The Effect of the Salt Water Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Adhesives Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Epoxy Adhesive Compounds
2.1.1. Epoxy Resin
2.1.2. Curing Agents
2.1.3. Calcium Carbonate Modifying Filler
2.2. Preparation of Epoxy Adhesive Compounds
2.3. Shape, Dimensions and Fabrication of the Adhesive Compound Samples
2.4. Environment and Aging Time
2.5. Experimental Tests
3. Results
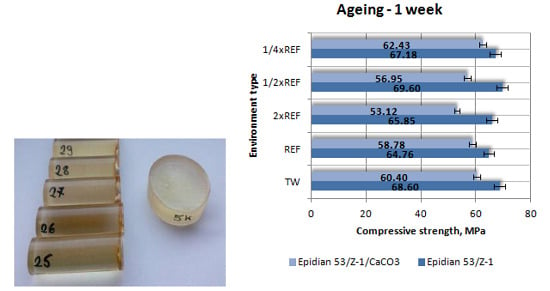
3.1. Strength Test Results
3.1.1. Compressive Strength
3.1.2. Compression Modulus
3.1.3. Compressive Strain
3.1.4. Mechanical Properties of References Samples
3.2. Microscopic Results
3.2.1. Reference Samples
3.2.2. Tap Water
3.2.3. Seawater Environment (Reference Salinity)
3.2.4. Environment with Double Reference Salinity
3.2.5. Environment with 1/2 Reference Salinity
3.2.6. Environment with 1/4 Reference Salinity
4. Discussion
- The mechanical properties of the studied epoxy adhesive compounds depend on the type of adhesive, aging time and tested environment;
- The highest compression modulus was obtained for the samples of Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 aged for three months in the environment containing a quarter of the reference salinity value;
- The samples of Epidian 53/Z-1 have the highest compression modulus value after one-month aging in the solution containing double reference salinity;
- The samples of Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 have the highest compression modulus values after aging for three months and one week;
- In most cases, the samples of Epidian 53/Z-1 aged in salt water for one month have higher compression modulus values;
- The compression modulus of the reference samples of Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 is 43% higher than that of the unmodified adhesive compound;
- The highest compressive strength was obtained for the Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 samples that were aged for three months in double reference salinity solution;
- The samples of Epidian 53/Z-1 aged for three months in the solution containing a quarter of the reference salinity value have the highest compressive strength;
- The samples of Epidian 53/Z-1 aged for one month and one week have considerably higher compressive strengths;
- The samples of Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 aged for three months have the highest compressive strength;
- The reference samples of both epoxy adhesive compounds have almost identical compressive strengths;
- The highest compressive strains were obtained for the samples of Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 aged for three months in the solution with double reference salinity;
- The highest compressive strain value was obtained for the Epidian 53/Z-1 samples aged in tap water for three months;
- The highest compressive strains were obtained for the Epidian 53/Z-1 samples aged for three months and one week;
- The samples of Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 aged for one week have a higher compressive strain;
- The compressive strain of the reference samples of Epidian 53/Z-1 is only 13% higher than that of the Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 samples;
- The microscopic examination has shown that the samples aged in salt water for three months undergo more changes;
- The cylindrical samples of Epidian 53/Z-1 aged in the solution with double reference salinity for three months and one month undergo only small changes.
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pizzi, A.; Mittal, K.Z. (Eds.) Handbook of Adhesive Technology; CRS Press Taylor & Frances Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 19–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.L.; Neville, H. Handbook of Epoxy Resins; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Rudawska, A. Epoxy adhesives. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology; Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.Z., Eds.; CRS Press Taylor & Frances Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 415–442. [Google Scholar]
- Pertie, E.M. Epoxy Adhesive Formulation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 3–19, 26–41, 43–53, 71–82, 85–98, 207–225, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Pethrick, R.A. Design and ageing of adhesives for structural adhesive bonding—A review. J. Mater. Design Appl. 2015, 229, 349–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudawska, A.; Brunella, V. The effect of ageing in water solution containing iron sulphate on the mechanical properties of epoxy adhesives. Polymers 2020, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudawska, A. The impact of seasoning conditions on mechanical properties of modified and unmodified epoxy adhesive compounds. Polymers 2019, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugiman, S.; Crocombe, A.D.; Aschroft, I.A. The fatigue response of environmentally degraded adhesively bonded aluminium structures. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 41, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heshmati, M.; Haghani, R.; Al-Emrani, M. Durability of CFRP/steel joints under cyclic wet-dry and freeze-thaw conditions. Compos. B 2017, 126, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, R.; Roy, A.; Grandidier, J.C. A study of the impact of humid aging on the strength of industrial adhesive joints. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 44, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, G.; Costa, M.; Banea, M.D.; da Silva, L.F.M. Water diffusion in double cantilever beam adhesive joints. Latin Am. J. Solid Struct. 2017, 14, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Neve, B.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Physical and chemical effects in an epoxy resin exposed to water vapour. J. Adhes. 1995, 49, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernades, P.; Viana, G.; Carbas, R.J.C.; Costa, M.; da Silva, L.F.M.; Banea, M.D. The influence of water on the fracture envelope of an adhesive joint. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2017, 89, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Botsis, J.; Cugnoni, J.; Coric, D. An experimental-numerical study of moisture absorption in an epoxy. Compos. A 2012, 43, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, M.; Haghani, R.; Al-Emrani, M. Effects of moisture on the long-term performance of adhesively bonded FRP/steel joints used in bridges. Compos. B 2016, 92, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiman, S.; Crocombe, A.D.; Aschroft, I.A. Experimental and numerical investigation of the static response of environmentally aged adhesively bonded joints. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 40, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefebvre, D.R.; Takahashi, K.M.; Muller, A.J.; Raju, V.R. Degradation of epoxy coatings in humid environments: The critical relative humidity for adhesion loss. