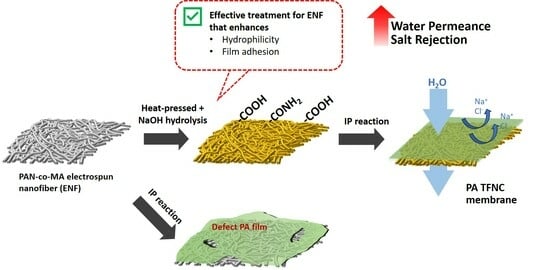
Evaluating Post-Treatment Effects on Electrospun Nanofiber as a Support for Polyamide Thin-Film Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofiber Support
2.2.1. Electrospinning and Heat Treatment
2.2.2. Hydrolysis Treatment
2.3. Fabrication of Thin Film Composite Membranes
2.4. Material Characterization
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.2. Pore Size Measurement
2.4.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.4. Contact Angle
2.4.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.4.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.4.7. Mechanical Strength Testing
2.5. Membrane Performance Evaluation
2.6. Membrane Stability Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Support Properties
3.2. Effect of Heat Treatment on Thin-Film Formation and Membrane Performance
3.3. The Effect of Combined Heat Treatment and Hydrolysis on Support Properties
3.4. The Effect of Combined Heat-Pressing and Hydrolysis on Thin-Film Formation and Membrane Performance
3.5. Performance Stability and Comparison
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klaysom, C.; Hermans, S.; Gahlaut, A.; Van Craenenbroeck, S.; Vankelecom, I.F. Polyamide/Polyacrylonitrile (PA/PAN) thin film composite osmosis membranes: Film optimization, characterization and performance evaluation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 445, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, K.Y.; Helmer, B.; Chung, T.-S. Thin-Film Composite Membranes and Formation Mechanism of Thin-Film Layers on Hydrophilic Cellulose Acetate Propionate Substrates for Forward Osmosis Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10039–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Choi, W.; Nam, S.-E.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.-H. Fabrication of polyamide thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes via support-free interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.E.; Yang, Z.; Long, L.; Zhou, S.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. A critical review on porous substrates of TFC polyamide membranes: Mechanisms, membrane performances, and future perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, M.; Hou, Y. Thin-Film Composite Membrane with Porous Interlayer Composed of Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Nanofiltration. Polymers 2023, 15, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Barhate, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Hot pressing of electrospun membrane composite and its influence on separation performance on thin film composite nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2011, 279, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Mei, X.; Han, J.; Yao, L.; Chen, S.; You, X.; Liao, Y. Impacts of hydrophobic, hydrophilic, superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic nanofibrous substrates on the thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selatile, M.K.; Ray, S.S.; Ojijo, V.; Sadiku, R. Recent developments in polymeric electrospun nanofibrous membranes for seawater desalination. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37915–37938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharabati, J.-A.; Guclu, S.; Erkoc-Ilter, S.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Unal, S.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Ozturk, I.; Koyuncu, I. Interfacially polymerized thin-film composite membranes: Impact of support layer pore size on active layer polymerization and seawater desalination performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, R.; Peng, X.; Li, N.; Dai, Z. Development of Support Layers and Their Impact on the Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes (TFC) for Water Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Lau, C.H.; Xiong, S.; Wei, W.; Liao, R.; Shen, L.; Lu, A.; Wang, Y. Zwitterion–Ag Complexes That Simultaneously Enhance Biofouling Resistance and Silver Binding Capability of Thin Film Composite Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15698–15708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emadzadeh, D.; Lau, W.; Matsuura, T.; Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Ismail, A. A novel thin film composite forward osmosis membrane prepared from PSf–TiO2 nanocomposite substrate for water desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Enhancing the flux of brackish water TFC RO membrane by improving support surface porosity via a secondary pore-forming method. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Kwon, S.J.; Shin, M.G.; Park, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, C.H.; Park, H.; Lee, J.-H. Polyethylene-supported high performance reverse osmosis membranes with enhanced mechanical and chemical durability. Desalination 2018, 436, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Deng, B. A review: The effect of the microporous support during interfacial polymerization on the morphology and performances of a thin film composite membrane for liquid purification. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35417–35428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, H.-R.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, P.-K.; Kim, I.-C.; Kim, J.