Effect of Dexamethasone on Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Diblock Copolymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polymerizations
2.3. Encapsulation of Dexamethasone (Dexa)
2.4. NMR Spectroscopy
2.5. GPC Measurements
2.6. UV/Vis Spectrophotometry
2.7. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.8. Optical Microscopy
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.10. Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering (WAXS)
2.11. Confocal Raman Microscopy (CRM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Diblock Copolymers
3.2. Thermoresponsive Behavior of Block Copolymers in PBS
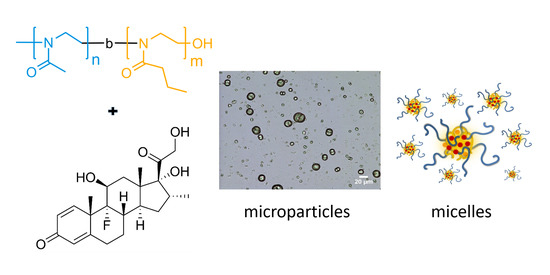
3.3. Formation of Microparticles in P1 Copolymer/Dexa Solutions
3.4. Formation of Microparticles in P1 Copolymer/Dexa Solutions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsehli, M. Polymeric nanocarriers as stimuli-responsive systems for targeted tumor (cancer) therapy: Recent advances in drug delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Zangabad, P.S.; Ghasemi, A.; Amiri, M.; Bahrami, M.; Malekzad, H.; Asl, H.G.; Mahdieh, Z.; Bozorgomid, M.; Ghasemi, A.; et al. Temperature-Responsive Smart Nanocarriers for Delivery of Therapeutic Agents: Applications and Recent Advances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21107–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Weber, C.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Thermoresponsive polymers with lower critical solution temperature: From fundamental aspects and measuring techniques to recommended turbidimetry conditions. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Fraylich, M.; Saunders, B.R. Thermoresponsive copolymers: From fundamental studies to applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxenhofer, R.; Han, Y.; Schulz, A.; Tong, J.; He, Z.; Kabanov, A.V.; Jordan, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)s as polymer therapeutics. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1613–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saeki, S.; Kuwahara, N.; Konno, S.; Kaneko, M. Upper and Lower Critical Solution Temperatures in poly(ethylene glycol) solutions. Macromolecules 1973, 6, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermagoret, A.; Fustin, C.A.; Bourguignon, M.; Detrembleur, C.; Jérôme, C.; Debuigne, A. One-pot controlled synthesis of double thermoresponsive N-vinylcaprolactam-based copolymers with tunable LCSTs. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Pluronic block copolymers: Evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alakhova, D.Y.; Kabanov, A.V. Pluronics and MDR reversal: An update. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2566–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocine, S.; Li, M.-H. Thermoresponsive self-assembled polymer colloids in water. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronek, J.; Kronekova, Z.; Luston, J.; Paulovicova, E.; Paulovicova, L.; Mendrek, B. In vitro bio-immunological and cytotoxicity studies of poly(2-oxazolines). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxenhofer, R.; Sahay, G.; Schulz, A.; Alakhova, D.; Bronich, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Kabanov, A. V Structure-property relationship in cytotoxicity and cell uptake of poly(2-oxazoline) amphiphiles. J. Control. Release 2011, 153, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, M.; Schroeder, S.; Tauhardt, L.; Kempe, K.; Schubert, U.S.; Fischer, D. In vitro hemocompatibility and cytotoxicity study of poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline) for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxenhofer, R.; Jordan, R. Click Chemistry with Poly(2-oxazoline)s. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossegger, E.; Schenk, V.; Wiesbrock, F. Design strategies for functionalized poly(2-oxazoline)s and derived materials. Polymers 2013, 5, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoogenboom, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)s: A polymer class with numerous potential applications. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7978–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luxenhofer, R.; Schulz, A.; Roques, C.; Li, S.; Bronich, T.K.; Batrakova, E.V.; Jordan, R.; Kabanov, A.V. Doubly amphiphilic poly(2-oxazoline)s as high-capacity delivery systems for hydrophobic drugs. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4972–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiue, G.H.; Chiang, H.Z.; Wang, C.H.; Juang, T.M. Nonviral gene carriers based on diblock copolymers of poly(2-ethyl-2- oxazoline) and linear polyethylenimine. Bioconjug. Chem. 2006, 17, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradi, R.; Acikgoz, C.; Textor, M. Polyoxazolines for nonfouling surface coatings—A direct comparison to the gold standard PEG. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoranova, A.; Kronekova, Z.; Zahoran, M.; Chorvat, D.; Janigova, I.; Kronek, J. Poly(2-oxazoline) Hydrogels Crosslinked with Aliphatic bis(2-oxazoline)s: Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Cell Cultivation. