Effect of Crosslinking Type on the Physical-Chemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Chitosan-Based Electrospun Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Solution Preparation
2.2.2. Electrospinning and Membrane Crosslinking
2.2.3. Morphological Investigation
2.2.4. Mechanical and Water-Related Characterization
2.2.5. Biological Tests
2.2.6. Adsorption–Desorption Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Morphology
3.2. Mechanical and Water-Related Properties
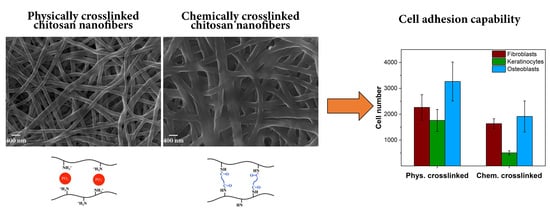
3.3. Biological Response
3.4. Drug Delivery Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borda, L.J.; Macquhae, F.E.; Kirsner, R.S. Wound Dressings: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2016, 5, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.F.; Bártolo, P.J. Traditional Therapies for Skin Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 208–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golan, Y. Current treatment options for acute skin and skin-structure infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, S206–S212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Bakhshayesh, A.R.; Annabi, N.; Khalilov, R.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Alizadeh-Ghodsi, M.; Davaran, S.; Montaseri, A. Recent advances on biomedical applications of scaffolds in wound healing and dermal tissue engineering. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouhan, D.; Dey, N.; Bhardwaj, N.; Mandal, B.B. Emerging and innovative approaches for wound healing and skin regeneration: Current status and advances. Biomaterials 2019, 216, 119267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Sun, X.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Fu, X.; Leong, K.W. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 209–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.H.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.C. Polymer-based hydrogel scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications: A mini-review. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, H.M.; Grant, A.; Ditata, J. The presence of oxygen in wound healing. Wounds 2016, 28, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, M.P.; Neto, A.I.; Correia, T.R.; Miguel, S.P.; Matsusaki, M.; Correia, I.J.; Mano, J.F. Bioinspired multilayer membranes as potential adhesive patches for skin wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Duan, X.P.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, D.P.; Long, Y.Z. Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S. Multi-layer alginate-polycaprolactone electrospun membranes as skin wound patches with drug delivery abilities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 31162–31171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Windbergs, M. Functional electrospun fibers for the treatment of human skin wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 119, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, M.A.; Amini, F.; Tan, C.K. Electrospun nanofibers in wound healing. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Scarfi, S.; Pozzolini, M.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Alginate-Based Electrospun Membranes Containing ZnO Nanoparticles as Potential Wound Healing Patches: Biological, Mechanical, and Physicochemical Characterization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Alloisio, M.; Vicini, S.; Castellano, M. Preparation of composite alginate-based electrospun membranes loaded with ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, M.; Alloisio, M.; Darawish, R.; Dodero, A.; Vicini, S. Electrospun composite mats of alginate with embedded silver nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, P. The controlled release of growth factor via modified coaxial electrospun fibres with emulsion or hydrogel as the core. Mater. Lett. 2016, 181, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martinez, E.J.; Cornejo Bravo, J.M.; Serrano Medina, A.; Pérez González, G.L.; Villarreal Gómez, L.J. A Summary of Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System: Drugs Loaded and Biopolymers Used as Matrices. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Lova, P.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Nanocomposite alginate-based electrospun membranes as novel adsorbent systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zong, M.H.; Linhardt, R.J.; Feng, K.; Wu, H. Electrospinning: A novel nano-encapsulation approach for bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Rheological properties of sodium alginate solutions in the presence of added salt: An application of Kulicke equation. Rheol. Acta 2020, 59, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.E.; Nuge, T.; Yeow, T.K.; Nordin, N. Electrospun Matrices from Natural Polymers for Skin Regeneration. In Nanostructured Polymer Composites for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, R.M.D.; Siqueira, N.M.; Prabhakaram, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning and electrospray of bio-based and natural polymers for biomaterials development. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Sodium alginate solutions: Correlation between rheological properties and spinnability. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8034–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxika, A.; Etxabide, A.; Uranga, J.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Chitosan as a bioactive polymer: Processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Selvakumar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kumar, N.S. Chitosan as an environment friendly biomaterial—A review on recent modifications and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, S.; Nezhad, M.N.; Zarrintaj, P.; Jafari, S.H.; Gholizadeh, S.S.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Chitosan in Biomedical Engineering: A Critical Review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.R.; Islam, M.N. Chitin and Chitosan: Structure, Properties and Applications in Biomedical Engineering. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, K.; Afifi, A.M.; Jahangirian, H.; Webster, T.J. Biomedical applications of chitosan electrospun nanofibers as a green polymer—Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. A review: Electrospinning of biopolymer nanofibers and their applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, S.; Mauri, M.; Vita, S.; Castellano, M. Alginate and alginate/hyaluronic acid membranes generated by electrospinning in wet conditions: Relationship between solution viscosity and spinnability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, P.M.; Peighambardoust, S.J. Review on recent progress in chitosan-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegrzynowska-Drzymalska, K.; Grebicka, P.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Chelminiak-Dudkiewicz, D.; Kaczmarek, H.; Goslinski, T.; Ziegler-Borowska, M. Crosslinking of Chitosan with Dialdehyde Chitosan as a New Approach for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellá, M.C.G.; Lima-Tenório, M.K.; Tenório-Neto, E.T.; Guilherme, M.R.; Muniz, E.C.; Rubira, A.F. Chitosan-based hydrogels: From preparation to biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Brunengo, E.; Alloisio, M.; Sionkowska, A.; Vicini, S.; Castellano, M. Chitosan-based electrospun membranes: Effects of solution viscosity, coagulant and crosslinker. