Thermosensitive Behavior and Antibacterial Activity of Cotton Fabric Modified with a Chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
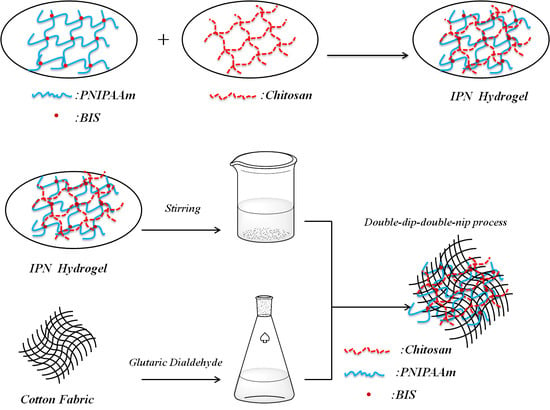
2.2. Synthesis of the IPN Hydrogel
2.3. Grafting of IPN Hydrogel onto Cotton Fabric
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Measurement of IPN Hydrogels Thermosensitive Behavior and LCST
2.6. Grafting Degree of Cotton Fabric
2.7. Measurement of Antimicrobial Activity of IPN Hydrogel Modified Cotton Fabric
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. TGA and FT-IR Characterization of IPN Hydrogels
3.2. Thermosensitive Behavior of the IPN Hydrogels
3.2.1. Transmittance Measurement of the IPN Hydrogels
3.2.2. Determination of IPN Hydrogels’ LCST
3.3. Grafting IPN Hydrogel onto Cotton Fabric
3.3.1. Grafting Degree of Cotton Fabric
3.3.2. FT-IR Analysis of Cotton Fabric
3.3.3. SEM Analysis of the Cotton Fabric.
3.3.4. Hydrophobicity of the IPN Hydrogel-Modified Cotton Fabric
3.3.5. Antibacterial Activity of the IPN Hydrogel-Modified Cotton Fabric
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, I.; Gupta, M.N. Smart polymeric materials: Emerging biochemical applications. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, M.A.C.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasparakis, G.; Vamvakaki, M. Multiresponsive polymers: Nano-sized assemblies, stimuli-sensitive gels and smart surfaces. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, H.; Park, S.H.; Kwon, D.Y.; Khang, G.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, M.S. Thermo-responsive injectable mPEG-polyester diblock copolymers for sustained drug release. Polymers 2014, 6, 2670–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, D.; Quilty, F.; Corrigan, O. Effect of drug physicochemical properties on swelling/deswelling kinetics and pulsatile drug release from thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, D.; Corrigan, O. Drug–polymer interactions and their effect on thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 313, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo-and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaev, I.Y.; Mattiasson, B. “Smart” polymers and what they could do in biotechnology and medicine. Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Q.H.; Wang, T.M. Thermoresponsive PNIPAAm-modified cotton fabric surfaces that switch between superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 4888–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audrey, T.; Nathalie, D.G.; Dragan, J.; Rino, M.; Marijn, M.C.G.W.; Christophe, L. Incorporation of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan microgel onto plasma functionalized cotton fiber surface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 352, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, S.; Florea, L.; Fraser, K.J.; Diamond, D. Swelling and shrinking properties of thermo-responsive polymeric ionic liquid hydrogels with embedded linear pNIPAAM. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5337–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.A.; Georgiou, T.K. Thermoresponsive polymers for biomedical applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1215–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, H.G. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Z.M.; Bao, Y.Z.; Weng, Z.X. Thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylonitrile) hydrogels with rapid response. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 14, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, C.; Boris, D.; Xavier, C. Surface modification of lyocell fibers by graft copolymerization of thermo-sensitive poly-N-isopropylacrylamide. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.R.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Zhu, H.J.; Wang, D.J.; Xin, J.H. In-situ study of the structure and dynamics of thermo-responsive PNIPAAm grafted on a cotton fabric. Polymer 2012, 53, 3577–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, J.B.; Ren, J. Switchable wettability of thermo-responsive biocompatible nanofibrous films created by electrospinning. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, D.; Cui, S. Novel hydroxyapatite/tussah silk fibroin/chitosan bone-like nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 2012, 68, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, S.Y.; An, Y.; Ke, F.Y.; Zhao, D.M.; Shen, Y.H.; Xu, H.Y. Chitosan/silk fibroin composite scaffolds for wound dressing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-H.; Hudson, S.M. Application of a fiber-reactive chitosan derivative to cotton fabric as an antimicrobial textile finish. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fang, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Synthesis and thermosensitive behavior of polyacrylamide copolymers and their applications in smart textiles. Polymers 2015, 7, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Yang, Y.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Ma, K.X. Preparation and characterization of fast response macroporous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6094–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Chu, C.C. Synthesis and properties of the semi-interpenetrating polymer network–like, thermosensitive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1935–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.C.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Liu, G.L.; Gao, D.W.; Wang, C.X. Preparation and properties of polyester fabrics grafted with O-carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.; King, M.W. Natural dye extracted from Chinese gall- the application of color and antibacterial activity to wool fabric. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Cheng, D.H.; Lu, S.; Huang, F.Y.; Li, G. Preparation of quaternary ammoniumsalt of chitosan nanoparticles and their textile propertieson Antheraea pernyi silk modification. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Tanaka, T. Volume phase transition and related phenomena of polymer gels. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2006, 109, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.D. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles and their application to Antheraea pernyi silk. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, W.W. Crosslinking chitosan into H3PO4/HNO3–NaNO2 oxidized cellulose fabrics as antibacterial-finished material. Coll. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Samples | Feed ratios of NIPAAm and chitosan | Decomposition temperature | Half decomposition temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| PNIPAAm | - | 327 °C | 394 °C |
| IPN-1 | 4:1 | 386 °C | 416 °C |
| IPN-2 | 2:1 | 389 °C | 424 °C |
| IPN-3 | 4:3 | 393 °C | 429 °C |
| IPN-4 | 1:1 | 390 °C | 427 °C |
| Hydrogel samples | DG/% (Before washing) | DG/% (After five times washing) |
|---|---|---|
| PNIPAAm | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| IPN-1 | 6.3 ± 0.4 | 4.9 ± 0.4 |
| IPN-2 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
| IPN-3 | 7.6 ± 0.6 | 6.1 ± 0.6 |
| IPN-4 | 8.1 ± 0.6 | 6.6 ± 0.6 |
| S. aureus | E. coli | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (Unmodified) cotton fabric (cfu/mL) | 2.47 × 106 | Control (Unmodified) cotton fabric (cfu/mL) | 2.34 × 106 |
| Modified cotton fabric (cfu/mL) | 0.7 × 104 | Modified cotton fabric (cfu/mL) | 1.1 × 104 |
| Bacterial reduction (%) | 99.72 | Bacterial reduction (%) | 99.53 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Hao, X.; Lin, J.; Cheng, D.; Lu, Y. Thermosensitive Behavior and Antibacterial Activity of Cotton Fabric Modified with a Chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogel. Polymers 2016, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040110
Wang B, Wu X, Li J, Hao X, Lin J, Cheng D, Lu Y. Thermosensitive Behavior and Antibacterial Activity of Cotton Fabric Modified with a Chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogel. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Boxiang, Xiaolin Wu, Jia Li, Xu Hao, Jie Lin, Dehong Cheng, and Yanhua Lu. 2016. "Thermosensitive Behavior and Antibacterial Activity of Cotton Fabric Modified with a Chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogel" Polymers 8, no. 4: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040110
APA StyleWang, B., Wu, X., Li, J., Hao, X., Lin, J., Cheng, D., & Lu, Y. (2016). Thermosensitive Behavior and Antibacterial Activity of Cotton Fabric Modified with a Chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogel. Polymers, 8(4), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040110