The Synthesis of Backbone Thermo and pH Responsive Hyperbranched Poly(Bis(N,N-Propyl Acryl Amide))s by RAFT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Synthesis of Hyperbranched Poly(bis(N,N-Propyl Acryl Amide) (HPNPAM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Reaction Mechanism of HPNPAM
3.2. The Parameters of HPMAM, HPNPAM and HPNBAM
3.3. Characterization for HPNPAMs
3.3.1. The Degree of Branching for HPNPAMs
3.3.2. α Value of HPNPAMs
3.3.3. FTIR Analysis of Monomer and Polymer
3.4. Effect of Reaction Conditions on Polymerization
3.4.1. Effect of Reaction Temperature on Polymerization
3.4.2. Effect of Reaction Time on Polymerization
3.4.3. Effect of CTA’s Concentration on Polymerization
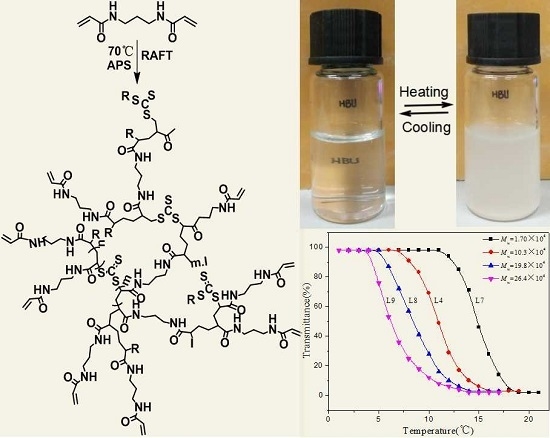
3.5. Temperature Response Performance of HPNPAMs
3.6. pH Response Performance of HPNPAMs
3.7. DLS and SEM Analysis
3.8. Cytotoxicity Test of HPNPAM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saravanakumar, G.; Kim, W.J. Intracellular Delivery; Spinger Netherlands: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 55–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Kotsuchibashi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Narain, R. Temperature-responsive hyperbranched amine-based polymers for solid-liquid separation. Langmur 2014, 30, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; Yan, D.Y. Supramolecular self-assembly and controllable drug release of thermosensitive hyperbranched multiarm copolymers. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.K.; Jiang, G.H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.Z. Synthesis and drug release properties of novel pH- and temperature-sensitive copolymers based on a hyperbranched polyether core. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 289, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Su, Y.; Wu, J.L.; Zhu, L.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yan, D.Y.; Zhu, B.S. Design and synthesis of thermo-responsive hyperbranched poly(amine-ester)s as acid-sensitive drug carriers. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Chen, Y. Preparation and characterization of novel thermoresponsive gold nanoparticles and their responsive catalysis properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.Z.; Han, M.C.; Cao, Y.H.; Ling, C.X.; Zhang, Y.Y. Temperature- and pH-responsive unimolecular micelles with a hydrophobic hyperbranched core. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xia, J.L.; Tian, H.Y.; Tang, Z.H.; He, C.L.; Chen, X.S. Thermo-/pH-dual responsive properties of hyperbranched polyethylenimine grafted by phenylalanine. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, L.P.; He, C.B.; Lu, X.H. Temperature and pH dual-responsive behavior of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based star-block copolymer with poly(acrylic acid-block-N-isopropylacrylamide) as arms. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.Z.; Hu, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ling, C.X.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.S. Synthesis of thermoresponsive unimolecular polymeric micelles with a hydrophilic hyperbranched poly(glycidol) core. Polym. J. 2011, 43, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z. Thermoresponsive hyperbranched polyethylenimines with isobutyramide functional groups. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.W.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.F.; Yan, D.Y. Terminal modification with 1-adamantylamine to endow hyperbranched polyamidoamine with thermo-/pH-responsive properties. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, C.; Yoshimura, K.; Harada, A.; Sakanishi, Y.; Kono, K. Synthesis and characterization of hyperbranched poly(glycidol) modified with pH- and temperature-sensitive groups. Bioconj. Chem. 2009, 20, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.F.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yan, D.Y. Backbone-thermoresponsive hyperbranched polyethers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8144–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Jia, Z.F.; Yan, D.Y.; Zhu, X.Y. Thermo-responsive highly branched polyethers by proton-transfer polymerization of 1,2,7,8-diepoxyoctane and multiols. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2007, 208, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.F.; Li, G.L.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, D.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.L.; Tu, C.L.; Sun, J. Hybrid polymerization of vinyl and hetero-ring groups of glycidyl methacrylate resulting in thermoresponsive hyperbranched polymers displaying a wide range of lower critical solution temperatures. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 7593–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, D.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y.; Yan, D.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhu, B.S. Synthesis of backbone thermo and pH dual-responsive hyperbranched poly(amine-ether)s through proton-transfer polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, D.L.; Deng, H.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yan, D.Y.; Zhu, B.S.; Zhu, X.Y. Backbone-thermoresponsive hyperbranched polyglycerol by random copolymerization of glycidol and 3-methyl-3-(hydroxymethyl)oxetane. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, R.; Sherrington, D.C. Synthesis of highly branched poly(methyl methacrylate)s using the “strathclyde methodology” in aqueous emulsion. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Li, G.; Bai, L.B.; Li, W.L.; Wang, S.J.; Ba, X.W.; Zhou, G.Q.; Zhao, H.C. Synthesis backbone-dual-responsive of hyperbranched poly(bis(N,N-ethyl acrylamide))s by RAFT. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, L.; Cameron, N.R. RAFT polymerization of methyl 6-O-Methacryloyl-α-d-glucoside in homogeneous aqueous medium. A detailed kinetic study at the low molecular weight limit of the process. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 6082–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Yan, D.Y.; Dong, W.Y.; Tian, Y. Temperature-responsive phase transition of polymer vesicles: Real-time morphology observation and molecular mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













| Samples | Monomer:CTA:I (mmol) | Temperature | Mw (× 104) | Mw/Mn | Conversion | α | DB | LCST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-a | 20:1:1 | 70 °C | 5.6 | 2.14 | 60% | 0.43 | 70% | - |
| L-b | 20:1:1 | 70 °C | 3.5 | 2.08 | 48% | - | 60% | - |
| L-c | 20:1:1 | 70 °C | 4.7 | 2.21 | 53% | 0.32 | 74% | 13 °C |
| Samples | Temperature | Mw (× 104) | Mw/Mn | Conversion | α | DB | LCST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 40 °C | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| L2 | 50 °C | 1.4 | 2.52 | 41% | 0.44 | 55% | 15 °C |
| L3 | 70 °C | 4.7 | 2.21 | 53% | 0.31 | 74% | 13 °C |
| L4 | 80 °C | 10.3 | 1.97 | 74% | 0.29 | 83% | 11 °C |
| L5 | 90 °C | 25.7 | 2.72 | 89% | 0.22 | 88% | 9 °C |
| L6 | 120 °C | gel | – | – | – | – | – |
| Samples | Time | Mw (× 104) | Mw/Mn | Conversion | α | DB | LCST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L7 | 24 h | 1.7 | 1.85 | 61% | 0.33 | 66% | 15 °C |
| L4 | 48 h | 10.3 | 1.97 | 74% | 0.29 | 83% | 11 °C |
| L8 | 72 h | 19.8 | 2.43 | 79% | 0.27 | 85% | 8 °C |
| L9 | 96 h | 26,4 | 2.98 | 83% | 0.22 | 89% | 6 °C |
| Samples | Monomer:CTA:I (mmol) | Mw (× 104) | Mw/Mn | Conversion | α | DB | LCST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L10 | 20:0.5:1 | 14.4 | 2.68 | 86% | 0.33 | 72% | 7 °C |
| L4 | 20:1:1 | 10,3 | 1.97 | 74% | 0.29 | 83% | 11 °C |
| L11 | 20:2:1 | 6.9 | 1.71 | 69% | 0.27 | 86% | 14 °C |
| L12 | 20:3:1 | 1.3 | 1.54 | 43% | 0.20 | 90% | 17 °C |
| L13 | 20:4:1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Samples | Mw (× 104) | Mw/Mn | Conversion | α | DB | LCST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L7 | 1.7 | 1.85 | 61% | 0.43 | 66% | 15 °C |
| L2 | 1.4 | 2.52 | 41% | 0.44 | 55% | 15 °C |
| L12 | 1.3 | 1.54 | 43% | 0.20 | 90% | 17 °C |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Zhang, D.; Bai, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ba, X. The Synthesis of Backbone Thermo and pH Responsive Hyperbranched Poly(Bis(N,N-Propyl Acryl Amide))s by RAFT. Polymers 2016, 8, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040135
Zhou S, Zhang D, Bai L, Zhao J, Wu Y, Zhao H, Ba X. The Synthesis of Backbone Thermo and pH Responsive Hyperbranched Poly(Bis(N,N-Propyl Acryl Amide))s by RAFT. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040135
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shijiao, Dongxin Zhang, Libin Bai, Jing Zhao, Yonggang Wu, Hongchi Zhao, and Xinwu Ba. 2016. "The Synthesis of Backbone Thermo and pH Responsive Hyperbranched Poly(Bis(N,N-Propyl Acryl Amide))s by RAFT" Polymers 8, no. 4: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040135
APA StyleZhou, S., Zhang, D., Bai, L., Zhao, J., Wu, Y., Zhao, H., & Ba, X. (2016). The Synthesis of Backbone Thermo and pH Responsive Hyperbranched Poly(Bis(N,N-Propyl Acryl Amide))s by RAFT. Polymers, 8(4), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040135