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Chitosan composites with inorganics, morphogenetic proteins and stem cells, for bone regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzolini, M.; Millo, E.; Oliveri, C.; Mirata, S.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Arkel, M.; Scarfì, S. Elicited ROS Scavenging Activity, Photoprotective, and Wound-Healing Properties of Collagen-Derived Peptides from the Marine Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozzolini, M.; Scarfì, S.; Gallus, L.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S.; Cortese, K.; Gagliani, M.; Bertolino, M.; Costa, G.; Giovine, M. Production, Characterization and Biocompatibility Evaluation of Collagen Membranes Derived from Marine Sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo, 1847. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bratskaya, S.; Privar, Y.; Nesterov, D.; Modin, E.; Kodess, M.; Slobodyuk, A.; Marinin, D.; Pestov, A. Chitosan Gels and Cryogels Cross-Linked with Diglycidyl Ethers of Ethylene Glycol and Polyethylene Glycol in Acidic Media. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobreiro-Almeida, R.; Fonseca, D.R.; Neves, N.M. Extracellular matrix electrospun membranes for mimicking natural renal filtration barriers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 103, 109866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, B.; Avrahami, R.; Baruch, L.; Efraim, Y.; Goldfracht, I.; Elul, O.; Davidov, T.; Gepstein, L.; Zussman, E.; Machluf, M. Electrospun Extracellular Matrix: Paving the Way to Tailor-Made Natural Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghazadeh, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Schot, M.; Kashaf, S.S.; Sharifi, F.; Jalilian, E.; Nuutila, K.; Giatsidis, G.; Mostafalu, P.; Derakhshandeh, H.; et al. Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 138–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsett-Martin, W.A. Rat models of skin wound healing: A review. Wound Repair Regen. 2004, 12, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janis, J.E.; Harrison, B. Wound Healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 199e–207e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Brunengo, E.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S. Investigation of the Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Membranes: A Design of Experiment Approach. Polymers 2020, 12, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Maleki, H.; Zavagna, L.; de la Ossa, J.G.; Linari, S.; Lazzeri, A.; Danti, S. Bio-based electrospun fibers for wound healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Siegel, R.A. Investigation of morphological, mechanical and biological properties of cellulose nanocrystal reinforced electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniasadi, M.; Xu, Z.; Cai, J.; Daryadel, S.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.; Naraghi, M.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Correlation of annealing temperature, morphology, and electro-mechanical properties of electrospun piezoelectric nanofibers. Polymer 2017, 127, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liao, J.; Hao, Y.; Ning, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Surface Wettability Switched Cell Adhesion and Detachment on Conducting Polymer Nanoarray. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacicedo, M.L.; Pacheco, G.; Islan, G.A.; Alvarez, V.A.; Barud, H.S.; Castro, G.R. Chitosan-bacterial cellulose patch of ciprofloxacin for wound dressing: Preparation and characterization studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Horst, B.; Chouhan, G.; Moiemen, N.S.; Grover, L.M. Advances in keratinocyte delivery in burn wound care. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 123, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshandeh, H.; Kashaf, S.S.; Aghabaglou, F.; Ghanavati, I.O.; Tamayol, A. Smart Bandages: The Future of Wound Care. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Tamayol, A.; Mostafalu, P.; Akbari, M.; Comotto, M.; Annabi, N.; Ghaderi, M.; Sonkusale, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Dermal Patch with Integrated Flexible Heater for on Demand Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Andrade, J.R.; Oliveira, M.F.; Da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals from Water and Wastewater Using Nonconventional Low-Cost Materials: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3103–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largitte, L.; Pasquier, R. A review of the kinetics adsorption models and their application to the adsorption of lead by an activated carbon. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rożek, P.; Król, M.; Mozgawa, W. Lightweight geopolymer-expanded glass composites for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19785–19791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the Adsorption in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]










| Crosslinking Type | WCA (°) | WVP (g/s·m·Pa) | MC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | 56 ± 5 | 9.3 · 10−12 | 11 ± 2 |
| Chemical | 71 ± 2 | 2.1 · 10−12 | 10 ± 1 |
| Dye | Adsorption Kinetics | Freundlich | Cumulative Release | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (mg/L) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | |||||
| qe (mg/g) | qe (mg/g) | kF ((mg·(L/mg)1/n)/g) | 1/n | C (mg/L) | R% | ||
| MB | 5 10 20 | --- | 0.15 0.37 0.82 | 2.0·10−2 | 1.31 | 40 80 160 | 12 17 21 |
| MO | 5 10 20 | 0.29 3.00 5.58 | --- | 17.0·10−2 0.2·10−2 | 0.97 2.21 | 40 80 160 | 12 24 40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dodero, A.; Scarfi, S.; Mirata, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Effect of Crosslinking Type on the Physical-Chemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Chitosan-Based Electrospun Membranes. Polymers 2021, 13, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050831
Dodero A, Scarfi S, Mirata S, Sionkowska A, Vicini S, Alloisio M, Castellano M. Effect of Crosslinking Type on the Physical-Chemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Chitosan-Based Electrospun Membranes. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050831
Chicago/Turabian StyleDodero, Andrea, Sonia Scarfi, Serena Mirata, Alina Sionkowska, Silvia Vicini, Marina Alloisio, and Maila Castellano. 2021. "Effect of Crosslinking Type on the Physical-Chemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Chitosan-Based Electrospun Membranes" Polymers 13, no. 5: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050831
APA StyleDodero, A., Scarfi, S., Mirata, S., Sionkowska, A., Vicini, S., Alloisio, M., & Castellano, M. (2021). Effect of Crosslinking Type on the Physical-Chemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Chitosan-Based Electrospun Membranes. Polymers, 13(5), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050831