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrámková, P.; Zahoranová, A.; Kroneková, Z.; Šišková, A.; Kronek, J. Poly(2-oxazoline) hydrogels by photoinduced thiol-ene “click” reaction using different dithiol crosslinkers. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hahn, L.; Yang, M.; Altmann, A.; Stahlhut, P.; Groll, J.; Luxenhofer, R. Improving printability of a thermoresponsive hydrogel biomaterial ink by nanoclay addition. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgarella, A.R.R.; Zahoranová, A.; Šrámková, P.; Majerčíková, M.; Pavlova, E.; Luxenhofer, R.; Kronek, J.; Lacík, I.; Ricotti, L. Investigation of drug release modulation from poly(2-oxazoline) micelles through ultrasound. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Zahoranova, A.; Mrlik, M.; Sramkova, P.; Minarik, A.; Sedlacik, M. Poly(2-oxazoline)-based magnetic hydrogels: Synthesis, performance and cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, V.R. Poly(2-oxazoline)s as materials for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Thijs, H.M.L.; Jochems, M.J.H.C.; Van Lankvelt, B.M.; Fijten, M.W.M.; Schubert, U.S. Tuning the LCST of poly(2-oxazoline)s by varying composition and molecular weight: Alternatives to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)? Chem. Commun. 2008, 5758–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, L.T.T.; Lambermont-Thijs, H.M.L.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R.; Kjøniksen, A.L. Thermoresponsive Poly(2-oxazoline) block copolymers exhibiting two cloud points: Complex multistep assembly behavior. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4337–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glassner, M.; Lava, K.; De La Rosa, V.R.; Hoogenboom, R. Tuning the LCST of poly(2-cyclopropyl-2-oxazoline) via gradient copolymerization with 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, 3118–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, A.; Kronek, J.; Bosowska, K.; Trzebicka, B.; Dworak, A. Star poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s-synthesis and thermosensitivity. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.; Tobolina, A.; Kirila, T.; Blokhin, A.; Razina, A.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Influence of core configuration and arm structure on solution properties of new thermosensitive star-shaped poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazolines). Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2018, 23, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponchioni, M.; Palmiero, U.C.; Moscatelli, D. Thermo-responsive polymers: Applications of smart materials in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, M.; Filippov, S.K.; Panek, J.; Novakova, M.; Mackova, H.; Kucka, J.; Vetvicka, D.; Ulbrich, K. Polyoxazoline Thermoresponsive Micelles as Radionuclide Delivery Systems a. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Kanada, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Ding, N.; Kanazaki, K.; Mukai, T.; Ono, M.; Saji, H. Enhanced Delivery of Radiolabeled Polyoxazoline into Tumors via Self-Aggregation under Hyperthermic Conditions. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.J.; Osawa, S.; Hayashi, K.; Toh, K.; Naito, M.; Min, H.S.; Yi, Y.; Kwon, I.C.; Kataoka, K.; et al. Dually Stabilized Triblock Copolymer Micelles with Hydrophilic Shell and Hydrophobic Interlayer for Systemic Antisense Oligonucleotide Delivery to Solid Tumor. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5770–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, M.; Esra, T.; Tiller, J.C. Full Thermal Switching of Enzymes by Thermoresponsive Poly (2-oxazoline)-Based Enzyme Inhibitors. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 13367–13371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mees, M.; Haladjova, E.; Momekova, D.; Momekov, G.; Shestakova, P.S.; Tsvetanov, C.B.; Hoogenboom, R.; Rangelov, S. Partially Hydrolyzed Poly(n-propyl-2-oxazoline): Synthesis, Aqueous Solution Properties, and Preparation of Gene Delivery Systems. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3580–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; Elmahi, E.; et al. Effect of Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Preliminary Report. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.S.; Geng, Y.; Discher, D.E.; Yang, S. Temperature-Controlled Assembly and Release from Polymer Vesicles of Poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly(N -isopropylacrylamide). Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Jaksch, S.; Schubel, R.; Wegener, E.; Di, Z.; Han, Y.; Meister, A.; Kressler, J.; Kabanov, A.V.; Luxenhofer, R.; et al. Drug-Induced Morphology Switch in Drug Delivery Systems Based on Poly(2-oxazoline)s. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2686–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppler, A.; Michael, M.L.; Schlauersbach, J.; Wiest, J.; Meinel, L.; Luxenhofer, R. Polymers Loading-Dependent Structural Model of Polymeric Micelles Encapsulating Curcumin by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy ** Angewandte. Polymers 2019, 58, 18540–18546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milonaki, Y.; Kaditi, E.