Melt Rheological Behavior and Morphology of Poly(ethylene oxide)/Natural Rubber-graft-Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Rheological Measurements
2.3. OM
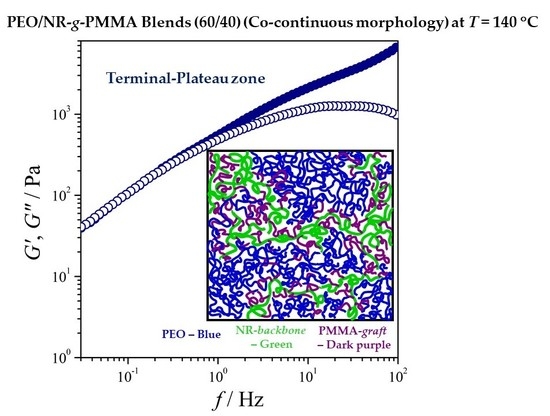
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties of the Parent Polymers
3.2. Rheological Characterization of the PEO/NR-g-PMMA Blends
3.2.1. Variation of Viscoelastic Modulus Function with Blend Composition
3.2.2. Variation of Melt Viscosity as a Function of Blend Composition
3.2.3. Van Gurp-Palmen Analysis of the PEO/NR-g-PMMA Blends
3.3. Morphological Studies of PEO/NR-g-PMMA Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koning, C.; Van Duin, M.; Pagnoulle, C.; Jerome, R. Strategies for Compatibilization of Polymer Blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1998, 23, 707–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasso-Gastinel, C.F.; Soltero-Martinez, J.F.A.; Mendizabal, E. Introduction: Modifiable Characteristics and Applications. In Modification of Polymer Properties, 1st ed.; Jasso-Gastinel, C.F., Kenny, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, R.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Kuwata, N.; Kawamura, J.; Hattori, T. Ac Impedance, DSC and FT-IR Investigations on (x) PVAc –(1 − x) PVdF Blends with LiClO4. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2006, 98, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idayu, S.; Halim, A.; Chan, C.H.; Winie, T. Thermal, Conductivity and Molecular Interaction Studies of Poly(Ethylene Oxide)/Poly(Methyl Acrylate) Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 371, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L. Ion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Based on Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Complexed with Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 Salt. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 92, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.; Walkenhorst, R.; Smith, M.; Selser, J.C.; Piet, G.; Bogoslovov, R. Role of Polymer Melt Viscoelastic Network Behavior in Lithium Ion Transport for PEO Melt/LiClO4 SPEs: The “wet Gel” Model. J. Power Sources 2000, 89, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Karim, S.R.; Sim, L.H.; Chan, C.H.; Zainal, N.F.A.; Masitah, A.K. Miscibility and Conductivities of PEO/PMMA-LiClO4 Solid Polymer Electrolyte. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 812, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.H.; Gan, S.N.; Chan, C.H.; Kammer, H.W.; Yahya, R. Compatibility and Conductivity of LiClO4 Free and Doped Polyacrylate-Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blends. Mater. Res. Innov. 2009, 13, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, F.; Chan, C.H.; Winie, T. Influence of Molar Mass on the Thermal Properties, Conductivity and Intermolecular Interaction of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Kammer, H.W.; Sim, L.H.; Yusoff, S.N.H.M.; Hashifudin, A.; Winie, T. Conductivity and Dielectric Relaxation of Li Salt in Poly(Ethylene Oxide) and Epoxidized Natural Rubber Polymer Electrolytes. Ionics 2014, 20, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Park, J.K.; Rhee, H.W. Conductivity and Thermal Studies of Solid Polymer Electrolytes Prepared by Blending Poly(Ethylene Oxide), Poly(Oligo[Oxyethylene]Oxysebacoyl) and Lithium Perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 1996, 83, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.L.; Morales, E. Ionic Conductive Polymer Systems Based on Polyether and Polyphosphazene Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 60, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, M.; Marwanta, E.; Ohno, H. Preparation and Characteristics of Natural Rubber/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Salt Hybrid Mixtures as Novel Polymer Electrolytes. Polymer 2000, 41, 9049–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Kuo, S.W.; Huang, C.F.; Chang, F.C. Investigating the Effect of Miscibility on the Ionic Conductivity of LiClO4/PEO/PCL Ternary Blends. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 8424–8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Ichino, T.; Rutt, J.S.; Nishi, S. New Dual-Phase Polymer Electrolytes Prepared from NBR/SBR Latices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichino, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Takeshita, Y.; Steven Rutt, S.N.J. New Concept for Polymer Electrolyte: Dual Phase Polymer Electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, Y.S.; Nesterov, A.E. Thermodynamics of Polymer Blends, 1st ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- López-Barrón, C.R.; Macosko, C.W. Rheology of Compatibilized Immiscible Blends with Droplet-Matrix and Cocontinuous Morphologies during Coarsening. J. Rheol. 