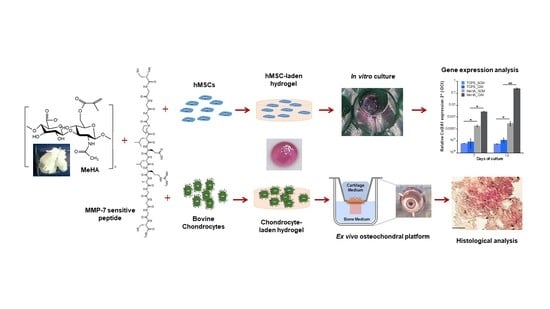
Biomimetic Cell-Laden MeHA Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Cartilage Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Functionalization of MeHA
2.3. Formation of MeHA and CS-MeHA Hydrogels
2.4. In Vitro Assessment of hMSC-Laden MeHA and CS-MeHA Hydrogels
2.4.1. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture
2.4.2. Cell Encapsulation
2.4.3. Cell Viability
2.4.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Ex Vivo Assessment of Chondrocyte-Laden MeHA Hydrogels
2.5.1. Isolation of Porcine Chondrocytes
2.5.2. Ex Vivo Explant Study
2.5.3. Metabolic Activity of Chondrocytes
2.5.4. Histological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Formation of MeHA and CS-MeHA Hydrogels
3.2. In Vitro Assessment of hMSC-Laden MeHA and CS-MeHA Hydrogels
3.2.1. Cell Viability
3.2.2. Biochemical Analysis
3.2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
3.3. Ex Vivo Assessment of Chondrocyte-Laden MeHA Hydrogels
3.3.1. Metabolic Activity of Chondrocytes
3.3.2. Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Athanasiou, K.; Darling, E.M.; Hu, J.C. Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Synthesis Lectures on Tissue Engineering; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010; Volume 3, ISBN 9781598298758. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, A.M.; Richardson, J.B. Articular cartilage: Structure, injuries and review of management. Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 87, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capito, R.M.; Spector, M. Scaffold-based articular cartilage repair. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. 2003, 22, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.B.; Mikos, A.G. Polymer Scaffold Fabrication. In Principles of Tissue Engineering, 3rd ed.; Lanza, R.P., Langer, R., Vacanti, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, N.-Y.; Kim, B.-W.; Yeo, W.-J.; Kim, H.-B.; Suh, D.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Seo, Y.-H.; Cho, J.-Y.; Chun, C.-W.; et al. Gel-type autologous chondrocyte (Chondron™) implantation for treatment of articular cartilage defects of the knee. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gikas, P.D.; Aston, W.J.S.; Briggs, T.W.R. Autologous chondrocyte implantation: Where do we stand now? J. Orthop. Sci. 2008, 13, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, J.; Behrens, P.; Schulz, A.P.; Oheim, R.; Kienast, B. Matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte implantation: A clinical follow-up at 15 years. Cartilage 2016, 7, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, M.W.; Ackerman, G.; Dines, J.S.; Grande, D. Emerging technologies and fourth generation issues in cartilage repair. Sports Med. Arthrosc. 2008, 16, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highley, C.B.; Prestwich, G.D.; Burdick, J.A. Recent advances in hyaluronic acid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2016, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Hilt, J.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Langer, R. Hydrogels in Biology and Medicine: From Molecular Principles to Bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachet, E.; Van den Berghe, H.; Bayma, E.; Block, M.; Auzély-Velty, R. Design of biomimetic cell-interactive substrates using hyaluronic acid hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.L.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A. Hydrogel design for cartilage tissue engineering: A case study with hyaluronic acid. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8771–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsanaktsidou, E.; Kammona, O.; Kiparissides, C. On the synthesis and characterization of biofunctional hyaluronic acid based injectable hydrogels for the repair of cartilage lesions. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 114, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Hou, C.; Tous, E.; Rai, R.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A. The influence of hyaluronic acid hydrogel crosslinking density and macromolecular diffusivity on human MSC chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parmar, P.A.; Chow, L.W.; St-Pierre, J.-P.; Horejs, C.-M.; Peng, Y.Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.M.; Stevens, M.M. Collagen-mimetic peptide-modifiable hydrogels for articular cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials 2015, 54, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khetan, S.; Katz, J.S.; Burdick, J.A. Sequential crosslinking to control cellular spreading in 3-dimensional hydrogels. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, J.A.; Chung, C.; Jia, X.; Randolph, M.A.; Langer, R. Controlled degradation and mechanical behavior of photopolymerized hyaluronic acid networks. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, W.; Du, B.; Liu, L.; Yang, J. A collagen mimetic peptide-modified hyaluronic acid hydrogel system with enzymatically mediated degradation for mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahney, C.S.; Hsu, C.-W.; Yoo, J.U.; West, J.L.; Johnstone, B. A bioresponsive hydrogel tuned to chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wei, K.; Bian, L. Cell-mediated degradation regulates human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy in MMP-sensitive hyaluronic acid hydrogels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.; Beecham, M.