Preparation, Thermal, and Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Polymeric Blends Based on Di(meth)acrylate Monomers
Abstract
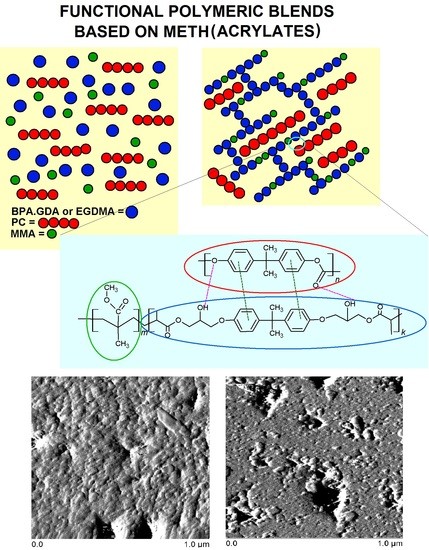
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Preparation of Blends
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization of PC Blends Using ATR/FT-IR
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Characterization
3.4. DMA Test
3.5. Hardness
3.6. Swelling Tests
3.7. Images of Obtained Blends—AFM Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strobl, G.R. Polymer Mixtures. In The Physics of Polymers Concepts for Understanding Their Structures and Behavior, 2nd ed.; Hoagland, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sionkowska, A. Current research on the blends of natural and synthetic polymers as new biomaterials: Review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1254–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Palermo, S.; Fragala, M.; Pappalardo, F. Characterization and processability of blends of polylactide acid with a new biodegradable medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate. J. Polym. Environ. 2015, 23, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnicki, A.; Gargol, M.; Podkościelna, B.; Nowak, J.; Gawdzik, B. Synthesis and characterization of polymeric blends based on polysulfone for special applications. In Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Integrated Optics: Sensors, Sensing Structures, and Methods, Szcyrk, Poland, 26 February–2 March 2018; SPIE - International Society for Optics and Photonics: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van Puyvelde, P.; Vananroye, A.; Cardinaels, R.; Moldenaers, P. Review on morphology development of immiscible blends in confined shear flow. Polymer 2008, 49, 5363–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utracki, L.A.; Wilkie, C.A. (Eds.) Polymer Blends Handbook, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gargol, M.; Fila, K.; Goliszek, M.; Puszka, A.; Podkościelna, B. Synthesis and characterization of polymeric blends as a new materials in optical fiber technology. In Optical Fibers And Their Applications, Book Series: Proceedings of SPIE; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grulke, E.A. Solubility Parameter Values. In Polymer Handbook, 1st ed.; Brandrup, J., Immergut, E.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Vasile, C.; Kulshereshtha, A.K.; Bumbu, G.G. Terminology. In Handbook of Polymer Blends and Composites, 1st ed.; Vasile, C., Kulshereshtha, A.K., Eds.; Rapra Technology Limited: Shawbury, UK, 2003; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Plattier, J.; Benyahia, L.; Dorget, M.; Niepceron, F.; Tassin, J.F. Viscosity-induced filler localisation in immiscible polymer blends. Polymer 2015, 59, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Morreale, M.; Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Ceraulo, M.; Scaffaro, R. Degradation of polymer blends: A brief review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 145, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puyvelde, P.; Velankar, S.; Moldenaers, P. Rheology and morphology of compatibilized polymer blends. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 6, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioboo, R.; Demnati, I.; Ali, M.A.; Sevkan, R.; Coninck, J.D. Superhydrophobicity of composite surfaces created from polymer blends. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, S.; Robin, J. Study and characterization of virgin and recycled LDPE/PP blends. Polymer 2002, 38, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, J.C.W. Academy of Applied Science Inc. Rines and Rines. Polymer Blends and Process for Preparation. U.S. Patent 6,177,377, 23 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Koning, C.; Van Duin, M.; Pagnouille, C.; Jerome, R. Strategies for compatibilization of polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1998, 23, 707–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchewks, J.; Laska, J. Blends of poly(L-Lactide) and poly(L-Lactide-Co-Trimethylene carbonate) as promising materials for bone and cartilage rissue engineering. Eng. Biomater. 