2014, 58, 1935–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Maani, A.; Sojoudi, H.; Heuzey, M.C.; Carreau, P.J. Interfacial and Rheological Properties of PLA/PBAT and PLA/PBSA Blends and Their Morphological Stability under Shear Flow. J. Rheol. 2015, 59, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.S.; Albert, J.N.L.; Schantz, A.B.; Epps, T.H. Mixed-Salt Effects on the Ionic Conductivity of Lithium-Doped PEO-Containing Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 8116–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, H.; Norder, B.; Van Dam, J.; Posthuma De Boer, A. Stability of Co-Continuous Polystyrene/Poly(Ether-Ester) Blends in Shear Flow. Polymer 1999, 40, 5223–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanović, M.; Delva, L.; Cardon, L.; Ragaert, K. The Effect of Injection Molding Temperature on the Morphology and Mechanical Properties of PP/PET Blends and Microfibrillar Composites. Polymers 2016, 8, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalali Dil, E.; Carreau, P.J.; Favis, B.D. Morphology, Miscibility and Continuity Development in Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Blends. Polymer 2015, 68, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shanks, R.A.; Long, Y. Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Polyethylene-Polypropylene Blends with Controlled Thermal History. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Tang, J.; Yuan, H.; Jin, R. Crystallization and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene Random Copolymer/Poly(Ethylene-Octene) Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Thomas, S. Morphology, Morphology Development and Mechanical Properties of Polystyrene/Polybutadiene Blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku-Agboola, O.; Sadiku, E.R.; Adegbola, A.T.; Biotidara, O.F. Rheological Properties of Polymers: Structure and Morphology of Molten Polymer Blends. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, M.; Arbe, A.; Colmenero, J.; Frick, B.; Stewart, J.R. Dynamic Confinement Effects in Polymer Blends. A Quasielastic Neutron Scattering Study of the Dynamics of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) in a Blend with Poly(Vinyl Acetate). Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Gong, J.; Zheng, Q. Dynamic Rheological Behavior and Morphology near Phase-Separated Region for a LCST-Type of Binary Polymer Blends. Polymer 2004, 45, 6725–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Prochazka, F.; Carrot, C. Cocontinuity in Immiscible Polymer Blends: A Gel Approach. J. Rheol. 2005, 49, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.A.; Macosko, C.W. Comparison of Methods for the Detection of Cocontinuity in Poly(Ethylene Oxide)/Polystyrene Blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Carreau, P.J.; Gerard, P. Rheological and Mechanical Properties of PEO/Block Copolymer Blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterinen, A.; Lipponen, S.; Rich, J.; Seppälä, J. Effect of Block Composition on Thermal Properties and Melt Viscosity of Poly[2-(Dimethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate], Poly(Ethylene Oxide) and Poly(Propylene Oxide) Block Co-Polymers. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Kammer, H.W. Properties of Solid Solutions of Poly(Ethylene Oxide)/Epoxidized Natural Rubber Blends and LiClO4. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.H.; Chan, C.H.; Kammer, H.W. Selective Localization of Lithium Perchlorate in Immiscible Blends of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) and Epoxidized Natural Rubber. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Science and Social Research (CSSR 2010), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 5–7 December 2010; pp. 499–503. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.H.; Sim, L.H.; Kammer, H.W.; Tan, W. The Influence of the Amorphous Polymer on Conductivity, Morphologies and Thermal Properties of Polyether-Based Blends with Addition of Inorganic Salt. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1455, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Nakason, C.; Pechurai, W.; Sahakaro, K.; Kaesaman, A. Rheological, Thermal, and Curing Properties of Natural Rubber-g-Poly(Methyl Methacrylate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 1600–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.F.A.; Chan, C.H. Crystallization and Melting Behavior of Compatibilized Polymer Blends. In Compatibilization of Polymer Blends; Ajitha, A.R., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 391–433. [Google Scholar]