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1991, 5, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, D.R.; Elliker, P.R.; Takahashi, K.M.; Raju, V.R.; Kaplan, M.L. The critical humidity effect in the adhesion of epoxy to glass: Role of hydrogen bonding. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2000, 14, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, R.; Roy, A.; Grandidier, J.C. Non-classical water diffusion in an industrial adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, B.P.; Tatar, J.; Douglas, E.P.; Hamilton, H.R. Effect of hydrothermal conditioning on epoxy adhesives used in FRP composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, M.; Davies, P.; Cognard, J.-Y.; Sohier, L.; Sauvant-Moynot, V.; Galy, J. Prediction of long term strength of adhesively bonded steel/epoxy joints in sea water. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2009, 29, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiore, V.; Calabrese, L.; Proverbio, E.; Galtieri, G.; Scalici, T.; Lo Presti, V.M. Pull-off adhesion of hybrid glass-steel adhesive joints in salt fog environments. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 2157–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, B. Effects of salt spray on the mechanical properties of aluminium-epoxy adhesive joints. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1588–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-L.; Xiong, J.-P.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, Y. Aging performance of epoxy adhesive in salt water. Adv. Mater. Res. 2006, 11–12, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Y.D.; Xv, H.Y.; Liu, W.B. The durability of adhesive/carbon-carbon composites joints in salt water. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2004, 24, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.W.; Xiao, J.Y.; Wang, Y.R. Accelerated aging behaviors of aluminium plate with composite patches under salt fog effect. Compos. B 2013, 44, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narynbek Ulu, K.; Huneau, B.; Le Gac, P.-Y.; Verron, E. Fatigue resistance of natural rubber in seawater with comparison to air. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 88, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciech Resins. Available online: http://www.ciechzywice.pl/pl/produkty/chemia-organiczna/zywice/zywice-epoksydowe (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Miturska, I.; Rudawska, A.; Müller, M.; Valášek, P. The Influence of Modification with Natural Fillers on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Adhesive Compositions after Storage Time. Materials 2020, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salinity. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salinity (accessed on 9 March 2018).
- Lettieri, M.; Frigione, M. Effects of humid environment on thermal and mechanical properties of a cold-curing structural epoxy adhesive. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthan, A.; Xian, G.; Thomas, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, X. Durability of an epoxy resin and its carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite upon immersion in water, acidic, and alkaline solutions. Polymers 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nash, N.H.; Portela, A.; Bachour-Sirerol, C.I.; Manolakis, I.; Comer, A.J. Effect of environmental conditioning on the properties of thermosetting-and thermoplastic-matrix composite materials by resin infusion for marine applications. Compos. B 2019, 177, 107271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Bending strength (MPa) | 80–100 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 70–90 |
| Shear strength of joint cured for 16 h at 20–25 °C, 6 h at 80 ± 2 °C (MPa), not lower than | 7.84 |
| Shear strength of joint cured for 7 days at 20–25 °C (MPa), not lower than | 5.86 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Viscosity, 25 °C (mPa·s) | 20–30 |
| Density, 20 °C (g/cm3) | 0.98 |
| Amino number (mgKOH/g) | min. 1100 |
| Characteristics of Epoxy Adhesive Compound Components | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variant of epoxy adhesive compounds | Unmodified | Modified |
| Resin type | Epidian 53 | Epidian 53 |
| Amount of resin, g | 100 | 100 |
| Curing agent type | Amine (triethylenetetramine) | Amine (triethylenetetramine) |
| Amount of curing agent, g | 80 | 80 |
| Filler type | - | Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) |
| Amount of filler, g | - | 2 |
| Epoxy compound designation | Epidian 53/Z-1 | Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 |
| Type of Environment | Salt Concentration | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Tap water | - | TW |
| Seawater (reference) | 35 g NaCl/1000 g tap water | REF |
| Seawater with 2× reference salinity | 70 g NaCl/1000 g tap water | 2× REF |
| Seawater with 1/2 reference salinity | 17.5 g NaCl/1000 g tap water | 1/2× REF |
| Seawater with 1/3 reference salinity | 8.8 g NaCl/1000 g tap water | 1/4× REF |
| Mechanical Properties | Adhesive Type | |
|---|---|---|
| Epidian 53/Z-1 | Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 | |
| Compressive strength, MPa | 71.06 | 72.22 |
| Compression modulus, MPa | 42.22 | 74.52 |
| Compressive strain, % | 6.40 | 5.52 |
| Epidian 53/Z-1 | Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 |
|---|---|
| Aged time: 3 months | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 month | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 week | |
 |  |
| Epidian 53/Z-1 | Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 |
|---|---|
| Aged time: 3 months | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 month | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 week | |
 |  |
| Epidian 53/Z-1 | Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 |
|---|---|
| Aged time: 3 months | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 month | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 week | |
 |  |
| Epidian 53/Z-1 | Epidian 53/Z-1/CaCO3 |
|---|---|
| Aged time: 3 months | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 month | |
 |  |
| Aged time: 1 week | |
 |  |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudawska, A. The Effect of the Salt Water Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Adhesives Compounds. Polymers 2020, 12, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040843
Rudawska A. The Effect of the Salt Water Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Adhesives Compounds. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040843
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudawska, Anna. 2020. "The Effect of the Salt Water Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Adhesives Compounds" Polymers 12, no. 4: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040843
APA StyleRudawska, A. (2020). The Effect of the Salt Water Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Adhesives Compounds. Polymers, 12(4), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040843