Edgren, M.R.; Wainson, A.A. Selective toxicity of buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) to melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 29, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, N.; Ricciarelli, R.; Nitti, M.; Marengo, B.; Furfaro, A.L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Marinari, U.M.; Domenicotti, C. Role of Glutathione in Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 972913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuoco, T.; Pappalardo, D.; Finne-Wistrand, A. Redox-Responsive Disulfide Cross-Linked PLA–PEG Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7052–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Liu, W.; Tu, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Preparation and in vitro properties of redox-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for paclitaxel delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 87, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H. Redox Sensitive Nanoparticles with Disulfide Bond Linked Sheddable Shell for Intracellular Drug Delivery. Med. Chem. 2014, 4, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, A.; Hayat, U.; Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Redox-responsive nano-carriers as tumor-targeted drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.V.; Ko, H.; Lee, J.; Park, J.H. Recent Progress and Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Polymers for Cancer Therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, R.; Xia, H.; Lu, X. Fast release behavior of block copolymer micelles under high intensity focused ultrasound/redox combined stimulus. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.; Guo, H.; Tian, X.; Liu, G.; Zheng, D.; Qi, L. Redox-responsive catiomer based on PEG-ss-chitosan oligosaccharide-ss-polyethylenimine copolymer for effective gene delivery. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Wen, H.Y.; Dong, H.Q.; Xue, W.M.; Pauletti, G.M.; Cai, X.J.; Xia, W.J.; Shi, D.; Li, Y.Y. Self-assembling nanomicelles of a novel camptothecin prodrug engineered with a redox-responsive release mechanism. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Thambi, T.; Choi, K.Y.; Son, S.; Ko, H.; Lee, M.C.; Jo, D.-G.; Chae, Y.S.; Kang, Y.M.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Bioreducible Shell-Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Kang, Y.; Wang, M. Glutathione-Responsive Polymeric Micelles Formed by a Biodegradable Amphiphilic Triblock Copolymer for Anticancer Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motornov, M.; Roiter, Y.; Tokarev, I.; Minko, S. Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles, nanogels and capsules for integrated multifunctional intelligent systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 174–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Urban, M.W. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanoparticles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Shen, Y.-M.; Gong, B. Dynamic Covalent Diblock Copolymers: Instructed Coupling, Micellation and Redox Responsiveness. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 7431–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Hoang, L.; Fougère, R.; Waché, Y. Increase in stability and change in supramolecular structure of β-carotene through encapsulation into polylactic acid nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Cingolani, A.; Moscatelli, D. Solvent Effect in PLA-PEG Based Nanoparticles Synthesis through Surfactant Free Polymerization. Macromol. Symp. 2013, 324, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalloz, A.; Bolzinger, M.-A.; Briançon, S.; Faivre, J.; Rabanel, J.-M.; Ac, A.G.; Hildgen, P.; Banquy, X. Subtle and unexpected role of PEG in tuning the penetration mechanisms of PLA-based nano-formulations into intact and impaired skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Mao, C.-Q.; Dou, S.; Shen, S.; Tan, Z.-B.; Wang, J. Triple negative breast cancer therapy with CDK1 siRNA delivered by cationic lipid assisted PEG-PLA nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2014, 192, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Al-Joufi, F.; Anwar, M.; Attia, M.F.; El-Bana, M.A. Curcumin-loaded PLA-PEG copolymer nanoparticles for treatment of liver inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovino, C.; Ayensu, I.; Tetteh, J.; Boateng, J.S. An integrated buccal delivery system combining chitosan films impregnated with peptide loaded PEG-b-PLA nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, J.; Warner, R.L.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Phan, S.H.; Kang, S.; Chung, J.; Wang, Z.; Datta, S.C.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Vitamin A Antagonizes Decreased Cell Growth and Elevated Collagen-Degrading Matrix Metalloproteinases and Stimulates Collagen Accumulation in Naturally Aged Human Skin1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allwood, M.C.; Plane, J.H. The wavelength-dependent degradation of vitamin A exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Meltzer, N.; Lindenbaum, S. Determination of the kinetics of degradation of 13-cis-retinoic acid and all-trans-retinoic acid in solution. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1993, 11, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyler, A.R.; Motto, M.G.; Naldi, R.E.; Facchine, K.L.; Hamburg, P.F.; Burinsky, D.J.; Dunphy, R.; Cotter, M.L. Characterizationf of autoxidation products of retinoic acid. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 7679–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, F.; Baines, A.; Stone, J.; Ryley, J. The kinetics of the loss of all-trans retinol at low and intermediate water activity in air in the dark. Food Chem. 1995, 52, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, C.W.; White, J.P.; Osta, E.G.; Patel, J.; Rajkumar, S.; Kirby, N.; Therrien, J.-P.; Zauscher, S. Encapsulation and controlled release of retinol from silicone particles for topical delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 278, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.; Choi, C.; Roh, S.; Kang, S.; Jang, M.; Nah, J. Retinol-encapsulated low molecular water-soluble chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 319, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.-J.; Oh, C.; Oh, S.-G. Controlled release of retinol from silica particles prepared in O/W/O emulsion: The effects of surfactants and polymers. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laredj-Bourezg, F.; Bolzinger, M.-A.; Pelletier, J.; Valour, J.-P.; Rovère, M.-R.; Smatti, B.; Chevalier, Y. Skin delivery by block copolymer nanoparticles (block copolymer micelles). Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentini, F.F.; Sponton, O.E.; Perez, A.A.; Santiago, L.G. Biopolymer nanoparticles for vehiculization and photochemical stability preservation of retinol. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourissou, D.; Martin-Vaca, B.; Dumitrescu, A.; Graullier, M.; Lacombe, F. Controlled Cationic Polymerization of Lactide. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9993–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Daoud, W.; Cheuk, K.; Lin, C. Newly Developed Techniques on Polycondensation, Ring-Opening Polymerization and Polymer Modification: Focus on Poly (Lactic Acid). Materials 2016, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasatsu, M.; Onishi, H.; Machida, Y. In vitro and in vivo characterization of nanoparticles made of MeO-PEG amine/PLA block copolymer and PLA. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Pan, K.; Yang, Y. Novel nanomicelles originating from hydroxyethyl starch-g-polylactide and their release behavior of docetaxel modulated by the PLA chain length. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoustafa, H.A.; Alshawsh, M.A.; Chik, Z. Technical aspects of preparing PEG-PLGA nanoparticles as carrier for chemotherapeutic agents by nanoprecipitation method. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahire, R.; Haldar, M.K.; Paul, S.; Ambre, A.H.; Meghnani, V.; Layek, B.; Katti, K.S.; Gange, K.N.; Singh, J.; Sarkar, K.; et al. Multifunctional polymersomes for cytosolic delivery of gemcitabine and doxorubicin to cancer cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6482–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer deposition following solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, S.; Heinze, T.; Becer, C.R.; Schubert, U.S. Synthetic polymeric nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, S.R.; Coughlin, E.B.; Hsu, S.L.; Golub, C.S.; Ling, G.H.; Tzivanis, M.J. Effect of midblock on the morphology and properties of blends of ABA triblock copolymers of PDLA-mid-block-PDLA with PLLA. Polymer 2012, 53, 3008–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgoustakis, K. Pegylated Poly(Lactide) and Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Nanoparticles: Preparation, Properties and Possible Applications in Drug Delivery. CDD 2004, 1, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, S.; Jindal, N.; Jindal, A.; Bansal, R. Nanocarriers and nanoparticles for skin care and dermatological treatments. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2013, 4, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Rong Qi, X.; Maitani, Y.; Nagai, T. PEG–PLA diblock copolymer micelle-like nanoparticles as all-trans-retinoic acid carrier: In vitro and in vivo characterizations. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.D.; Mehra, S.; Jadhav, S.; Bellare, J.R. All-trans retinoic acid loaded block copolymer nanoparticles efficiently induce cellular differentiation in HL-60 cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Truong, N.K.V.; Shin, S.; Jeong, S.H. A robust experimental design method to optimize formulations of retinol solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.-P.; Lim, S.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, C.-K. Stabilization of all-trans retinol by loading lipophilic antioxidants in solid lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandar, N.G.; Simovic, S.; Prestidge, C.A. Chemical stability and phase distribution of all-trans-retinol in nanoparticle-coated emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 376, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.P. Redox potential of GSH/GSSG couple: Assay and biological significance. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 348, pp. 93–112. ISBN 978-0-12-182251-4. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, O.W. Biologic and pharmacologic regulation of mammalian glutathione synthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.V.; Jones, D.P.; Guenthner, T.M.; Lash, L.H.; Lauterburg, B.H. Compartmentation of Glutathione: Implications for the Study of Toxicity and Disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 140, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, P.; Fowler, S. Spectrofluorometric studies of the lipid probe, nile red. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 781–789. [Google Scholar]
- Bej, R.; Dey, P.; Ghosh, S. Disulfide chemistry in responsive aggregation of amphiphilic systems. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Hennink, W.E.; Zhong, Z. Reduction-sensitive polymers and bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2180–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers–A systematic review of in vitro data. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckenbach, L.; Baron, J.M.; Merk, H.F.; Löffler, H.; Amann, P.M. Retinoid treatment of skin diseases. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2015, 25, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.K.; Simmons, J.L.; Parsons, P.G.; Boyle, G.M. Topical treatments for skin cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 153, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |










| Characteristics | Nile Red-Labelled Nanocarriers | Retinol-Loaded Nanocarriers | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) | 100.5 ± 2.7 | 98.7 ± 2.2 |
| Polydispersity Index | 0.126 ± 0.013 | 0.101 ± 0.011 | |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −25.7 ± 2.3 | −21.6 ± 1.6 | |
| Retinol (mg/mL) | - | 0.28 ± 0.04 | |
| 1 month 4 °C | Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) | 98.0 ± 2.4 | 94.1 ± 1.6 |
| Polydispersity Index | 0.115 ± 0.017 | 0.093 ± 0.010 | |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −27.8 ± 3.1 | −20.7 ± 3.6 | |
| Retinol (mg/mL) | - | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Gheluwe, L.; Buchy, E.; Chourpa, I.; Munnier, E. Three-Step Synthesis of a Redox-Responsive Blend of PEG–block–PLA and PLA and Application to the Nanoencapsulation of Retinol. Polymers 2020, 12, 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102350
Van Gheluwe L, Buchy E, Chourpa I, Munnier E. Three-Step Synthesis of a Redox-Responsive Blend of PEG–block–PLA and PLA and Application to the Nanoencapsulation of Retinol. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102350
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Gheluwe, Louise, Eric Buchy, Igor Chourpa, and Emilie Munnier. 2020. "Three-Step Synthesis of a Redox-Responsive Blend of PEG–block–PLA and PLA and Application to the Nanoencapsulation of Retinol" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102350
APA StyleVan Gheluwe, L., Buchy, E., Chourpa, I., & Munnier, E. (2020). Three-Step Synthesis of a Redox-Responsive Blend of PEG–block–PLA and PLA and Application to the Nanoencapsulation of Retinol. Polymers, 12(10), 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102350