Parametric Study and Electrocatalyst of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Single-Cell PEM Electrolyzer
2.2. Operation of the PEM Electrolyzer
2.3. Determination of PEM Electrolyzer Performance
- E = electrical energy consumption (kWh/kg H2)
- Icell = cell current (A)
- Vcell = cell voltage (V)
- = hydrogen flowrate (L/h)
- = density of hydrogen (0.0813 kg/m3) at 1 bar, 25 °C
- η = cell voltaic efficiency (%)
- VTN = thermoneutral voltage = 1.48 V
- Vcell = cell voltage
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Water Feed Flowrate
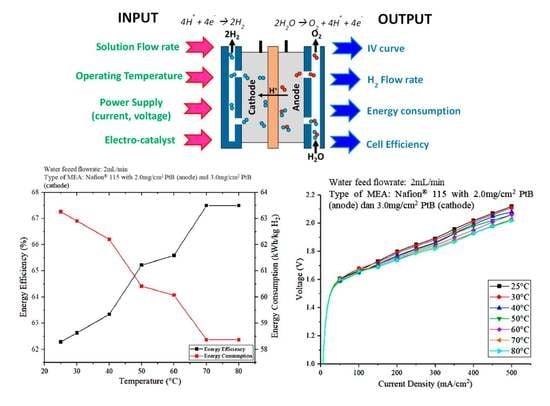
3.2. Effect of Operating Temperature
3.3. Effect of Electrode Type
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melián, E.P.; Díaz, O.G.; Méndez, A.O.; López, C.R.; Suárez, M.N.; Rodríguez, J.M.D.; Navío, J.A.; Hevia, D.F.; Peña, J.P. Efficient and affordable hydrogen production by water photo-splitting using TiO2-based photocatalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ahmad, H.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Minggu, L.J.; Kassim, M. Hydrogen from photo-catalytic water splitting process: A review Cite this paper Hydrogen from photo-catalytic water splitting process: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleman, F.; Dincer, I.; Agelin-Chaab, M. Environmental impact assessment and comparison of some hydrogen production options. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 6976–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.N.A.; Masdar, M.S.; Rosli, M.I.; Majlan, E.H.; Husaini, T.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Daud, W.R.W. Overview biohydrogen technologies and application in fuel cell technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, S.Z. Hydrogen: A brief overview on its sources, production and environmental impact. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 10605–10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuku, H.; Alshami, I.; Goh, J.; Masdar, M.S.; Loh, K.S. Review on bipolar plates for low-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzer. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 20583–20600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Sverdrup, G.; Mann, M.K.; Maness, P.C.; Kroposki, B.; Ghirardi, M.; Evans, R.J.; Blake, D. Renewable hydrogen production. Int. J. Energy Res. 2008, 32, 379–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H2 Bulletin. Hydrogen Production through Electrolysis. Available online: https://www.h2bulletin.com/knowledge/hydrogen-production-through-electrolysis/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Cummins Inc. Electrolyzers 101: What They Are, How They Work and Where They Fit in a Green Economy. Available online: https://www.cummins.com/news/2020/11/16/electrolyzers-101-what-they-are-how-they-work-and-where-they-fit-green-economy (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Abdol Rahim, A.H.; Tijani, A.S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Hanapi, S. An overview of polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyzer for hydrogen production: Modeling and mass transport. J. Power Sources 2016, 309, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Kamarudin, S.K. A review of alkaline solid polymer membrane in the application of AEM electrolyzer: Materials and characterization. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 18337–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallandat, N.; Romanowicz, K.; Züttel, A. An Analytical Model for the Electrolyser Performance Derived from Materials Parameters. J. Power Energy Eng. 2017, 5, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursúa, A.; Gandía, L.M.; Sanchis, P. Hydrogen production from water electrolysis: Current status and future trends. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghyani, S.; Fakhradini, E.; Afshari, E.; Baniasadi, M.Y. Abdollahzadeh Jamalabadi, M. Safdari Shadloo, Optimization of operating parameters of a polymer exchange membrane electrolyzer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 6403–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, S.; Angelo, B.; Nejat Veziroğlu, T. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy, Compendium of Hydrogen Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Paris, France, 2015; Volume 1, Chapter 9; pp. 255–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bessarabov, D.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, N. PEM Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production: Principles and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Chapter 1; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tijani, A.S.; Ghani, M.F.A.; Rahim, A.H.A.; Muritala, I.K.; Binti Mazlan, F.A. Electrochemical characteristics of (PEM) electrolyzer under influence of charge transfer coefficient. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 27177–27189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamet, Ö.F.; Acar, M.C.; Mat, M.D.; Kaplan, Y. Effects of operating parameters on the performance of a high-pressure proton exchange membrane electrolyzer. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majasan, J.O.; Cho, J.I.S.; Dedigama, I.; Tsaoulidis, D.; Shearing, P.; Brett, D.J.L. Two-phase flow behaviour and performance of polymer electrolyte membrane electrolysers: Electrochemical and optical characterization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 15659–15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Araya, S.S.; Kær, S.K. Effect of Current Density, Temperature and Pressure on Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyser Stack. Int. J. Energy Power Eng. 2014, 15, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Scott, K. The effects of ionomer content on PEM water electrolyser membrane electrode assembly performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 35, 12029–12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozain, C.; Mayousse, E.; Guillet, N.; Millet, P. Influence of iridium oxide loadings on the performance of PEM water electrolysis cells: Part I–Pure IrO2-based anodes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 182, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Baglio, V.; Van Dijk, N.; Merlo, L.; Aricò, A.S. Enhanced performance and durability of low catalyst loading PEM water electrolyser based on a short-side chain perfluorosulfonic ionomer. Appl. Energy 2017, 192, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, W.; Na, Y. Effect of Gravity and Various Operating Conditions on Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis Cell Performance. Membranes 2021, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, A.; Scott, K.; Basu, S. Dynamic modeling and simulation of a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 14779–14786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratlamwala, T.A.H.; Dincer, I. Electrochemical, Energy, Exergy and Exergoeconomic Analyses of Hybrid Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Reactor for Cu-Cl Cycle. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275716340_Electrochemical_energy_exergy_and_exergoeconomic_analyses_of_hybrid_photocatalytic_hydrogen_production_reactor_for_Cu-Cl_Cycle (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Linse, N.; Gubler, L.; Scherer, G.G.; Wokaun, A. The effect of platinum on carbon corrosion behavior in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7541–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugirumubano, A.; Jae Shin, H.; Kwac, L.K.; Kim, H.G. Numerical Simulation of the Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Electrolyzer. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2016, 13, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Baglio, V.; Grigoriev, S.A.; Merlo, L.; Fateev, V.N.; Aricò, A.S. The influence of iridium chemical oxidation state on the performance and durability of oxygen evolution catalysts in PEM electrolysis. J. Power Sources 2017, 366, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Characteristic | Specification |
|---|---|
| Active area | 6.0 cm × 6.0 cm |
| Electrolyte membrane | Nafion®® 115 |
| Electrocatalyst at the cathode side | 3.0 mg/cm2 Platinum Black (PtB) |
| Electrocatalyst at the anode side |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor Azam, A.M.I.; Li, N.K.; Zulkefli, N.N.; Masdar, M.S.; Majlan, E.H.; Baharuddin, N.A.; Mohd Zainoodin, A.; Mohamad Yunus, R.; Shamsul, N.S.; Husaini, T.; et al. Parametric Study and Electrocatalyst of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis Performance. Polymers 2023, 15, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030560
Noor Azam AMI, Li NK, Zulkefli NN, Masdar MS, Majlan EH, Baharuddin NA, Mohd Zainoodin A, Mohamad Yunus R, Shamsul NS, Husaini T, et al. Parametric Study and Electrocatalyst of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis Performance. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030560
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor Azam, Adam Mohd Izhan, Ng Khai Li, Nurul Noramelya Zulkefli, Mohd Shahbudin Masdar, Edy Herianto Majlan, Nurul Akidah Baharuddin, Azran Mohd Zainoodin, Rozan Mohamad Yunus, Noor Shahirah Shamsul, Teuku Husaini, and et al. 2023. "Parametric Study and Electrocatalyst of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis Performance" Polymers 15, no. 3: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030560
APA StyleNoor Azam, A. M. I., Li, N. K., Zulkefli, N. N., Masdar, M. S., Majlan, E. H., Baharuddin, N. A., Mohd Zainoodin, A., Mohamad Yunus, R., Shamsul, N. S., Husaini, T., & Shaffee, S. N. A. (2023). Parametric Study and Electrocatalyst of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis Performance. Polymers, 15(3), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030560