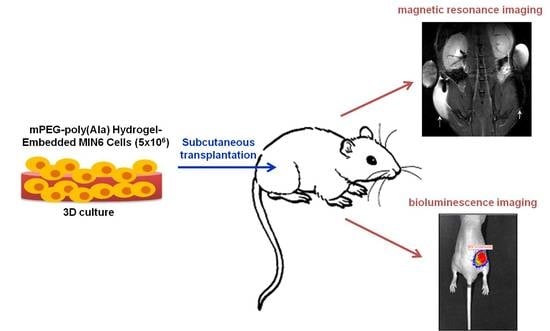
Noninvasive Tracking of mPEG-poly(Ala) Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of l-alanine N-carboxyanhydride (NCA-Ala) and mPEG-poly(Ala) diblock copolymers
2.3. Culture of MIN6 Cells
2.4. Uptake of Chitosan-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (CSPIO) Nanoparticles by MIN6 Cells
2.5. In vitro MR Scanning
2.6. In vivo Transplantation and Imaging
2.7. Histological Study of Grafts of Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Uptake of CSPIO Nanoparticles by MIN6 Cells
3.2. In vitro MR Image of MIN6 Cells
3.3. In Vivo MR Images of Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation
3.4. In Vivo Bioluminescence Images of Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation
3.5. Subcutaneous Grafts of Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, E.A.; Paty, B.W.; Senior, P.A.; Bigam, D.; Alfadhli, E.; Kneteman, N.M.; Lakey, J.R.; Shapiro, A.M. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamble, A.; Pepper, A.R.; Bruni, A.; Shapiro, A.M.J. The journey of islet cell transplantation and future development. Islets 2018, 10, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajab, A. Islet Transplantation: Alternative Sites. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2010, 10, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, T.; Kin, T.; Kashkoush, S.; Gala-Lopez, B.; Bigam, D.L.; Kneteman, N.M.; Koh, A.; Senior, P.A.; Shapiro, A.M. Portal vein thrombosis is a potentially preventable complication in clinical islet transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawahara, T.; Kin, T.; Shapiro, A.M. A comparison of islet autotransplantation with allotransplantation and factors elevating acute portal pressure in clinical islet transplantation. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2012, 19, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, J.H.; Hsu, B.R.; Kuo, C.H. Islet transplantation at subcutaneous and intramuscular sites. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 3479–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, N.; Aoki, T.; Yoshimatsu, G.; Tsuchiya, H.; Hata, T.; Katayose, Y.; Egawa, S.; Unno, M. Strategy for clinical setting in intramuscular and subcutaneous islet transplantation. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2014, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Vulesevic, B.; Ellis, C.; Korbutt, G.S.; Suuronen, E.J. Vascularization of collagen-chitosan scaffolds with circulating progenitor cells as potential site for islet transplantation. J. Control Release 2011, 152 (Suppl. 1), e196–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.-H.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Polymer-based hydrogel scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications: A mini-review. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liao, J.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Biocompatible and photoluminescent carbon dots/hydroxyapatite/PVA dual-network composite hydrogel scaffold and their properties. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Si, X.; Ding, X.; Duan, L.; Xiao, C. pH-responsive hydrogels based on the self-assembly of short polypeptides for controlled release of peptide and protein drugs. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lim, J.H.; Nam, H.Y.; Lim, H.J.; Shin, J.S.; Shin, J.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Jin, S.M.; et al. In situ application of hydrogel-type fibrin-islet composite optimized for rapid glycemic control by subcutaneous xenogeneic porcine islet transplantation. J. Control Release 2012, 162, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, A.E.; Cober, N.; Sefton, M.V. Modular tissue engineering for the vascularization of subcutaneously transplanted pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9337–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Lake, R.; Park, S.; Edwards, S.; Jones, C.; Jeong, K.J. Injectable Macroporous Hydrogel Formed by Enzymatic Cross-Linking of Gelatin Microgels. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2018, 1, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, Q.; Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Antimicrobial hydrogels: Promising materials for medical application. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2217–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qutachi, O.; Wright, E.J.; Bray, G.; Hamid, O.A.; Rose, F.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Delcassian, D. Improved delivery of PLGA microparticles and microparticle-cell scaffolds in clinical needle gauges using modified viscosity formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 546, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, C.; Hai, B.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.; Tan, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Song, C. Chitosan conduits filled with simvastatin/Pluronic F-127 hydrogel promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Magalhães, M.; Veiga, F.; Figueiras, A. Poloxamers, poloxamines and polymeric micelles: Definition, structure and therapeutic applications in cancer. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 25, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Alsberg, E. Bioactive factor delivery strategies from engineered polymer hydrogels for therapeutic medicine. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1236–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Anderson, M.A.; Ao, Y.; Khakh, B.S.; Fan, J.; Deming, T.J.; Sofroniew, M.V. Tunable diblock copolypeptide hydrogel depots for local delivery of hydrophobic molecules in healthy and injured central nervous system. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huettner, N.; Dargaville, T.R.; Forget, A. Discovering cell-adhesion peptides in tissue engineering: Beyond RGD. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Lai, P.-L.; Lin, Y.-K.; Peng, S.; Lee, L.