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Amphiphilic gradient copolymers of 2-methyl- and 2-phenyl-2-oxazoline: Self-organization in aqueous media and drug encapsulation. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoranová, A.; Mrlík, M.; Tomanová, K.; Kronek, J.; Luxenhofer, R. ABA and BAB Triblock Copolymers Based on 2-Methyl-2-oxazoline and 2-n-Propyl-2-oxazoline: Synthesis and Thermoresponsive Behavior in Water. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, H.; Seeliger, W. Cyclische Imidsäureester aus Nitrilen und Aminoalkoholen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem 1974, 6, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Schulz, A.; Wan, X.; Seitz, J.; Bludau, H.; Alakhova, D.Y.; Darr, D.B.; Perou, C.M.; Jordan, R.; Ojima, I.; et al. Poly(2-oxazoline) based micelles with high capacity for 3rd generation taxoids: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2015, 208, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Struble, E.B.; Kirschbaum, N.; Liu, J.; Marszal, E.; Shapiro, M. Characterization of Therapeutic Proteins; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 21, ISBN 9783319753805. [Google Scholar]
- Wyffels, L.; Verbrugghen, T.; Monnery, B.D.; Glassner, M.; Stroobants, S.; Hoogenboom, R.; Staelens, S. μPET imaging of the pharmacokinetic behavior of medium and high molar mass 89Zr-labeled poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) in comparison to poly(ethylene glycol). J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riabtseva, A.; Kaberov, L.I.; Noirez, L.; Ryukhtin, V.; Nardin, C.; Verbraeken, B.; Hoogenboom, R.; Stepanek, P.; Filippov, S.K. Structural characterization of nanoparticles formed by fluorinated poly(2-oxazoline)-based polyphiles. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ďorďovič, V.; Verbraeken, B.; Hogenboom, R.; Kereïche, S.; Matějíček, P.; Uchman, M. Tuning of Thermoresponsivity of a Poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline) Block Copolymer by Interaction with Surface-Active and Chaotropic Metallacarborane Anion. Chem. An Asian J. 2018, 13, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Sato, T.; Terao, K.; Qiu, X.P.; Winnik, F.M. Self-association of a thermosensitive poly(alkyl-2-oxazoline) block copolymer in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 6111–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-H.; Cölfen, H.; Hartmann, J.; Antonietti, M. Biomimetic Crystallization of Calcium Carbonate Spherules with Controlled Surface Structures and Sizes by Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszko-Torbus, N.; Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Bochenek, M.; Lipowska-Kur, D.; Dworak, A.; Wałach, W. Thermal and crystalline properties of poly(2-oxazoline)s. Polym. Chem. 2019, 11, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasenack, N.; Müller, B.W. Dissolution rate enhancement by in situ micronization of poorly water-soluble drugs. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Wu, C.; Chang, J. Advances in synthesis of calcium phosphate crystals with controlled size and shape. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4071–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample | DP | Ratio (Theor.) nPrOx:MeOx | Mn Theor. (g·mol−1) | Mn Exp. (g·mol−1) (GPC) | Ratio (NMR) nPrOx:MeOx | Đ (GPC) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 100 | 20:80 (0.25) | 9100 | 9100 | 0.21 | 1.55 | 72 |
| P2 | 100 | 10:90 (0.11) | 8800 | 5700 | 0.11 | 1.88 | 73 |
| P3 | 200 | 40:160 (0.25) | 18,200 | 11,300 | 0.22 | 1.85 | 81 |
| P4 | 200 | 20:180 (0.11) | 17,600 | 10,700 | 0.13 | 1.71 | 85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majerčíková, M.; Nádaždy, P.; Chorvát, D.; Satrapinskyy, L.; Valentová, H.; Kroneková, Z.; Šiffalovič, P.; Kronek, J.; Zahoranová, A. Effect of Dexamethasone on Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Diblock Copolymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091357
Majerčíková M, Nádaždy P, Chorvát D, Satrapinskyy L, Valentová H, Kroneková Z, Šiffalovič P, Kronek J, Zahoranová A. Effect of Dexamethasone on Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Diblock Copolymers. Polymers. 2021; 13(9):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091357
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajerčíková, Monika, Peter Nádaždy, Dušan Chorvát, Leonid Satrapinskyy, Helena Valentová, Zuzana Kroneková, Peter Šiffalovič, Juraj Kronek, and Anna Zahoranová. 2021. "Effect of Dexamethasone on Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Diblock Copolymers" Polymers 13, no. 9: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091357
APA StyleMajerčíková, M., Nádaždy, P., Chorvát, D., Satrapinskyy, L., Valentová, H., Kroneková, Z., Šiffalovič, P., Kronek, J., & Zahoranová, A. (2021). Effect of Dexamethasone on Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Diblock Copolymers. Polymers, 13(9), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091357