Studies on Preparation of Poly(3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine)-Polylactide Copolymers and the Effect of the Structure of the Copolymers on Their Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of PDOPA(TBDMS)2
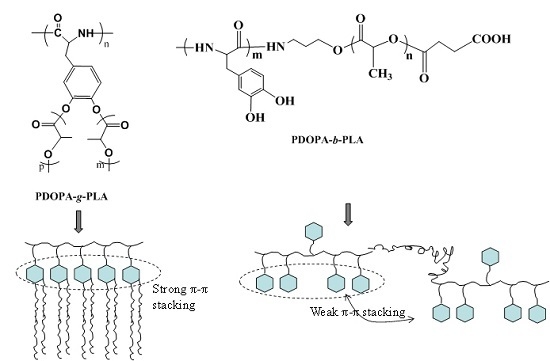
2.3. Synthesis of PDOPA-g-PLA Copolymer
2.4. Synthesis of PDOPA-b-PLA Copolymer
2.5. Hydrolytic Degradation of the Copolymers
2.6. Cell Adhesion of the Copolymers
2.7. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization
3.2. Solubility
3.3. Thermal Property
3.4. Hydrolytic Degradation
3.5. Biocompatibility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coombs, J.; Hall, K. Chemicals and polymers from biomass. Renew. Energ. 1998, 15, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mülhaupt, R. Green polymer chemistry and bio-based plastics: Dreams and reality. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Etxeberria, A.; Varga, A.L.; Sarasua, J.R. Synthesis and characterization of ω-pentadecalactone-co-ε-decalactone copolymers: Evaluation of thermal, mechanical and biodegradation properties. Polymer 2015, 81, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.P.; O’Connor, K.; Seeram, R. Current progress on bio-based polymers and their future trends. Prog. Biomater. 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furkan, H.; Isikgor, C.; Remzi, B. Lignocellulosic biomass: A sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 4497–4559. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Seino, H.; Ren, J.; Hatanaka, K.; Yoshie, N. Bio-based furan polymers with self-healing ability. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolau, B.J.; Perera, M.A.; Brachova, L.; Shanks, B. Platform biochemicals for a biorenewable chemical industry. Plant. J. 2008, 54, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mialon, L.; Vanderhenst, R.; Pemba, A.G.; Miller, S.A. Polyalkylenehydroxybenzoates (PAHBs): Biorenewable aromatic/aliphatic polyesters from lignin. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.F.; Ren, J.J.; Shi, D.J.; Ma, P.M.; Li, X.; Duan, F.; Ni, Z.B.; Chen, M.Q. Hydrolyzable and bio-based polyester/nano-hydroxyapatite nanocomposites: Sructure and properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoichet, M.S. Polymer scaffolds for biomaterials applications. Macromolecules 2009, 43, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.H. High molecular weight polylactic acid polymers. In Biopolymers from Renewable Resources; Springer: Berlin, Germany/Heidelberg, Heidelberg, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Itry, R.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A. Biopolymer blends based on poly(lactic acid): Shear and elongation rheology/structure/blowing process relationships. Polymers 2015, 7, 939–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I. End-life prediction of commercial PLA used for food packaging through short term TGA experiments: Real chance or low reliability? Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 32, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.; You, W.; He, J.; Yu, M.H. Dynamic mechanical properties and thermal stability of poly(lactic acid) and poly(butylene succinate) blends composites. J. Fiber Bioengin. Inform. 2013, 6, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Siracusa, V. Kinetic study of the thermal and thermo-oxidative degradations of polylactide-modified films for food packaging. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 112, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.M.; Shen, T.F.; Xu, P.W.; Dong, W.F.; Lemstra, P.J.; Chen, M.Q. Superior performance of fully biobased poly(lactide) via stereocomplexation-induced phase separation: Structure versus property. ACS. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, D.A.; Basu, B.; Webster, T.J. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid): Carbon nanofiber composites for myocardial tissue engineering applications. Acta. Biomater. 2011, 7, 3101–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.Q.; Yang, K.; Ji, P.; Yu, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of poly(l-lactic acid)-poly(ε-caprolactone) multiblock copolymers by melt polycondensation. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5045–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Kim, H.S.; Shim, J.H.; Yoon, J.S. Role of epoxy groups on clay surface in the improvement of morphology of poly(l-lactide)/clay composites. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3738–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.M.; Jiang, L.; Xu, P.W.; Dong, W.F.; Chen, M.Q.; Lemstra, P.J. Rapid stereocomplexation between enantiomeric comb-Shaped cellulose-g-poly(l-lactide) nanohybrids and poly(d-lactide) from the melt. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3723–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, S.M.; Ghzaoui, A.E.; Nouailhas, H.; Zhuo, R.X. Synthesis and gelation properties of PEG-PLA-PEG triblock copolymers obtained by coupling monohydroxylated PEG-PLA with adipoyl chloride. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, L.C.; Li, C.C.; Zhu, W.X.; Zhang, D.; Guan, G.H.; Xiao, Y.N. Synthesis and properties of biodegradable multiblock poly(ester-carbonate) comprising of poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(butylene carbonate) with hexamethylene diisocyanate as chain-extender. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.P.; Li, J.H.; Chen, M.Q.; Ren, J.J.; Ni, Z.B.; Liu, X.Y. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyester P(DHCA-co-LA). Acta. Polym. Sin. 2010, 3, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.J.; Hua, J.T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.Q. Synthesis of bio-based poly(lactic acid-co-hydroxy decanonate) copolymers with thermal stability and ductility. Polymers 2015, 7, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedó, J.; Saiz-Poseu, J.; Busqué, F.; Ruiz-Molina, D. Catechol-based biomimetic functional materials. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 653–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulay, S. Dopa/catechol-tethered polymers: Bioadhesives and biomimetic adhesive materials. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 436–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wei, W.; Menyo, M.S.; Masic, A.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N. Adhesion of mussel foot protein-3 to TiO2 surfaces: The effect of pH. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, A.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zelikin, A.N.; Tjipto, E.; Caruso, F. Self-polymerization of dopamine as a versatile and robust technique to prepare polymer capsules. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3042–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrówczyński, R.; Nan, A.; Turcu, R.; Leistner, J.; Liebscher, J. Polydopamine–A versatile coating for surface-initiated ring-opening polymerization of lactide to polylactide. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.K.; Das, S.; Linstadt, R.; Kaufman, Y.; Martinez-Rodriguez, N.R.; Mirshafian, R.; Kesselman, E.; Talmon, Y.; Lipshutz, B.H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; et al. High-performance mussel-inspired adhesives of reduced complexity. Nature Commun. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.K.; Lee, D.W.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. Surface-initiated self-healing of polymers in aqueous media. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.J.; Liu, R.J.; Dong, W.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Chen, M.Q.; Akashi, M. pH-Dependent and self-healing properties of mussel modified PVC hydrogels in metal-free environment. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82252–82258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Müllner, M.; Koeverden, M.P.; Noi, K.F.; Zhu, W.; Caruso, F. Engineering fluorescent poly(dopamine) capsules. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B. A reversible wet/dry adhesive inspired by mussels and geckos. Nature 2007, 448, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.J.; Liu, R.J.; Ma, F.D.; Chen, D.Y.; Chen, M.Q.; Akashi, M. Studies on synthesis, characterization and functionalization of poly(3,4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine). Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.L.; Li, X.J.; Chen, M.Q.; Akashi, M. Fabrication of rod-like nanocapsules based on polylactide and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine for drug delivery system. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 103414–103420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, M.J.; Wilker, J.J. Synthesis of peptides containing DOPA (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine). Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6139–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, J.; Lu, T.; Jing, X. A biodegradable triblock copolymer poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide)-b-poly(l-lysine): Synthesis, self-assembly, and RGD peptide modification. Polymer 2007, 48, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaurio, E.; Zuza, E.; Sarasua, J.R. Miscibility and specific interactions in blends of poly(l-lactide) with poly(vinylphenol). Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | nPDOPA:nLA | Mn × 10−4 a | Mw/Mn a | Tm (°C) b | Td,5% (°C) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDOPA | / | 0.2 | 1.24 | 237 | / |
| PDOPA-g-PLA5 | 1:5 | 0.6 | 1.19 | 169 | 350 |
| PDOPA-g-PLA10 | 1:10 | 0.8 | 1.26 | 171 | 349 |
| PDOPA-g-PLA20 | 1:20 | 1.0 | 1.41 | 173 | 349 |
| PDOPA-g-PLA50 | 1:50 | 1.3 | 1.60 | 175 | 345 |
| PDOPA-g-PLA100 | 1:100 | 1.3 | 1.79 | 175 | 341 |
| PLA | / | 0.4 | 1.18 | 162 | 240 |
| Sample | nPDOPA: nPLA | Mn× 10−4 a | Mw/Mn a | Tm (°C) b | Td,5% (°C) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDOPA | / | 0.2 | 1.24 | 237 | / |
| PDOPA50-b-PLA | 50:1 | 2.0 | 1.20 | 180 | 321 |
| PDOPA20-b-PLA | 20:1 | 2.0 | 1.27 | 180 | 316 |
| PDOPA10-b-PLA | 10:1 | 1.8 | 1.23 | 178 | 310 |
| PDOPA5-b-PLA | 5:1 | 1.5 | 1.29 | 175 | 309 |
| PDOPA-b-PLA | 1:1 | 1.3 | 1.44 | 171 | 281 |
| PDOPA-b-PLA5 | 1:5 | 1.5 | 1.35 | 174 | 283 |
| PDOPA-b-PLA10 | 1:10 | 1.8 | 1.33 | 177 | 277 |
| PDOPA-b-PLA20 | 1:20 | 2.2 | 1.35 | 179 | 273 |
| PDOPA-b-PLA50 | 1:50 | 2.3 | 1.44 | 181 | 263 |
| PLA | / | 0.4 | 1.18 | 162 | 240 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, D.; Shen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, C.; Chen, M. Studies on Preparation of Poly(3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine)-Polylactide Copolymers and the Effect of the Structure of the Copolymers on Their Properties. Polymers 2016, 8, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030092
Shi D, Shen J, Zhao Z, Shi C, Chen M. Studies on Preparation of Poly(3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine)-Polylactide Copolymers and the Effect of the Structure of the Copolymers on Their Properties. Polymers. 2016; 8(3):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030092
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Dongjian, Jiali Shen, Zenghui Zhao, Chang Shi, and Mingqing Chen. 2016. "Studies on Preparation of Poly(3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine)-Polylactide Copolymers and the Effect of the Structure of the Copolymers on Their Properties" Polymers 8, no. 3: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030092
APA StyleShi, D., Shen, J., Zhao, Z., Shi, C., & Chen, M. (2016). Studies on Preparation of Poly(3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine)-Polylactide Copolymers and the Effect of the Structure of the Copolymers on Their Properties. Polymers, 8(3), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030092