-H. Synergetic effect of graphene oxide nanosheets embedded in the active and support layers on the performance of thin-film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Z.C.; Lau, W.J.; Lai, G.S.; Meng, J.; Gao, H.; Ismail, A.F. Facile fabrication of polyethyleneimine interlayer-assisted graphene oxide incorporated reverse osmosis membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2022, 526, 115502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Immobilization of sulfonated polysulfone via 2D LDH nanosheets during phase-inversion: A novel strategy towards greener membrane synthesis and enhanced desalination performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hsiao, B.S. Electrospun nanofiber membranes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 12, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Kang, H.; Li, N.; Teng, K.; Sun, W.; Xu, Z.; Qian, X.; Liu, Q. Chitosan sub-layer binding and bridging for nanofiber-based composite forward osmosis membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Chu, B.; Hsiao, B.S. Thin-film nanofibrous composite reverse osmosis membranes for desalination. Desalination 2017, 420, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Lu, J.-P.; Zhao, L.-L.; Lu, T.-D.; Cao, X.-L.; Jia, T.-Z.; Wang, Y.-C.; Sun, S.-P. Electrospun transition layer that enhances the structure and performance of thin-film nanofibrous composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, S.; Al-Ajrash, S.M.N.; Klosterman, D.A.; Crosson, K.M.; Crosson, G.S.; Vasquez, E.S. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(acrylonitrile-co-Methyl Acrylate)/Lignin Nanofibers: Effects of Lignin Type and Total Polymer Concentration. Polymers 2021, 13, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tognia, M.; Guo, D.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Lin, H. Facile preparation of polyacrylonitrile-co-methylacrylate based integrally skinned asymmetric nanofiltration membranes for sustainable molecular separation: An one-step method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 546, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rajabi, M.M.; Almanassra, I.W.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Atieh, M.A.; Laoui, T.; Khalil, K.A. Facile Coaxial Electrospinning Synthesis of Polyacrylonitrile/Cellulose Acetate Nanofiber Membrane for Oil–Water Separations. Polymers 2023, 15, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, D.; Qin, L.; Chen, R.; Xu, G.; Su, Z.; Cheng, J.; Xie, S.; Cheng, F.; Ko, F. Transparent PAN:TiO2 and PAN-co-PMA:TiO2 Nanofiber Composite Membranes with High Efficiency in Particulate Matter Pollutants Filtration. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sundarrajan, S.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Influence of electrospun fiber size on the separation efficiency of thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 392–393, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Y. Facilely cyclization-modified PAN nanofiber substrate of thin film composite membrane for ultrafast polar solvent separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.; Jegal, J.; Lee, K. Preparation and characterization of nanofiltration composite membranes using polyacrylonitrile (PAN). II. Preparation and characterization of polyamide composite membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard D1708−13; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Kedchaikulrat, P.; Vankelecom, I.F.; Faungnawakij, K.; Klaysom, C. Effects of colloidal TiO2 and additives on the interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposite membranes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 601, 125046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Woo, Y.C.; Tijing, L.D.; Shim, W.-G.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Effect of heat-press conditions on electrospun membranes for desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 378, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Ge, A.; Liang, X.; Lu, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L. Comparison of the physical properties of heat-treated and hydrophobic modified glass fiber felt. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 51 (Suppl. S1), 1422S–1440S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Wang, R.; Field, R.W. Direct contact membrane distillation: An experimental and analytical investigation of the effect of membrane thickness upon transmembrane flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liew, S.R.; Bai, R. Simultaneous alkaline hydrolysis and non-solvent induced phase separation method for polyacrylonitrile (PAN) membrane with highly hydrophilic and enhanced anti-fouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, L.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Kang, J.; Pu, S.; Chen, D.; Ma, R.; An, K.; Liu, G.; et al. Electrospun nanofiber based forward osmosis membrane using graphene oxide as substrate modifier for enhanced water flux and rejection performance. Desalination 2021, 518, 115283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacan, I.; Erdogan, G. The influence of thermal stabilization stage on the molecular structure of polyacrylonitrile fibers prior to the carbonization stage. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Chen, D.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Kang, J.; Xu, R.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M. Influence of support layer pore size on interfacial polymerization and polyamide selective layer characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, R.; Yalcinkaya, F. Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibrous Membranes for Point-of-Use Water and Air Cleaning. ChemistryOpen 2019, 8, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Cheng, R.; Yi, M.; Hung, W.-S.; Japip, S.; Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. Polyamide-based membranes with structural homogeneity for ultrafast molecular sieving. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Atikah, M.S.N.