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A. The influence of degradation Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on In vitro Neocartilage Formation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4287–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khetan, S.; Guvendiren, M.; Legant, W.R.; Cohen, D.M.; Chen, C.S.; Burdick, J.A. Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holloway, J.L.; Ma, H.; Rai, R.; Burdick, J.A. Modulating hydrogel crosslink density and degradation to control bone morphogenetic protein delivery and in vivo bone formation. J. Control. Release 2014, 191, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodell, C.B.; Wade, R.J.; Purcell, B.P.; Dusaj, N.N.; Burdick, J.A. Selective proteolytic degradation of guest−host assembled, injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, Y.; Tae, G.; Lee, K.B.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, I.S.; Noh, I.; Sun, K. Synthesis and characterization of matrix metalloprotease sensitive-low molecular weight hyaluronic acid based hydrogels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3311–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisenbrey, E.A.; Bryant, S.J. A MMP7-sensitive photoclickable biomimetic hydrogel for MSC encapsulation towards engineering human cartilage. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, P.A.; Skaalure, S.C.; Chow, L.W.; St-Pierre, J.-P.; Stoichevska, V.; Peng, Y.Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.M.; Stevens, M.M. Temporally degradable collagen-mimetic hydrogels tuned to chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2016, 99, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parmar, P.A.; St-Pierre, J.-P.; Chow, L.W.; Spicer, C.D.; Stoichevska, V.; Peng, Y.Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.M.; Stevens, M.M. Enhanced Articular cartilage by human mesenchymal stem cells in enzymatically mediated transiently RGDS-functionalized collagen-mimetic hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.; Erickson, I.E.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A. Differential behavior of auricular and articular chondrocytes in hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackwitz, L.; Djouad, F.; Janjanin, S.; Nöth, U.; Tuan, R.S. Functional cartilage repair capacity of de-differentiated, chondrocyte and mesenchymal stem cell-laden hydrogels in vitro. Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2014, 22, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, G.; Xu, X.; Abdou, P.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, D.; Gu, Z. Advances of injectable hydrogel-based scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2019, 6, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erickson, I.E.; Huang, A.H.; Chung, C.; Li, R.T.; Burdick, J.A.; Mauck, R.L. Differential Maturation and Structure–Function Relationships in Mesenchymal Stem Cell and Chondrocyte-Seeded Hydrogels. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; O’Connell, C.D.; Onofrillo, C.; Choong, P.F.M.; Di Bella, C.; Duchi, S. Human articular cartilage repair: Sources and detection of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in photo-crosslinkable hydrogel bioscaffolds. STEM Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilela, C.A.; Correia, C.; Oliveira, J.M.; Sousa, R.A.; Espregueira-Mendes, J.; Reis, R.L. Cartilage Repair Using Hydrogels: A Critical Review of in Vivo Experimental Designs. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiller, K.L.; Maher, S.A.; Lowman, A.M. Hydrogels for the Repair of Articular Cartilage Defects. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2011, 17, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, A.H.; Yeger-McKeever, M.; Stein, A.; Mauck, R.L. Tensile properties of engineered cartilage formed from chondrocyte- and MSC- laden hydrogels. Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2008, 16, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidlits, S.K.; Khaing, Z.Z.; Petersen, R.R.; Nickels, J.D.; Vanscoy, J.E.; Shear, J.B.; Schmidt, C.E. The effects of hyaluronic acid hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties on neural progenitor cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, S.M.; McGarvey, J.R.; Wang, H.; Nikou, A.; Arama, L.; Koomalsingh, K.J.; Kondo, N.; Gorman, J.H., III; Pilla, J.J.; Gorman, R.C.; et al. MRI evaluation of injectable hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel therapy to limit ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 2015, 69, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arndt, K.-F.; Krahl, F.; Richter, S.; Steiner, G. Swelling Related Processes in Hydrogels; Gerlagh, G., Arndt, K.-F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Hydrogel Sensors and Actuators. Springer Series on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors 6. [Google Scholar]
