The Entangled Conductive Structure of CB/PA6/PP MFCs and Their Electromechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
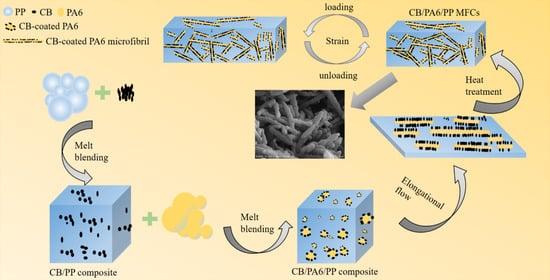
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology
3.2. Electrically Conductive Properties
3.3. Electromechanical Properties
3.3.1. Electromechanical Properties under Uniaxial Tension-Strain
3.3.2. Electromechanical Properties under Cyclic Tension-Strain
3.3.3. Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, T.; Li, J.-L.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.-W. Carbon nanotubes induced microstructure and property changes of polycarbonate/poly(butylene terephthalate) blend. Compos. Part B 2018, 133, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Jia, L.-C.; Yan, D.-X.; Gao, J.-F.; Zhang, X.-P.; Ren, P.-G.; Li, Z.-M. Simultaneously improved electromagnetic interference shielding and mechanical performance of segregated carbon nanotube/polypropylene composite via solid phase molding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Pei, S.; Qian, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.-M.; et al. Superhigh Electromagnetic Interference Shielding of Ultrathin Aligned Pristine Graphene Nanosheets Film. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, N.; Li, N.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Liquid sensing behaviors of conductive polypropylene composites containing hybrid fillers of carbon fiber and carbon black. Compos. Part B 2016, 94, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Jang, J.; Hong, K.; Kim, K.N.; Han, J.H.; Shin, K.; Park, C.E. Poly(3-hexylthiophene) wrapped carbon nanotube/poly(dimethylsiloxane) composites for use in finger-sensing piezoresistive pressure sensors. Carbon 2011, 49, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgousis, G.; Pandis, C.; Chatzimanolis-Moustakas, C.; Kyritsis, A.; Kontou, E.; Pissis, P.; Krajci, J.; Chodak, I.; Tabciarova, J.; Micusik, M.; et al. Study of the reinforcing mechanism and strain sensing in a carbon black filled elastomer. Compos. Part B 2015, 80, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Balasubramaniam, K.; Ramaprabhu, S. Functionalized graphene reinforced thermoplastic nanocomposites as strain sensors in structural health monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 12626–12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Yan, X.; Guo, J.; Guo, Z. Electrically conductive thermoplastic elastomer nanocomposites at ultralow graphene loading levels for strain sensor applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.; Poetschke, P.; Wiegand, N.; Krause, B.; Voit, B. Tuning the Network Structure in Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites Using Carbon Black: Toward Improvements of Conductivity and Piezoresistive Sensitivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14190–14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, M.H.G.; Buschhorn, S.T.; Gehrmann, J.; Schulte, K. Piezoresistive response of epoxy composites with carbon nanoparticles under tensile load. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Sui, K.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W. Balance the electrical properties and mechanical properties of carbon black filled immiscible polymer blends with a double percolation structure. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Peng, S.-P.; Bao, R.-Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B. Low percolation threshold and balanced electrical and mechanical performances in polypropylene/carbon black composites with a continuous segregated structure. Compos. Part B 2016, 99, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. The effect of filler dimensionality on the electromechanical performance of polydimethylsiloxane based conductive nanocomposites for flexible strain sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 139, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Zheng, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Shen, C. A comparison between strain sensing behaviors of carbon black/polypropylene and carbon nanotubes/polypropylene electrically conductive composites. Compos. Part A 2013, 48, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Song, H.; Guo, Z. Comparative assessment of the strain-sensing behaviors of polylactic acid nanocomposites: Reduced graphene oxide or carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2318–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Quijano, J.R.; Poetschke, P.; Bruenig, H.; Heinrich, G. Strain sensing, electrical and mechanical properties of polycarbonate/multiwall carbon nanotube monofilament fibers fabricated by melt spinning. Polymer 2016, 82, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, W. Selective Localization of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/Polylactide Blend. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeger, L.; Wichmann, M.H.G.; Meyer, L.O.; Schulte, K. Load and health monitoring in glass fibre reinforced composites with an electrically conductive nanocomposite epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, G.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Synergistic effect of carbon fibers on the conductive properties of a segregated carbon black/polypropylene composite. Mater. Lett. 2014, 129, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, W.; Jing, M.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Largely Enhanced Stretching Sensitivity of Polyurethane/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites via Incorporation of Cellulose Nanofiber. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lou, D.