p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
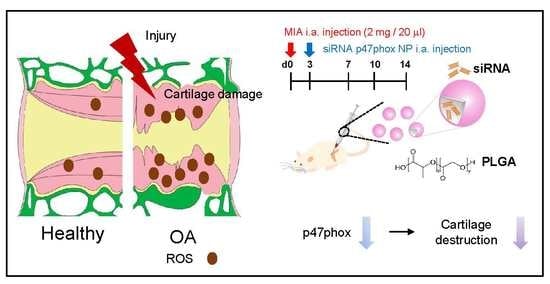
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Osteoarthritis Model
2.2. Human Chondrocyte
2.3. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.4. Behavior Test
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. DHE Staining
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Preparation of siRNA-Encapsulated PLGA Nanoparticles
2.9. Colloidal Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. p47phox and ROS Were Highly Expressed in Chondrocyte Clusters in Human OA Tissues
3.2. p47phox Was Highly Expressed in the Chondrocytes of MIA-Induced OA Rats
3.3. Colloidal Characterization of p47phox siRNA-Encapsulated PLGA NPs
3.4. Inhibition of p47phox by NP-Delivered siRNA Attenuated Pain Behaviors, Cartilage Damage, and ROS Production in Knee Joints with MIA-Induced OA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoshiyama, Y.; Otsuki, S.; Oda, S.; Kurokawa, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Jotoku, T.; Tamura, R.; Okamoto, Y.; Lotz, M.K.; Neo, M. Chondrocyte clusters adjacent to sites of cartilage degeneration have characteristics of progenitor cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.M.; Kisiday, J.D.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Grodzinsky, A.J.; Frisbie, D.D. Synoviocytes protect cartilage from the effects of injury in vitro. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandell, L.J.; Aigner, T. Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis. An introduction: Cell biology of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. 2001, 3, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.M.; Palmer, E.A.; Archer, C.W. Fibroblast growth factor-2 induced chondrocyte cluster formation in experimentally wounded articular cartilage is blocked by soluble Jagged-1. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto-Hermida, A.; Fernandez-Moreno, M.; Pertega-Diaz, S.; Oreiro, N.; Fernandez-Lopez, C.; Blanco, F.J.; Rego-Perez, I. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups modulate the radiographic progression of Spanish patients with osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotin, Y.; Kurz, B.; Aigner, T. Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: Friends or foes? Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005, 13, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepetsos, P.; Papavassiliou, A.G. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altindag, O.; Erel, O.; Aksoy, N.; Selek, S.; Celik, H.; Karaoglanoglu, M. Increased oxidative stress and its relation with collagen metabolism in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2007, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.M.; Guilak, F.; Weinberg, J.B.; Fermor, B. Reactive nitrogen and oxygen species in interleukin-1-mediated DNA damage associated with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupuy, C.; Ohayon, R.; Valent, A.; Noel-Hudson, M.S.; Deme, D.; Virion, A. Purification of a novel flavoprotein involved in the thyroid NADPH oxidase. Cloning of the porcine and human cdnas. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37265–37269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geiszt, M.; Leto, T.L. The Nox family of NAD(P)H oxidases: Host defense and beyond. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51715–51718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, M.W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Brann, D.W. NADPH oxidase in brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.M.; Mullen, A.M.; Yun, S.; Wientjes, F.; Brouns, G.Y.; Thrasher, A.J.; Shah, A.M. Essential role of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47(phox) in endothelial cell superoxide production in response to phorbol ester and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; Lemarechal, H.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Poiraudeau, S.; Ekindjian, O.G.; Borderie, D. Superoxide production and NADPH oxidase expression in human rheumatoid synovial cells: Regulation by interleukin-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, I.; Lim, S.D.; Lee, J.K.; Seok, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hur, G.M. Methotrexate suppresses the interleukin-6 induced generation of reactive oxygen species in the synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunopharmacology 2000, 47, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, P.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Hsiao, L.D.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, C.M. Heme oxygenase 1 attenuates interleukin-1beta-induced cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression via a decrease in NADPH oxidase/reactive oxygen species/activator protein 1 activation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevet, S.; Gavazzi, G.; Grange, L.; Dupuy, C.; Lardy, B. Reactive oxygen species and NADPH oxidase 4 involvement in osteoarthritis. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 111, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F.; Hazane-Puch, F.; Pinosa, C.; Nguyen, M.V.; Grange, L.; Soldini, A.; Rubens-Duval, B.; Dupuy, C.; Morel, F.; Lardy, B. IL-1beta mediates MMP secretion and IL-1beta neosynthesis via upregulation of p22(phox) and NOX4 activity in human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepetsos, P.; Pampanos, A.; Lallos, S.; Kanavakis, E.; Korres, D.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Efstathopoulos, N. Association of NADPH oxidase p22phox gene C242T, A640G and -930A/G polymorphisms with primary knee osteoarthritis in the Greek population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 5491–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, L.; Nguyen, M.V.; Lardy, B.; Derouazi, M.; Campion, Y.; Trocme, C.; Paclet, M.H.; Gaudin, P.; Morel, F. NAD(P)H oxidase activity of Nox4 in chondrocytes is both inducible and involved in collagenase expression. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavijo-Cornejo, D.; Martinez-Flores, K.; Silva-Luna, K.; Martinez-Nava, G.A.; Fernandez-Torres, J.; Zamudio-Cuevas, Y.; Guadalupe Santamaria-Olmedo, M.; Granados-Montiel, J.; Pineda, C.; Lopez-Reyes, A. The Overexpression of NALP3 Inflammasome in Knee Osteoarthritis Is Associated with Synovial Membrane Prolidase and NADPH Oxidase 2. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1472567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Dalen, S.C.M.; Kruisbergen, N.N.L.; Walgreen, B.; Helsen, M.M.A.; Sloetjes, A.W.; Cremers, N.A.J.; Koenders, M.I.; van de Loo, F.A.J.; Roth, J.; Vogl, T.; et al. The role of NOX2-derived reactive oxygen species in collagenase-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; Simonneau, C.; Therond, P.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Poiraudeau, S.; Ekindjian, O.G.; Borderie, D. Implication of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) in the regulation of human synoviocyte NADPH oxidase (Nox2) activity. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuhara, R.; Miyamoto, Y.; Akaike, T.; Akuta, T.; Nakamura, M.; Takami, M.; Morimura, N.; Yasu, K.; Kamijo, R. Interleukin-1beta induces death in chondrocyte-like ATDC5 cells through mitochondrial dysfunction and energy depletion in a reactive nitrogen and oxygen species-dependent manner. Biochem. J. 2005, 389, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Funato, S.; Yasuhara, R.; Yoshimura, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Suzawa, T.; Chikazu, D.; Mishima, K.; Baba, K.; Kamijo, R. Extracellular matrix loss in chondrocytes after exposure to interleukin-1beta in NADPH oxidase-dependent manner. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 368, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yasuhara, R.; Maruyama, T.; Akiyama, T.; Yamada, A.; Takami, M.; Suzawa, T.; Tsunawaki, S.; Tachikawa, T.; et al. Monocarboxylate transporter-1 is required for cell death in mouse chondrocytic ATDC5 cells exposed to interleukin-1beta via late phase activation of nuclear factor kappaB and expression of phagocyte-type NADPH oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14744–14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panday, A.; Sahoo, M.K.; Osorio, D.; Batra, S. NADPH oxidases: An overview from structure to innate immunity-associated pathologies. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozov, I.; Lotan, O.; Joseph, G.; Gorzalczany, Y.; Pick, E. Mapping of functional domains in p47(phox) involved in the activation of NADPH oxidase by “peptide walking”. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15435–15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kou, L.; Xiao, S.; Sun, R.; Bao, S.; Yao, Q.; Chen, R. Biomaterial-engineered intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operti, M.C.; Dolen, Y.; Keulen, J.; van Dinther, E.A.W.; Figdor, C.G.; Tagit, O. Microfluidics-Assisted Size Tuning and Biological Evaluation of PLGA Particles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, B.; Eijkel, G.B.; Heeren, R.M.; Karperien, M.; Post, J.N.; Cillero-Pastor, B. Oxygen Regulates Lipid Profiles in Human Primary Chondrocyte Cultures. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, S456–S457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, D.H.; Kim, H.W.; Yoon, S.Y.; Seo, H.S.; Kwon, Y.B.; Kim, K.W.; Han, H.J.; Beitz, A.J.; Na, H.S.; Lee, J.H. Intrathecal injection of the sigma(1) receptor antagonist BD1047 blocks both mechanical allodynia and increases in spinal NR1 expression during the induction phase of rodent neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Yin, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, W.