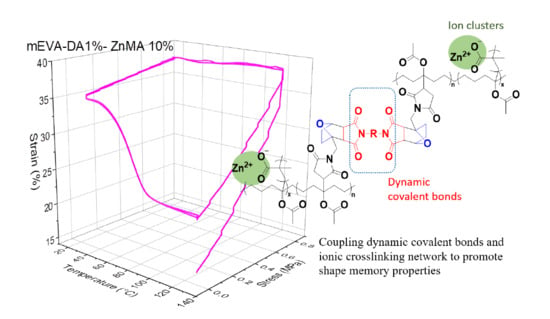
Coupling Dynamic Covalent Bonds and Ionic Crosslinking Network to Promote Shape Memory Properties of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Copolymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formation of Reversible Crosslinking Networks
3.2. Mechanical Performance of Reversibly Crosslinked mEVA
3.3. Shape Memory Behaviour of Reversibly Crosslinked mEVA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lu, J. Recent advances in shape-memory polymers: Structure, mechanism, functionality, modeling and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1720–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wong, M.-C.; Guo, Q.; Jia, T.; Hao, J. Healable and shape-memory dual functional polymers for reliable and multipurpose mechanical energy harvesting devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16267–16276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, A.; Okano, T. Pulsatile drug release control using hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Urban, M.W. Self-healing polymeric materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7446–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Qi, H.J.; Xie, T. Recent progress in shape memory polymer: New behavior, enabling materials, and mechanistic understanding. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 49–50, 79–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergman, S.D.; Wudl, F. Mendable polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrett, J.A.; Becer, C.R.; Haddleton, D.M. Self-healing and self-mendable polymers. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Weiss, R.A. Effect of Crosslinking on Shape-Memory Behavior of Zinc Stearate/Ionomer Compounds. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasi, P.; Hernández Santana, M.; Carretero-González, J.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Thermo-reversible crosslinked natural rubber: A Diels–Alder route for reuse and self-healing properties in elastomers. Polymer 2019, 175, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Niu, H.; He, Z.; Li, Y. Thermoreversible cross-linking of ethylene/propylene copolymer rubbers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4494–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgar, L.; Hagting, E.; Koek, W.-J.; Picchioni, F.; Duin, M. Thermoreversible Cross-Linking of Furan-Containing Ethylene/Vinyl Acetate Rubber with Bismaleimide. Polymers 2017, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.X.; He, Z.Z.; Yang, J.H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Crystallization controlled shape memory behaviors of dynamically vulcanized poly(l-lactide)/poly(ethylene vinyl acetate) blends. Polym. Test. 2016, 51, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hua, J.; Wang, Z. Facile design of heat-triggered shape memory ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer/nitrile-butadiene thermoplastic vulcanizates via zinc dimethacrylate induced interfacial compatibilization. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jia, Y.-G.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, X.X. Multiple and two-way reversible shape memory polymers: Design strategies and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 105, 100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Lin, B.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y. Design of Self-Healing Supramolecular Rubbers by Introducing Ionic Cross-Links into Natural Rubber via a Controlled Vulcanization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17728–17737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, B.; Fu, L. Self-Healing Natural Rubber with Tailorable Mechanical Properties Based on Ionic Supramolecular Hybrid Network. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29363–29373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckow, M.; Mordvinkin, A.; Roy, M.; Singha, N.K.; Heinrich, G.; Voit, B.; Saalwächter, K.; Böhme, F. Tuning the Properties and Self-Healing Behavior of Ionically Modified Poly(isobutylene-co-isoprene) Rubber. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grande, A.M.; Castelnovo, L.; Landro, L.D.; Giacomuzzo, C.; Francesconi, A.; Rahman, M.A. Rate-dependent self-healing behavior of an ethylene-co-methacrylic acid ionomer under high-energy impact conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Huete, N.; Post, W.; Laza, J.M.; Vilas, J.L.; León, L.M.; García, S.J. Effect of the blend ratio on the shape memory and self-healing behaviour of ionomer-polycyclooctene crosslinked polymer blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwaily, S.E.; Badawy, M.M.; Hassan, H.H.; Madani, M. Influence of thermal aging on crosslinking density of boron carbide/natural rubber composites. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulke, E.A. Solubility Parameter Values. In Polymer Handbook, 4th ed.; Brandrup, J., Immergut, E.H., Grulke, E.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999; p. VII-683. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, L.; Tian, M.; Geng, H.; Zhang, L. Study on mechanical properties of elastomers reinforced by zinc dimethacrylate. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, L.; Shen, D.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L. Infrared study on in situ polymerization of zinc dimethacrylate in poly(α-octylene-co-ethylene) elastomer. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Yamada, B.; Tsuji, M.; Sakurai, S. In situ copolymerization behaviour of zinc dimethacrylate and 2-(N-ethylperfluoro-octanesulphonamido)ethyl acrylate in hydrogenated nitrile–butadiene rubber during peroxide crosslinking. Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Asada, M.; Toyoda, A. Polymerization behavior of zinc methacrylate study of zinc methacrylate/rubber/peroxide compounds, Part 2. J. Jpn. Rubber Soc. 1994, 67, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomura, A.; Takano, J.; Toyoda, A.; Saito, T. Structural analysis of high strength HNBR/ZDMA composites. J. Jpn. Rubber Soc. 1993, 66, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qin, H.; Mather, P. Review of Progress in Shape-Memory Polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Xu, M. Shape memory effect of ethylene–vinyl acetate copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.; Xia, H.; Chen, H.; Qiu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ni, Q.-Q. Two-way reversible shape memory polymer: Synthesis and characterization of benzoyl peroxide-crosslinked poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate). Mater. Lett. 2020, 258, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T. Recent advances in polymer shape memory. Polymer 2011, 52, 4985–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirole, A.; Nicharat, A.; Perotto, C.U.; Weder, C. Tailoring the Properties of a Shape-Memory Polyurethane via Nanocomposite Formation and Nucleation. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicharat, A.; Shirole, A.; Foster, E.J.; Weder, C. Thermally activated shape memory behavior of melt-mixed polyurethane/cellulose nanocrystal composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Tang, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhang, L. An advanced elastomer with an unprecedented combination of excellent mechanical properties and high self-healing capability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25660–25671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, C. Shape memory and self-healing behavior of styrene–butadiene–styrene/ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer (SBS/EMAA) elastomers containing ionic interaction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| % Shape Recovery | % Shape Fixity | |
|---|---|---|
| mEVA | 51.5 | 80.1 |
| mEVA-DA1 | 95.6 | 82.3 |
| mEVA-ZnMA 10 wt % | 99.0 | 93.7 |
| mEVA-DA1-ZnMA 10 wt % | 99.4 | 76.4 |
| Sample | Dissipating Energy (MJ m−3) | Fixing Ratio (%) | Recovery Ratio (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Stress at 200% Extension | Dissipating Energy (MJ m−3) | |||||
| First Cycle | First Cycle | 0 min | 10 min | at 130 °C | at 130 °C | at 130 °C | |
| mEVA | 4.8 | 39 | 24 | 37 | 100 | 90 | 69 |
| mEVA-DA 1 | 7.6 | 42 | 29 | 52 | 100 | 87 | 75 |
| mEVA-ZnMA 10 wt % | 8.3 | 48 | 28 | 46 | 100 | 104 | 80 |
| mEVA-DA1-ZnMA 10 wt % | 10.6 | 49 | 28 | 49 | 100 | 100 | 88 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Narayana Kurup, S.; Ellingford, C.; Li, J.; Wan, C. Coupling Dynamic Covalent Bonds and Ionic Crosslinking Network to Promote Shape Memory Properties of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Copolymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040983
Wu W, Narayana Kurup S, Ellingford C, Li J, Wan C. Coupling Dynamic Covalent Bonds and Ionic Crosslinking Network to Promote Shape Memory Properties of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Copolymers. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040983
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wenjing, Sreeni Narayana Kurup, Christopher Ellingford, Jie Li, and Chaoying Wan. 2020. "Coupling Dynamic Covalent Bonds and Ionic Crosslinking Network to Promote Shape Memory Properties of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Copolymers" Polymers 12, no. 4: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040983
APA StyleWu, W., Narayana Kurup, S., Ellingford, C., Li, J., & Wan, C. (2020). Coupling Dynamic Covalent Bonds and Ionic Crosslinking Network to Promote Shape Memory Properties of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Copolymers. Polymers, 12(4), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040983