2018, 145, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Isayev, A.I. (Ed.) Encyclopedia of Polymer Blends, 1st ed.; Wiley-VSC: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Debier, D.; Devaux, J.; Legras, R. Blends of Bisphenol A Polycarbonate and Acrylic Polymers I. A Chemical Reaction Mechanism. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1995, 33, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debier, D.; Legras, R.; Canova, L. Blends of Bisphenol-A Polycarbonate and Acrylic Polymers: III. Effect of Imide Concentration on Compatibility. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1997, 35, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaif, N.; Pagnoulle, C.; Jérôme, R. Reactive compatibilization of PC/PVDF polymer blends by zinc carboxylate containing poly(methylmethacrylate) ionomers. Polymers 2000, 41, 5551–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Kar, K.K.; Kumar, V. Studies on the effect of compatibilizers on mechanical, thermal and flow properties of polycarbonate/poly (butylene terephthalate) blends. Mater. Res. Express. 2018, 5, 015306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Macedo, T.C.P.; Da Silva Reinaldo, J.; Pereira, L.M.; DoRêgo, J.K.M.A.; Ueki, M.M.; Damasceno, I.Z.; Ito, E.N. Effect of Processing Conditions on the Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Elastomeric Poly (Methyl Methacrylate)/Polycarbonate Blends. Macromol. Symp. 2019, 383, 1800049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abtahi, A.; Johson, S.; Park, S.M.; Luo, X.; Liang, Z.; Mei, J.; Graham, K.R. Designing π-conjugated polymer blends with improved thermoelectric power factors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 19774–19785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, H.; He, H.; Ribbe, A.E.; Thayumanavan, S. Blended Assemblies of Amphiphilic Random and Block Copolymers for Tunable Encapsulation and Release of Hydrophobic Guest Molecules. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 2713–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savagian, L.R.; Österholm, A.M.; Shen, D.E.; Christiansen, D.T.; Kuepfert, M.; Reynolds, J.R. Conjugated Polymer Blends for High Contrast Black-to-Transmissive Electrochromism. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauenstein, O.; Reiter, M.; Agarwal, S.; Rieger, B.; Greiner, A. Bio-based polycarbonate from limonene oxide and CO2 with high molecular weight, excellent thermal resistance, hardness and transparency. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugil, Y.; Hoyeon, K.; Yongsok, S. Synthesis and characterization of isosorbide based polycarbonates. Polymer 2019, 179, 121685. [Google Scholar]
- Biles, J.E.; McNeal, T.P.; Begley, T.H.; Hollifield, H.C. Determination of bisphenol-A in reusable polycarbonate food-contact plastics and migration to food-simulating liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3541–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneau, H.C. Release of bisphenol a from polycarbonate-A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 386–402. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriacos, D. (Ed.) Polycarbonates. In Brydson’s Plastics Materials, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 17, pp. 457–485. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, M.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dan, Y. Aging induced ductile-brittle-ductile transition in bisphenol A polycarbonate. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, M.; Niu, X.Y.; Shi, Z.S.; Cui, Z.C.; Chen, C.M.; Zhang, D.N. Synthesis and characterization of novel fluorinated polycarbonate negative-type photoresist for optical waveguide. Polymer 2015, 61, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, W.J.; Horie, K.; Hess, M.; Stepto, R.F.T. Definition of terms related to polymer blends, blends and multiphase polymeric materials. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickelbick, G. (Ed.) Hybrid Materials Synthesis, Characterization, Appliation, 1st ed.; Wiley-VSC: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Pfaendtner, J.; Broadbelt, L.J. Ab initio study of acrylate polymerization reactions: Methyl methacrylate and methyl acrylate propagation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, E.P.; Cano, C.I.; Van Dalen, J.; Pipes, R.B. Reduction in fixture time of a two component structural acrylic adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2008, 28, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fila, K.; Goliszek, M.; Podkościelna, B.; Podgórski, M. Polymer side-chain modification in methacrylate and styrene copolymers through thiol-thioester dynamic exchange. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 136, 109918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goliszek, M.; Podkościelna, B.; Klepka, T.; Sevastyanova, O. Preparation, Thermal, and Mechanical Characterization of UV-Cured Polymer Biocomposites with Lignin. Polymers 2020, 12, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiesiak, M.; Podkościelna, B.; Sevastanova, O. Thermal degradation behavior of lignin-modified porous styrene-divinylbenzene and styrene-bisphenol A glycerolate diacrylate copolymer microspheres. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2017, 123, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salasinska, K.; Barczewski, M.; Borucka, M.; Górny, L.R.; Kozikowski, P.; Celiński, M.; Gajek, A. Thermal stability, fire and smoke behaviour of epoxy composites modified with plant waste fillers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faria, L.O.; Moreira, R.L. Structural and kinetic transitions in P(VDF–TrFE)/PMMA blends. Polymer 1999, 40, 4465–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrystafi, I.; Kontonasaki, E.; Anastasiou, A.D.; Patsiaoura, D.; Papadopoulou, L.; Vourlias, G.; Vouvouldi, E.; Bikiaris, D. Mechanical and thermal properties of PMMA resin composites for interim fixed prostheses reinforced with calcium β-pyrophosphate. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2020, 112, 104094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavade, C.; Singh, N.L.; Singh, D.; Shah, S.; Tripathi, A.; Avasthi, D.K. Study of Dielectrical Properties of Swift Heavy Ion Induced Modifications in Metal Oxide/PMMA Nanocomposites. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2010, 117, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, I.M.; Sweeney, J. Mechanical Properties of Solid Polymer, 3rd ed.; Wiley: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Worzakowska, M. Synthesis, characterization, thermal, and viscoelastic properties of an unsaturated epoxy polyester cured with different hardeners. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 3582–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabros, A.; Gawdzik, B. Methacrylate monomer as an alternative to styrene in typical polyester–styrene copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargol, M.; Klepka, T.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Podkościelna, B. Synthesis and Thermo-Mechanical Study of Epoxy Resin-Based Composites with Waste Fibers of Hemp as an Eco-Friendly Filler. Polymers 2021, 13, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabros, A.; Gawdzik, B.; Podkościelna, B.; Goliszek, M.; Pączkowski, P. Composites of Unsaturated Polyester Resins with Microcrystalline Cellulose and Its Derivatives. Materials 2020, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Q.Y.; Ying, S.J.; Luo, Y.X. Solvent cast blends of PMMA microspheres in bisphenol-A-polycarbonate. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2014, 43, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, M.; Mathur, V.; Gupta, S.; Baboo, M.; Sharma, K.; Saxena, N.S. Morphology, miscibility and mechanical properties of PMMA/PC blends. Phase Transit. 2009, 82, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, E.M.; Su, C.C. Kinetic effects on phase heterogeneity in bisphenol-A polycarbonate/poly(methyl methacrylate) blends. Polymer 1996, 37, 5189–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singht, A.K.; Mishra, R.K.; Prakash, R.; Maiti, P.; Kumar Singh, A.; Pandey, D. Specific interactions in partially miscible polycarbonate (PC)/poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) blends. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 486, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goliszek, M.A.; Podkościelna, B. Synthesis and characterization of polymer biocomposites with lignin. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.P.C.; Reinaldo, J.S.; Rodrigues, A.H.V.; Macedo, T.C.P.; Silva, B.L.; Ito, E.N. Influence of Morphology on Fracture Propagation of PMMAe/PC Blend in Tensile Tests at High Strain Rate. Macromol. Symp. 2020, 394, 2000153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Sample | BPA.GDA/EGDMA + MMA | BPA.GDA/EGDMA + MMA + 1% PC | BPA.GDA/EGDMA + MMA + 5% PC | BPA.GDA/EGDMA + MMA + 10% PC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMA (g) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| BPA.GDA/EGDMA (g) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| PC (wt.%) | 0 | 1 | 5 | 10 |
| CH2Cl2 (cm3) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Initiator (g) | 0.200 | 0.202 | 0.210 | 0.220 |
| Material | T5% a (oC) | T10% b (oC) | T50% c (oC) | Tmax d (oC) | RM e (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 471 | 484 | 516 | - | 516 | - | - | 25.58 |
| PMMA f | 213 | 272 | 355 | 180 | 250 | 367 | - | 0.40 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA | 323 | 347 | 406 | 407 | - | - | - | 11.12 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 1% PC | 309 | 326 | 381 | 374 | 536 | - | - | 1.39 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 5% PC | 321 | 339 | 393 | 391 | 577 | - | - | 4.50 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 10% PC | 304 | 329 | 395 | 384 | 567 | - | - | 8.23 |
| EGDMA + MMA | 157 | 233 | 330 | 121 | 245 | 320 | 420 | 2.07 |
| EGDMA + MMA + 1% PC | 241 | 258 | 307 | 137 | - | 301 | 442 | 1.44 |
| EGDMA + MMA + 5% PC | 237 | 264 | 329 | 137 | 258 | 320 | 396 | 2.58 |
| EGDMA + MMA + 10% PC | 234 | 257 | 331 | 135 | 245 | 320 | 397 | 3.10 |
| Sample | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Trecryst (°C) | ΔHrecryst (J/g) | Tg 1 (°C) | Tg 2 (°C) | Tp (°C) | ΔHp (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | - | - | - | - | 146 | 146 | - | - |
| BPA.GDA + MMA | 72 | 11.7 | - | - | - | 92 | 140 | 3.1 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 1% PC | 62 | 20.9 | 101 | 8.7 | 127 | 120 | - | - |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 5% PC | 62 | 14.1 | 107 | 12.1 | 131 | 128 | - | - |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 10% PC | 71 | 15.0 | - | - | - | - | 136 | 8.1 |
| EGDMA + MMA | 71 | 3.0 | - | - | - | - | 166 | 28.3 |
| EGDMA + MMA + 1% PC | 77 | 2.4 | - | - | - | - | 163 | 26.7 |
| EGDMA + MMA + 5% PC | 66 | 6.8 | - | - | - | - | 166 | 23.2 |
| EGDMA + MMA + 10% PC | 63 | 7.4 | - | - | - | - | 164 | 19.7 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) | tan δ max | E’’ (MPa) | FWHM (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tan δ | E’’ | ||||
| PC BPA.GDA + MMA | 144 105.5 | 121 87.7 | 0.16 0.67 | 57.9 260 | 37.8 32.6 |
| BPA.GDA+ MMA + 1% PC | 97.3 | 71.1 | 0.39 | 100 | 34.6 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 5% PC | ~80; 99.4 | 59.9 | 0.44 | 177 | 47.6 |
| BPA.GDA + MMA + 10% PC | ~90; 108.4 | 72.9 | 0.33 | 99 | 44.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wnuczek, K.; Puszka, A.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Podkościelna, B. Preparation, Thermal, and Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Polymeric Blends Based on Di(meth)acrylate Monomers. Polymers 2021, 13, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060878
Wnuczek K, Puszka A, Klapiszewski Ł, Podkościelna B. Preparation, Thermal, and Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Polymeric Blends Based on Di(meth)acrylate Monomers. Polymers. 2021; 13(6):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060878
Chicago/Turabian StyleWnuczek, Krystyna, Andrzej Puszka, Łukasz Klapiszewski, and Beata Podkościelna. 2021. "Preparation, Thermal, and Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Polymeric Blends Based on Di(meth)acrylate Monomers" Polymers 13, no. 6: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060878
APA StyleWnuczek, K., Puszka, A., Klapiszewski, Ł., & Podkościelna, B. (2021). Preparation, Thermal, and Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Polymeric Blends Based on Di(meth)acrylate Monomers. Polymers, 13(6), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060878