-Y.; Chen, C.-N.; Chu, I.-M. A poloxamer-polypeptide thermosensitive hydrogel as a cell scaffold and sustained release depot. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2976–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, H.; Asano, T.; Tsukuda, K.; Katagiri, H.; Inukai, K.; Anai, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Yazaki, Y.; Miyazaki, J.I.; Oka, Y. Pancreatic beta cell line MIN6 exhibits characteristics of glucose metabolism and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion similar to those of normal islets. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobel, D.O.; Ramasubramanian, B.; Mitnaul, L. Characterization of a mouse model of islet transplantation using MIN-6 cells. Islets 2020, 12, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Akagi, T.; Asaoka, T.; Eguchi, H.; Sasaki, K.; Iwagami, Y.; Yamada, D.; Noda, T.; Kawamoto, K.; Gotoh, K.; et al. Layer-by-layer cell coating technique using extracellular matrix facilitates rapid fabrication and function of pancreatic β-cell spheroids. Biomaterials 2018, 160, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wu, C.W.; Lin, J.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Cheng, M.H.; Chu, I.M. Promoting chondrocyte cell clustering through tuning of a poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(peptide) thermosensitive hydrogel with distinctive microarchitecture. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 76, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kao, C.-W.; Wu, S.-T.; Chen, C.-L.; Shen, C.-R.; Juang, J.-H.; Chu, I.-M. In situ gelling-polypeptide hydrogel systems for the subcutaneous transplantation of MIN6 cells. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jun, H.S. In Vivo Imaging of Transplanted Pancreatic Islets. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y. Islet Transplantation Imaging in vivo. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3301–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Z.-T.; Wang, J.-F.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Shen, C.-R.; Wang, J.-J.; Yen, T.-C. In situ preparation of high relaxivity iron oxide nanoparticles by coating with chitosan: A potential MRI contrast agent useful for cell tracking. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, J.H.; Shen, C.R.; Wang, J.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Chien, Y.W.; Kuo, H.Y.; Chen, F.R.; Chen, M.H.; Yen, T.C.; Tsai, Z.T. Magnetic resonance imaging of mouse islet grafts labeled with novel chitosan-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Shen, C.R.; Kuo, C.H.; Chien, Y.W.; Kuo, H.Y.; Tsai, Z.T.; Yen, T.C. Magnetic resonance imaging of transplanted mouse islets labeled with chitosan-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 2104–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, J.H.; Shen, C.R.; Wang, J.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Lin, M.Y.; Wu, S.T.; Tsai, Z.T.; Yen, T.C. Magnetic resonance imaging study of mouse islet allotransplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 4217–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.-R.; Juang, J.-H.; Tsai, Z.-T.; Wu, S.-T.; Tsai, F.-Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, C.-L.; Yen, T.-C. Preparation, characterization and application of superparamagnetic iron oxide encapsulated with N-[(2-hydroxy-3-trimethylammonium) propyl] chitosan chloride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-P.; Juang, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-J.; Kuo, C.-W.; Hsieh, L.-H.; Huang, C.-C. Enhancement of subcutaneously transplanted β cell survival using 3D stem cell spheroids with proangiogenic and prosurvival potential. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, e1900254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, J.H.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Wu, Y.J.; Weir, G.C. Beneficial influence of glycemic control upon the growth and function of transplanted islets. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Ahn, B.C.; Lee, H.W.; Hwang, M.H.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Sung, Y.K.; Lee, J. In vivo monitoring of survival and proliferation of hair stem cells in a hair follicle generation animal model. Mol. Imaging 2013, 12, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.S.; Tang, C.; Cao, F.; Xie, X.; van der Bogt, K.; Hwang, A.; Connolly, A.J.; Robbins, R.C.; Wu, J.C. Effects of cell number on teratoma formation by human embryonic stem cells. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juang, J.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kao, C.-W.; Chen, C.-L.; Wu, S.-T.; Lin, S.-H.; Shen, C.-R.; Wang, J.-J.; Tsai, Z.-T.; et al. Noninvasive Tracking of mPEG-poly(Ala) Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation in Mice. Polymers 2021, 13, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060885
Juang J-H, Lin H-C, Chen C-Y, Kao C-W, Chen C-L, Wu S-T, Lin S-H, Shen C-R, Wang J-J, Tsai Z-T, et al. Noninvasive Tracking of mPEG-poly(Ala) Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation in Mice. Polymers. 2021; 13(6):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060885
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuang, Jyuhn-Huarng, Hsiu-Chao Lin, Chen-Yi Chen, Chen-Wei Kao, Chen-Ling Chen, Shu-Ting Wu, Sung-Han Lin, Chia-Rui Shen, Jiun-Jie Wang, Zei-Tsan Tsai, and et al. 2021. "Noninvasive Tracking of mPEG-poly(Ala) Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation in Mice" Polymers 13, no. 6: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060885
APA StyleJuang, J. -H., Lin, H. -C., Chen, C. -Y., Kao, C. -W., Chen, C. -L., Wu, S. -T., Lin, S. -H., Shen, C. -R., Wang, J. -J., Tsai, Z. -T., & Chu, I. -M. (2021). Noninvasive Tracking of mPEG-poly(Ala) Hydrogel-Embedded MIN6 Cells after Subcutaneous Transplantation in Mice. Polymers, 13(6), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060885