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Rafiqah, S.A.; Aisyah, H.A.; Nurazzi, N.M.; Norrrahim, M.N.F. Effect of hydrolysis time on the morphological, physical, chemical, and thermal behavior of sugar palm nanocrystalline cellulose (Arenga pinnata (Wurmb.) Merr). Text. Res. J. 2020, 91, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Jeong, Y.G.; Yoon, Y.I.; Park, W.H. Effect of alkaline hydrolysis on cyclization reaction of PAN nanofibers. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.; Yang, E.; Kang, D.-H.; Yoon, M.-H.; Kim, I.S. Underwater superoleophobic modified polysulfone electrospun membrane with efficient antifouling for ultrafast gravitational oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Nandgaonkar, A.G.; Lu, K.; Krause, W.E.; Lucia, L.A.; Wei, Q. Laccase immobilized on PAN/O-MMT composite nanofibers support for substrate bioremediation: A de novo adsorption and biocatalytic synergy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 41420–41427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Yang, S.M.; Hsin, A.; Chang, Y.K. Dye-Affinity Nanofibrous Membrane for Adsorption of Lysozyme: Preparation and Performance Evaluation. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Moreno, I.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L. Characterization and Optimization of the Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyacrylonitrile Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austria, H.F.M.; Lecaros, R.L.G.; Hung, W.-S.; Tayo, L.L.; Hu, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-A.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Investigation of salt penetration mechanism in hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile asymmetric membranes for pervaporation desalination. Desalination 2019, 463, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, F.; Li, S.; Yin, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Qi, H. Alkaline Hydrolysis of Waste Acrylic Fibers Using the Micro-Water Method and Its Application in Drilling Fluid Gel Systems. Gels 2023, 9, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, C.-H.; Ma, H.-R.; Ding, Y.-R.; Jia, S.-T. Fabrication of PAN Electrospun Nanofibers Modified by Tannin for Effective Removal of Trace Cr(III) in Organic Complex from Wastewater. Polymers 2020, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeong, Y.G.; Yoon, Y.I.; Park, W.H. Hydrolysis of oxidized polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous webs and selective adsorption of harmful heavy metal ions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 143, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; McCutcheon, J.R. Impact of support layer pore size on performance of thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 483, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xia, M.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H. Facile preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride substrate supported thin film composite polyamide nanofiltration: Effect of substrate pore size. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 638, 119699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, D.; Li, G.; Liang, H.; Wiesner, M.R. The role of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals placement in the performance of thin-film composite (TFC) membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 617, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Hoek, E.M. Impacts of support membrane structure and chemistry on polyamide–polysulfone interfacial composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 336, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, M.; Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A. Effect of lag time in interfacial polymerization on polyamide composite membrane with different hydrophilic sub layers. Desalination 2012, 284, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Gao, F.; Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Chen, D.; Liu, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Influences of support layer hydrophilicity on morphology and performances of polyamide thin-film composite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Weinman, S.T. A review on the synthesis of fully aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2021, 502, 114939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.-N.; Lind, M.L.; Hoek, E.M.; McCutcheon, J.R. Electrospun nanofiber supported thin film composite membranes for engineered osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 385–386, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.-X.; Wang, T.-Y.; Wu, X.-Q.; Chen, J.-P.; Zhao, Q.-B.; Zheng, Y.-M. Alleviation of Reverse Salt Leakage across Nanofiber Supported Thin-Film Composite Forward Osmosis Membrane via Heat-Curing in Hot Water. Membranes 2021, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, M.R.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Millare, J.C.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, H.-A.; Lee, K.-R. Vacuum-Assisted Interfacial Polymerization Technique for Enhanced Pervaporation Separation Performance of Thin-Film Composite Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Impacts of Surface Hydrophilicity of Carboxylated Polyethersulfone Supports on the Characteristics and Permselectivity of PA-TFC Nanofiltration Membranes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jye, L.W.; Ismail, A.F. Nanofiltration Membranes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, B.P.; Marchesini, S.; Chemello, G.; Morgan, D.J.; Vyas, N.; Howe, T.; Radnik, J.; Clifford, C.A.; Pollard, A.J. The influence of sample preparation on XPS quantification of oxygen-functionalised graphene nanoplatelets. Carbon 2023, 211, 118054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.; Duke, M.C.; Tardy, B.L.; Oldfield, D.; Dagastine, R.R.; Orbell, J.D.; Dumée, L.F. Charge tunable thin-film composite membranes by gamma-ray triggered surface polymerization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-H.; Chao, W.