- Böke, F.; Labude, N.; Lauria, I.; Ernst, S.; Müller-Newen, G.; Neuss, S.; Fischer, H. Biological activation of bioinert medical High Performance Oxide Ceramics by hydrolytically stable immobilization of c(RGDyK) and BMP-2. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 38669–38680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamzyk, C.; Kachel, P.; Hoss, M.; Gremse, F.; Modabber, A.; Hölzle, F.; Tolba, R.; Neuss, S.; Lethaus, B. Bone tissue engineering using polyetherketoneketone scaffolds combined with autologous mesenchymal stem cells in a sheep calvarial defect model. J. Cranio Maxill. Surg. 2016, 44, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Heo, J.; Hwang, Y.; Kwak, S.-Y.; Park, O.K.; Kim, H.; Varghese, S.; Hwang, N.S. Extracellular-Matrix-Based and Arg-Gly-Asp–Modified Photopolymerizing Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, F.; Krüger, M.; Gonzalez de Torre, I.; Quintanilla Sierra, L.; Alonso Rodrigo, M.; Kock, L.; Rodriguez-Cabello, J.C. Cartilage Regeneration in Preannealed Silk Elastin-Like Co-Recombinamers Injectable Hydrogel Embedded with Mature Chondrocytes in an Ex Vivo Culture Platform. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4333–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, A.; Meeuwsen, A.B.F.; Ehlicke, F.; Hansmann, J.; Mulder, L.; Smits, A.I.P.M.; Walles, H.; Kock, L.M. Ex vivo culture platform for assessment of cartilage repair treatment strategies. ALTEX Altern. Anim. Exp. 2017, 34, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slide#DMS 065. Available online: https://www.dartmouth.edu/~anatomy/Histo/lab_2/bone/DMS065/popup.htmlv (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Jooybar, E.; Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Alvi, M.; Mousavi, A.; Karperien, M.; Dijkstra, P.J. An injectable platelet lysate-hyaluronic acid hydrogel supports cellular activities and induces chondrogenesis of encapsulated mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Beck, A.M.; Shimomura, K.; Sohn, J.; Fritch, M.R.; Deng, Y.; Kilroy, E.J.; Tang, Y.; Alexander, P.G.; Tuan, R.S. Optimization of photocrosslinked gelatin/hyaluronic acid hybrid scaffold for the repair of cartilage defect. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.P.; Podgorski, M.; Chatani, S.; Gong, T.; Xi, W.; Fenoli, C.R.; Bowman, C.N. The thiol-Michael addition click reaction: A powerful and widely used tool in materials chemistry. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 724–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, D.T.; Alliston, T.; Weaver, V.M. A tense situation: Forcing tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, W.S.; Lim, T.C.; Kurisawa, M.; Spector, M. Modulation of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis in a tunable hyaluronic acid hydrogel microenvironment. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3835–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Choi, J.H.; Shin, M.E.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, P.Y.; Kim, N.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Evaluation of cartilage regeneration of chondrocyte encapsulated gellan gum-based hyaluronic acid blended hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouser, V.H.M.; Dautzenberg, N.M.M.; Levato, R.; van Rijen, M.H.P.; Dhert, W.J.A.; Malda, J.; Gawlitta, D. Ex Vivo Model Unravelling Cell Distribution Effect in Hydrogels for Cartilage Repair. ALTEX Altern Anim. Exp. 2018, 35, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, C.; Bay-Jensen, A.-C.; Pap, T.; Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; Quasnichka, H.; Barret-Jolley, R.; Mobasheri, A.; Henrotin, Y. Chondrocyte secretome: A source of novel insights and exploratory biomarkers of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2017, 25, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Base Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 5′-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCA-3′ | 5′-AATGAAGGGGTCATTGATGG-3′ | 108 |
| COL1A1 | 5′-AGGACAAGAGGCATGTCTGGTT-3′ | 5′-GGACATCAGGCGCAGGAA-3′ | 122 |
| COL2A1 | 5′-CATCCCACCCTCTCACAGTT-3′ | 5′-GCCTCTGCCTTGACCCGAAG-3′ | 136 |
| ACAN | 5′-TCGAGGACAGCGAGGCC-3′ | 5′-TCGAGGGTGTAGCGTGTAGAGA-3′ | 85 |
| MMP13 | 5′-ACCGGCAAAAGCCACTTTAT-3′ | 5′-TGTCTGGCGTTTTTGGATGT-3′ | 109 |
| COL10A1 | 5′-ACAGGCATAAAAGGCCCACT-3′ | 5′-GACCAGGAGTACCTTGCTCTC-3′ | 106 |
| Hydrogel Type | Gelation Onset (s) | G’ (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| MeHA | 457 ± 68.1 | 8.6 ± 1.5 |
| CS-MeHA | 529 ± 36.5 | 2.5 ± 0.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsanaktsidou, E.; Kammona, O.; Labude, N.; Neuss, S.; Krüger, M.; Kock, L.; Kiparissides, C. Biomimetic Cell-Laden MeHA Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Cartilage Tissue. Polymers 2020, 12, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071598
Tsanaktsidou E, Kammona O, Labude N, Neuss S, Krüger M, Kock L, Kiparissides C. Biomimetic Cell-Laden MeHA Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Cartilage Tissue. Polymers. 2020; 12(7):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071598
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsanaktsidou, Evgenia, Olga Kammona, Norina Labude, Sabine Neuss, Melanie Krüger, Linda Kock, and Costas Kiparissides. 2020. "Biomimetic Cell-Laden MeHA Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Cartilage Tissue" Polymers 12, no. 7: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071598
APA StyleTsanaktsidou, E., Kammona, O., Labude, N., Neuss, S., Krüger, M., Kock, L., & Kiparissides, C. (2020). Biomimetic Cell-Laden MeHA Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Cartilage Tissue. Polymers, 12(7), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071598