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, D.W.; Hong, J. Foxp3 plasmid-encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles attenuate pain behavior in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Nanomedicine 2019, 18, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.; Kim, H.G.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kwon, H.H.; Baek, H.; Yi, M.H.; Zhang, E.; Kim, J.J.; Hong, J.; et al. Uncoupled Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Enhances p-Tau in Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Mouse Model. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 1601–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Yin, Y.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Triantafillu, U.L.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Hong, J.; et al. p38 siRNA-encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles alleviate neuropathic pain behavior in rats by inhibiting microglia activation. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, L.; Aitta, J.; Hyvonen, S.; Karjalainen, M.; Hirvonen, J. Improved entrapment efficiency of hydrophilic drug substance during nanoprecipitation of poly(l)lactide nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karim, A.; Amin, A.K.; Hall, A.C. The clustering and morphology of chondrocytes in normal and mildly degenerate human femoral head cartilage studied by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Anat. 2018, 232, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrens, J.F. Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J. Physiol. 2003, 552, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.; Sousa-Valente, J.; Malcangio, M. The Monoiodoacetate Model of Osteoarthritis Pain in the Mouse. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, e53746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.; Kunduru, K.R.; Basu, A.; Mizrahi, B.; Domb, A.J.; Khan, W. Injectable formulations of poly(lactic acid) and its copolymers in clinical use. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lababidi, N.; Sigal, V.; Koenneke, A.; Schwarzkopf, K.; Manz, A.; Schneider, M. Microfluidics as tool to prepare size-tunable PLGA nanoparticles with high curcumin encapsulation for efficient mucus penetration. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2280–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Goggins, J.; Amin, S.; LaValley, M.P.; Guermazi, A.; Genant, H.; Gale, D.; Felson, D.T. Increase in bone marrow lesions associated with cartilage loss: A longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study of knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, S.; Giorgi, C.; Suski, J.M.; Agnoletto, C.; Bononi, A.; Bonora, M.; De Marchi, E.; Missiroli, S.; Patergnani, S.; Poletti, F.; et al. Mitochondria-ros crosstalk in the control of cell death and aging. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 329635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Gang, Y.; Bai, L. Alterations of autophagy in knee cartilage by treatment with treadmill exercise in a rat osteoarthritis model. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Benna, J.; Dang, P.M.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; Marie, J.C.; Braut-Boucher, F. p47phox, the phagocyte NADPH oxidase/NOX2 organizer: Structure, phosphorylation and implication in diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faust, L.R.; El Benna, J.; Babior, B.M.; Chanock, S.J. The phosphorylation targets of p47phox, a subunit of the respiratory burst oxidase. Functions of the individual target serines as evaluated by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, H.J.; Park, H.; Shin, N.; Kwon, H.H.; Yin, Y.; Hwang, J.-A.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, S.; Joo, Y.; et al. p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis. Polymers 2020, 12, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020443
Shin HJ, Park H, Shin N, Kwon HH, Yin Y, Hwang J-A, Kim SI, Kim SR, Kim S, Joo Y, et al. p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020443
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Hyo Jung, Hyewon Park, Nara Shin, Hyeok Hee Kwon, Yuhua Yin, Jeong-Ah Hwang, Song I Kim, Sang Ryong Kim, Sooil Kim, Yongbum Joo, and et al. 2020. "p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis" Polymers 12, no. 2: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020443
APA StyleShin, H. J., Park, H., Shin, N., Kwon, H. H., Yin, Y., Hwang, J. -A., Kim, S. I., Kim, S. R., Kim, S., Joo, Y., Kim, Y., Kim, J., Beom, J., & Kim, D. W. (2020). p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis. Polymers, 12(2), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020443