-C.; Li, C.-L.; Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Hung, W.-S.; Liaw, D.-J.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. A study on the characteristics and pervaporation performance of polyamide thin-film composite membranes with modified polyacrylonitrile as substrate for bioethanol dehydration. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Lau, V.J.; Ji, Y.L.; Huang, S.H.; An, Q.F.; Caparanga, A.R.; Tsai, H.A.; Hung, W.S.; Hu, C.C.; Lee, K.R.; et al. Correlating PSf Support Physicochemical Properties with the Formation of Piperazine-Based Polyamide and Evaluating the Resultant Nanofiltration Membrane Performance. Polymers 2017, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Cheng, P.; Fan, K.; Gao, Y.; Xia, S.; Wang, X.-M.; Xie, Y.F.; Huang, X. Hexane Treatment to Facilely Tailor Polyamide Nanofiltration Membrane Performance: The Critical Role of Treatment Duration. ACS ES&T Eng. 2023, 3, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wen, X.; Zhao, Y. Improvement of osmosis performance by n-hexane rinse: A missing parameter when developing thin film composite membrane. Desalination 2023, 567, 116951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Heath, D.E.; Kentish, S.E. Composite Membranes with Nanofibrous Cross-Hatched Supports for Reverse Osmosis Desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 44720–44730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabtah, F.G.; Alkhouzaam, A.; Khraisheh, M. New Insights into the Mechanical Behavior of Thin-Film Composite Polymeric Membranes. Polymers 2022, 14, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Huang, P.; Zhao, F.; Dong, H.; Niu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. Enhancing the long-term separation stability of TFC membrane by the covalent bond between synthetic 81 amino-substituted polyethersulfone substrate and polyamide layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Support | Fiber Diameter (nm) | Mean Flow Pore Pressure (bar) | Mean Pore Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-spun ENF | 150 ± 30 | 0.51 | 1.26 |
| hp-ENF 120 | 200 ± 30 | 0.70 | 0.91 |
| hp-ENF 140 | 220 ± 40 | 0.79 | 0.81 |
| hp-ENF 160 | 240 ± 60 | 1.02 | 0.63 |
| Hydrolysis Temperature (°C) | Fiber Diameter (nm) | Mean Pore Size (µm) | I1665/I2242 | I1565/I2242 | WCA (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-hydrolyzed | 200 ± 30 | 0.91 | 0 | 0 | 25.5 ± 7.2 |
| 30 | 120 ± 20 | 0.71 | 0.157 | 0.055 | 0 |
| 50 | 120 ± 10 | 0.66 | 1.024 | 5.941 | 0 |
| Hydrolysis Temperature (°C) | n-Hexane Rinsing | PA Layer Thickness (nm) | I1446/I1541 (FTIR) | O/N Ratio (XPS) | A (LMH bar−1) | R (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-hydrolyzed | no | 700 ± 50 | 0.270 | 3.24 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 83.0 ± 6.4 |
| 30 | no | 410 ± 50 | 0.299 | 1.94 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 97.6 ± 1.0 |
| 30 | yes | 380 ± 40 | 0.309 | 1.85 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 96.8 ± 0.4 |
| 50 | no | 430 ± 40 | 0.314 | 3.58 | 2.7 ± 0.0 | 98.0 ± 0.4 |
| Membranes | Feed Solution | Operating Pressure (bar) | A (LMH bar−1) | R (%) | Mechanical Properties | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Strain at Break (%) | ||||||
| hp-TFNC | NaCl (2000 ppm) | 5 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 83 ± 6.4 | 20.1 ± 4.1 | 27.1 ± 4.4 | This work |
| hp-TFNC 120-30 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 97.6 ± 1.0 | 16.3 ± 2.5 | 24.5 ± 3.7 | This work | ||
| hp-TFNC 120-30-Hex | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 96.8 ± 0.4 | 21.7 ± 1.0 | 27.5 ± 0.9 | This work | ||
| hp-TFNC 120-50 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 98.0 ± 0.4 | 17.6 ± 7.5 | 24.7 ± 0.9 | This work | ||
| TFNC from PVDF | NaCl (1000 ppm) | 8 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 91.2 ± 1.3 | 5.4 ± 0.7 | 27.1 ± 0.9 | [7] |
| TFNC from PAN/CA | NaCl (500 ppm) | 7 | 2.8 ± 0.9 | 97.5 ± 0.4 | N/A | N/A | [21] |
| TFNC from PSU | NaCl (2000 ppm) | 20 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 98.7 ± 0.1 | 40 | 3.5 | [69] |
| TFC from hydrolyzed PAN prepared from phase inversion * | NaCl (5850 ppm) | 10 | 0.91 | 89.95 | N/A | N/A | [1] |
| TFC from support prepared from phase inversion | NaCl (2000 ppm) | 15.5 | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 96.7 ± 1.4 | N/A | N/A | [3] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Augusty, A.C.; Rangkupan, R.; Klaysom, C. Evaluating Post-Treatment Effects on Electrospun Nanofiber as a Support for Polyamide Thin-Film Formation. Polymers 2024, 16, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050713
Augusty AC, Rangkupan R, Klaysom C. Evaluating Post-Treatment Effects on Electrospun Nanofiber as a Support for Polyamide Thin-Film Formation. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050713
Chicago/Turabian StyleAugusty, Anniza Cornelia, Ratthapol Rangkupan, and Chalida Klaysom. 2024. "Evaluating Post-Treatment Effects on Electrospun Nanofiber as a Support for Polyamide Thin-Film Formation" Polymers 16, no. 5: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050713
APA StyleAugusty, A. C., Rangkupan, R., & Klaysom, C. (2024). Evaluating Post-Treatment Effects on Electrospun Nanofiber as a Support for Polyamide Thin-Film Formation. Polymers, 16(5), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050713