- Zainal, N.F.A.; Hein, M.; Abetz, V.; Ali, A.M.M.; Chan, C.H. Thermal Properties and Morphology of Compatible Poly(Ethylene Oxide)/Natural Rubber-Graft-Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Blends. Macromol. Symp. 2018, 382, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; Internet Version 2005; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 2660. [Google Scholar]
- Walkenhorst, R.; Selser, J.C.; Piet, G. Long-Ranged Relaxations in Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Melts: Evidence for Network Behavior. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 11043–11050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, F.; Chan, C.H.; Guo, Q. Rheology and Microscopic Heterogeneity of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 376, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangpakdee, J.; Tanaka, Y. Characterization of Sol and Gel in Hevea Natural Rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1997, 70, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolere, S.; Bottier, C.; Vaysse, L.; Bonfils, F. Characterisation of Macrogel Composition from Industrial Natural Rubber Samples: Influence of Proteins on the Macrogel Crosslink Density. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tangpakdee, J.; Tanaka, Y. Purification of Natural Rubber. J. Rubb. Res. 1997, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Tangpakdee, J.; Tanaka, Y. Branching in Natural Rubber. J. Rubb. Res. 1998, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Toki, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Ichikawa, N.; Tanaka, Y. Strain-Induced Crystallization of Natural Rubber: Effect of Proteins and Phospholipids. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2008, 81, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Structural Characterization of Natural Polyisoprenes: Solve the Mystery of Natural Rubber Based on Structural Study. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2001, 74, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolere, S.; Cazevieille, C.; Sainte-Beuve, J.; Bonfils, F. New Insights on Natural Rubber Microgel Structure Thanks to a New Method for Microaggregates Extraction. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 80, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J. Influence of Gel Content on the Physical Properties of Unfilled and Carbon Black Filled Natural Rubber Vulcanizates. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Man, C.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Dan, Y. Toughening of Polylactide with Natural Rubber Grafted with Poly(Butyl Acrylate). Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Han, C.D. Oscillatory Shear Flow Behaviour of a Thermotropic Liquid-Crystalline Polymer. Polymer 1994, 35, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980; pp. 366–403. [Google Scholar]
- Stamboulides, C.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Rheology and Processing of Molten Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Resins. Int. Polym. Process. 2006, 21, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Ougizawa, T. Binary Miscible Blends of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate)/Poly(α-Methyl Styrene-Co-Acrylonitrile): I. Rheological Behavior. J. Macromol. Sci.-Phys. 2002, 41, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.D. Multiphase Flow in Polymer Processing. In Rheology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.H.; Choi-Feng, C.; Li, D.J.; Han, C.D. Effect of Flow Geometry on the Rheology of Dispersed Two-Phase Blends of Polystyrene and Poly(Methyl Methacrylate). Polymer 1995, 36, 2451–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.P.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Tuning the Compatibility to Achieve Toughened Biobased Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Terephthalate) Blends. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 27709–27724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, P.; Cao, Z.; Meng, Q.; Fu, S.; Fang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Ye, J. Effect of Lignin Incorporation and Reactive Compatibilization on the Morphological, Rheological, and Mechanical Properties of ABS Resin. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2012, 51, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Rheological Characterization of Droplet-Matrix versus Co-Continuous Morphology. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2006, 45, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Graphite Oxide-Driven Miscibility in PVDF/PMMA Blends: Assessment through Dynamic Rheology Method. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 96, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Phase Behavior and Its Viscoelastic Responses of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) and Poly(Styrene-Co-Maleic Anhydride) Blend Systems. Polym. Bull. 2006, 56, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, P.; Paul, D.R. Formation of Co-Continuous Structures in Melt-Mixed Immiscible Polymer Blends. J. Macromol. Sci.-Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 87–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitric, J.; Médéric, P.; Moan, M.; Jarrin, J. Influence of Composition and Morphology on Rheological Properties of Polyethylene/ Polyamide Blends. Polymer 1998, 39, 4849–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.A.; Macosko, C.W. Detection of Cocontinuity in Immiscible Polymer-Polymer Blends. In Proceedings of the 3rd Pacific RIM Conference on Rheology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–13 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Omonov, T.S.; Harrats, C.; Moldenaers, P.; Groeninckx, G. Phase Continuity Detection and Phase Inversion Phenomena in Immiscible Polypropylene/Polystyrene Blends with Different Viscosity Ratios. Polymer 2007, 48, 5917–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Constituent | PEO | NR-g-PMMA |
|---|---|---|
| Mηa (g·mol−1) | 300,000 | – |
| Mwb (g·mol−1) | – | 394,000 |
| Mnb (g·mol−1) | – | 116,000 |
| Tmc (°C) | 66 | – |
| ΔHref (J·g−1) | 188.3 e | – |
| Tgd (°C) | −58 | −66, 120 |
| Molecular structure |  |  |
| Supplier | Thermo Fisher, Pittsburgh, PA, USA | Green HPSP (M) SdnBhd, Petaling Jaya, Malaysia |
| PEO/NR-g-PMMA Blends. | Power law exponent of | R2 | Power law exponent of | R2 | (Hz) | Remark (c.f Figure 4a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100/0 | 1.09 ± 0.02 | 0.997 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.999 | 0.90 b | Transition from a terminal zone to a plateau zone |
| 1.08 ± 0.12 a | – | 0.88 ± 0.08 a | – | – | ||
| 90/10 | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 0.992 | 0.91 ± 0.02 | 0.995 | 0.50 b | |
| 70/30 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.998 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.999 | 0.11 b | |
| 60/40 | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 0.999 | 0.81 ± 0.01 | 0.999 | 0.080 b | |
| 50/50 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 0.999 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.999 | – | Plateau zone |
| 40/60 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.999 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.998 | – | |
| 10/90 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.978 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.999 | – | |
| 0/100 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.987 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.891 | 20 c | Transition from a plateau zone to a transition zone |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zainal, N.F.A.; Lai, S.A.; Chan, C.H. Melt Rheological Behavior and Morphology of Poly(ethylene oxide)/Natural Rubber-graft-Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blends. Polymers 2020, 12, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030724
Zainal NFA, Lai SA, Chan CH. Melt Rheological Behavior and Morphology of Poly(ethylene oxide)/Natural Rubber-graft-Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blends. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030724
Chicago/Turabian StyleZainal, Nurul Fatahah Asyqin, Say Aik Lai, and Chin Han Chan. 2020. "Melt Rheological Behavior and Morphology of Poly(ethylene oxide)/Natural Rubber-graft-Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blends" Polymers 12, no. 3: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030724
APA StyleZainal, N. F. A., Lai, S. A., & Chan, C. H. (2020). Melt Rheological Behavior and Morphology of Poly(ethylene oxide)/Natural Rubber-graft-Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blends. Polymers, 12(3), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030724