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, C. Bridging the segregated structure in conductive polypropylene composites: An effective strategy to balance the sensitivity and stability of strain sensing performances. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 163, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lu, C.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, X. Cellulose nanowhisker modulated 3D hierarchical conductive structure of carbon black/natural rubber nanocomposites for liquid and strain sensing application. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 124, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Carbon nanotube chains in a shape memory polymer/carbon black composite: To significantly reduce the electrical resistivity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Dai, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. A highly stretchable and stable strain sensor based on hybrid carbon nanofillers/polydimethylsiloxane conductive composites for large human motions monitoring. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, S.; Ji, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Ma, Y.; Xie, L. The Formation of a Highly Oriented Structure and Improvement of Properties in PP/PA6 Polymer Blends during Extrusion-Stretching. Polymers 2020, 12, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, R.J.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Fakirov, S. Fibrillar polymer-polymer composites: Morphology, properties and applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 6758–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Park, C.B. Dispersed polypropylene fibrils improve the foaming ability of a polyethylene matrix. Polymer 2014, 55, 4199–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Dai, K.; Tang, J.-H.; Ji, X.; Li, Z.-M. Anisotropically conductive polymer composites with a selective distribution of carbon black in an in situ microfibrillar reinforced blend. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1430–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Li, Z.-M.; Li, S.-N.; Zhang, X.-N. Easy Fabrication and Resistivity-Temperature Behavior of an Anisotropically Conductive Carbon Nanotube-Polymer Composite. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shante, V.K.S.; Kirkpatrick, S. An introduction to percolation theory. Adv. Phys. 1971, 20, 325–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Segregated conductive polymer composite with synergistically electrical and mechanical properties. Compos. Part A 2018, 105, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Su, Y.; Bingxi, W.; Yi, P. A method to simultaneously determine the resistivity, volume expansion and temperature relation of filled conductive polymers. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1997, 16, 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Polymer Interface and Adhesion.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Song, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Q. Characterization of carbon black-filled immiscible polypropylene/polystyrene blends. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, B.; Sundqvist, B. Resistivity of a composite conducting polymer as a function of temperature, pressure, and environment: Applications as a pressure and gas concentration transducer. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Xu, X.-B.; Li, Z.-M. Electrically conductive carbon black (CB) filled in situ microfibrillar poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/polyethylene (PE) composite with a selective CB distribution. Polymer 2007, 48, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balberg, I. Tunneling and nonuniversal conductivity in composite materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balberg, I. A comprehensive picture of the electrical phenomena in carbon black-polymer composites. Carbon 2002, 40, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.G.; Paleo, A.J.; van Hattum, F.W.J.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Polypropylene-Carbon Nanofiber Composites as Strain-Gauge Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2603–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Component | Surface Tension γ (mN/m) | Dispersive Surface Energy γd (mN/m) | Polar Surface Energy γp (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CB | 85.50 | 82.36 | 3.14 |
| PA6 | 37.19 | 35.00 | 2.19 |
| PP | 17.62 | 17.25 | 0.37 |
| Equation | γCB-PP (mN/m) | γCB-PA6 (mN/m) | γPP-PA6 (mN/m) | ɷa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric–mean equation | 19.28 | 44.75 | 7.32 | 3.48 |
| Harmonic–mean equation | 10.07 | 25.58 | 3.87 | 4.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, H.; Ji, H.; Li, G.; Wan, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xie, L. The Entangled Conductive Structure of CB/PA6/PP MFCs and Their Electromechanical Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060961
Wang Y, Liu S, Zhu H, Ji H, Li G, Wan Z, Ma Y, Xie L. The Entangled Conductive Structure of CB/PA6/PP MFCs and Their Electromechanical Properties. Polymers. 2021; 13(6):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060961
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Song Liu, Huihao Zhu, Huajian Ji, Guo Li, Zhou Wan, Yulu Ma, and Linsheng Xie. 2021. "The Entangled Conductive Structure of CB/PA6/PP MFCs and Their Electromechanical Properties" Polymers 13, no. 6: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060961
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, S., Zhu, H., Ji, H., Li, G., Wan, Z., Ma, Y., & Xie, L. (2021). The Entangled Conductive Structure of CB/PA6/PP MFCs and Their Electromechanical Properties. Polymers, 13(6), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060961