Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide–Gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
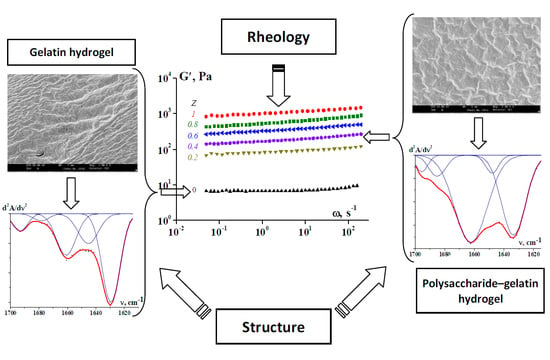
- periodic oscillations at a constant temperature (14 °C) and a different frequency, ω, in a range of 0.0628–628 rad/s in the domain of linear viscoelastic behaviour;
- -
- at a constant temperature of 14 °C and a constant frequency of 6.28 rad/s to follow the “aging” of the samples;
- -
- at a constant frequency of 6.28 rad/s and increasing the temperature at a rate of 2 K/min;
- -
- in rate-controlled shearing mode with a range of shear rates, , of 10−3–102 s−1 or in stress with the yield stress σ control mode in a range of 0.01–200 Pa.
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semenova, M.G.; Dickinson, E. Biopolymers in Food Colloids: Thermodynamics and Molecular Interactions, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; McClements, D.J. Progress in natural emulsifiers for utilization in food emulsions. Curr. Opin. Food. Sci. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Colloids in food: Ingredients, structure, and stability. Annu. Rev. Food. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural emulsifiers—Biosurfactants, phospholipids, biopolymers, and colloidal particles: Molecular and physicochemical basis of functional performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joye, I.J.; McClements, D.J. Biopolymer-based delivery systems: Challenges and opportunities. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.A.; Hashemi, J.; Prentice, C. Development of novel bioactives delivery systems by micro/nanotechnology. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Turgeon, S.L. Protein/polysaccharide complexes and coacervates in food systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, M.; Moiseenko, D.; Grigorovich, N.; Anokhina, M.; Antipova, A.; Belyakova, L.; Polikarpov, Y.; Tsapkina, E. Protein–polysaccharide interactions and digestion of the complex particles. In Food Structure, Digestion and Health; Boland, M., Golding, M., Singh, H., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, M. Protein–polysaccharide associative interactions in the design of tailor-made colloidal particles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Q. Assembly of Protein−Polysaccharide Complexes for Delivery of Bioactive Ingredients: A Perspective Paper. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Vovk, M.A.; Tolstoy, P.M. Formation of κ-carrageenan–gelatin polyelectrolyte complexes studied by 1H NMR, UV spectroscopy and kinematic viscosity measurements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Sokolan, N.I. The chitosan-gelatin (bio)polyelectrolyte complexes formation in an acidic medium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kolotova, D.S.; Kuchina, Y.A. Interactions between gelatin and sodium alginate: UV and FTIR studies. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabek, J.F. Experimental Methods in Polymer Chemistry: Physical Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Vebster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Izmailova, V.N.; Derkach, S.R.; Sakvarelidze, M.A.; Levachev, S.M.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Yampol’skaya, G.P. Gelation in gelatin and gelatin-containing multicomponent blends. Polym. Sci. C 2004, 46, 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. Gelatin. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 142–163. [Google Scholar]
- Goudoulas, N.B.; Germann, N. Phase transition kinetics and rheology of gelatin-alginate mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Peh, Y.R.; Pekerti, B.N.; Fu, C.; Bansal, N.; Yang, H. Nanostructural analysis and textural modification of tilapia fish gelatin affected by gellan and calcium chloride addition. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.; Voron’Ko, N.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.; Gordeeva, A.; Faizullin, D.; Gusev, Y.A.; Zuev, Y.F.; Makshakova, O. Molecular structure and properties of κ-carrageenan-gelatin gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranoto, Y.; Lee, C.M.; Park, H.J. Characterizations of fish gelatin films added with gellan and k-carrageenan. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J. Molecular interactions in gelatin/chitosan composite films. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, J.; Giraudier, S.; Larreta-Garde, V. Controlled remodeling of a protein-polysaccharide mixed gel: Examples of gelatin-hyaluronic acid mixtures. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Structure and rheology of highly concentrated emulsions. Modern view. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2015, 84, 803–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G. A modern look on yield stress fluids. Rheol. Acta 2017, 56, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I. The Rheology of Hydrogels Based on Chitosan–Gelatin (Bio)polyelectrolyte Complexes. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystupa, D.A.; Donald, A.M. Infrared Study of Gelatin Conformations in the Gel and Sol States. Polym. Gels Netw. 1996, 4, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Erboz, E.N. Determination of critical gelation conditions of κ-carrageenan by viscosimetric and FT-IR analyses. Food Res. Internat. 2010, 43, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dai, Y.N.; Zhang, J.P.; Wang, A.Q.; Wei, Q. Chitosan-alginate nanoparticles as a novel drug delivery system for nifedipine. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 4, 221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qui, T.; Cosgrove, T.; Denbow, M.L. A small-angle neutron scattering and rheology study of the composite of chitosan and gelatin. Colloid Surf. B 2009, 70, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinyl Alcohol-Gelatin Hydrogel Membranes for Biomedical Applications. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2007, 8, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L. Blend Films from sodium alginate and gelatin solutions. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2001, 38, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimets, I.; Wellner, N.; Smith, A.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Farhat, I.; Mitchell, J. Mechanical properties with respect to water content of gelatin films in glassy state. Polymer 2005, 46, 12577–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, H.; Cheng, Q.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z. Sodium Alginate–Gelatin Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes with Both High Water Vapor Permeance and High Permselectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroszczyk, H.; Sztuka, K.; Wolska, J.; Wojtasz-Pajak, A.; Kolodziejska, I. Interactions of fish gelatin and chitosan in uncrosslinked and crosslinked with EDC films: FT-IR study. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Kong, K.; Yang, H. Structural Modification of Fish Gelatin by the Addition of Gellan, j-Carrageenan, and Salts Mimics the Critical Physicochemical Properties of Pork Gelatin. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lii, C.-Y.; Liaw, S.C.; Lai, V.M.-F.; Tomasik, P. Xanthan gum–gelatin complexes. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almrhag, O.; George, P.; Bannikova, A.; Katopo, L.; Chaudhary, D.; Kasapis, D. Investigation on the phase behaviour of gelatin/agarose mixture in an environment of reduced solvent quality. Food Chem. 2003, 136, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taravel, M.N.; Domard, A. Collagen and its interaction with chitosan: II. Influence of the physicochemical characteristics of collagen. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of acid soluble collagen and gelatin from skins and bones of young and adult Nile perch. Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared Spectroscopy of Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Yu, S. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis of Protein Secondary Structures. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sinica. 2007, 39, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, K.J.; Veis, A. Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy of Collagen and Gelatin Solutions: Deconvolution of the Amide I Band for Conformational Studies. Biopolymers 1988, 27, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Huang, P.; Caughey, W.S. Protein secondary structures in water from second-derivative Amid I infrared spectra. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 3303–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, G.S.; Al-Alawi, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Guizani, N. Fourier transforminfrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of extracted gelatin from shaari (Lithrinusmicrodon) skin: Effects of extraction conditions. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Sionkowska, A.; Wisniewski, M.; Skopinska, J.; Kennedy, C.J.; Wess, T.J. Molecular interactions in collagen and chitosan blends. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, C.W.; Wilker, J.J.; Schmidt, G. A review on tough and sticky hydrogels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.T.; Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L. Formation and functional properties of protein–polysaccharide electrostatic hydrogels in comparison to protein or polysaccharide hydrogels. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2017, 239, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S.; Natale, G.; Virgilio, N.; Heuzey, M.-C. Synergistic gelation of gelatin B with xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Swedlund, P.J.; Hemar, Y. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin gel as influenced by κ-Carrageenan. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Component | Wave Number ν (cm−1) | Type of Vibration |
|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | 3400–3300 | Stretching vibrations of NH groups (amide A) |
| 1700–1600 | Stretching vibrations of CO– and CN– groups (amide I) | |
| 1575–1480 | Deformation vibrations of NH– groups and stretching vibrations of CN groups (amide II) | |
| 1300–1230 | Stretching vibrations of CN groups (amide III) | |
| Sodium alginate | 3600–3200 | Stretching vibration of OH groups |
| 1580–1620 | Asymmetric stretches of COO groups | |
| 1400–1420 | Symmetric stretches of COO groups | |
| 1300–1320 | Stretching vibration of CO groups | |
| 1070–1090 | Mannuronic units | |
| 1025–1035 | Guluronic units | |
| 815–820 | α-configuration of guluronic units | |
| k-carrageenan | 3600–3200 | Stretching vibration of OH groups |
| 1270–1230 | Vibration of the sulfate group | |
| 1100–1080 | Glycosidic bonds | |
| 1070, 928–933 | 3,6-anhydridegalactose group | |
| 840–850 | D-galactose-4-sulfate group | |
| Chitosan | 3600–3200 | Stretching vibrations of NH groups and OH groups |
| 2960–2880 | Symmetric and asymmetric stretches of CH groups | |
| 1670-1620 | Stretching vibrations of CO groups (amide I) | |
| 1325-1320 | Stretching vibrations of CN groups (amide III) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G. Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide–Gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure. Polymers 2020, 12, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020266
Derkach SR, Kuchina YA, Kolotova DS, Voron’ko NG. Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide–Gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020266
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerkach, Svetlana R., Yuliya A. Kuchina, Daria S. Kolotova, and Nikolay G. Voron’ko. 2020. "Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide–Gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure" Polymers 12, no. 2: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020266
APA StyleDerkach, S. R., Kuchina, Y. A., Kolotova, D. S., & Voron’ko, N. G. (2020). Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide–Gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure. Polymers, 12(2), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020266