Smart Homopolymer Microgels: Influence of the Monomer Structure on the Particle Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of the Homopolymer Microgels
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.5. Light Scattering
2.5.1. Photon Correlation Spectroscopy
2.5.2. Static Light Scattering
2.6. Turbidity Measurements
2.7. Fluorescence Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
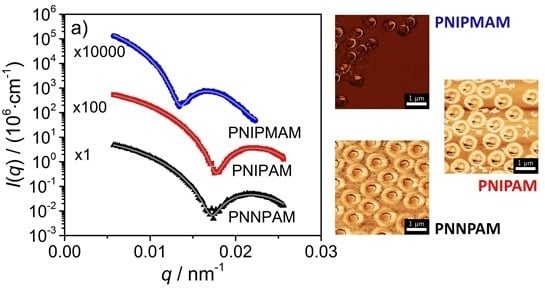
3.1. Imaging Techniques
3.2. Static Light Scattering (SLS)
3.3. Swelling Behavior
3.3.1. Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (PCS)
3.3.2. Turbidity Measurements
3.3.3. Fluorescence Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelton, R. Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2000, 85, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtering, W.; Saunders, B.R. Gel architectures and their complexity. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3695–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pich, A.; Richtering, W. Polymer nanogels and microgels. Polym. Sci. A Compr. Ref. 2012, 6, 309–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hellweg, T. Responsive core-shell microgels: Synthesis, characterization, and possible applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 14, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, C.; Fleige, E.; Vogtt, K.; Szekely, N.; Lindner, P.; Burchard, W.; Haag, R.; Ballauff, M. The multi-domain nanoparticle structure of a universal core-multi-shell nanocarrier. Polymer 2014, 55, 6735–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertle, Y.; Hellweg, T. Thermoresponsive copolymer microgels. J. Mate. Chem. B 2013, 43, 5874–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.; Pelton, R. Highly pH and temperature responsive microgels functionalized with vinylacetic acid. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.; Ramos, J.; Vincent, B. Equilibrium and kinetic aspects of the uptake of poly(etylene oxide) by copolymer microgel particles of N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.; Lyon, L. Soft nanotechnology with soft nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7686–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellert, S.; Richter, M.; Hellweg, T.; von Klitzing, R.; Hertle, Y. Responsive microgels at surfaces and interfaces. Z. Phys. Chem. 2014, 229, 1125–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Ballauff, M.; Drechsler, M. Thermoresponsive core-shell particles as carrier systems for metallic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3930–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballauff, M.; Lu, Y. ”Smart” nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and applications. Polymer 2007, 48, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M. Thermosensitive core-shell microgels: From colloidal model systems to nanoreactors. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 767–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pich, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Lu, Y.; Boyko, V.; Adler, H.J.P. Temperature-sensitive hybrid microgels with magnetic properties. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10706–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.P.B.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, L.; Ho, K.M.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M.; Li, P. Facile synthesis of gold/polymer nanocomposite particles using polymeric amine-based particles as dual reductants and templates. Polymer 2015, 76, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellweg, T.; Kratz, K.; Pouget, S.; Eimer, W. Internal dynamics in colloidal PNIPAM microgel particles immobilised in a mesoscopic crystal. Colloids Surf. A 2002, 202, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Richtering, W. Influence of polymerization conditions on the structure of temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duracher, D.; Elaïssari, A.; Pichot, C. Preparation of poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) latexes kinetic studies and characterization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1999, 37, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, M.; Freudensprung, I.; Hellweg, T. Linearly thermoresponsive core-shell microgels: Towards a new class of nanoactuators. Polymer 2012, 53, 6096–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, B.; Zeiser, M.; Hellweg, T. Non NIPAM based smart microgels: Systematic variation of the volume phase transition temperature by copolymerization. Z. Phys. Chem. 2012, 226, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Nakamura, K.; Kamikubo, T.; Ishii, S.; Tani, K.; Mori, T.; Sato, T. Hydrogen-bond-assisted syndiotactic-specific radical polymerizations of N-alkylacrylamides: The effect of the N-substituents on the stereospecificities and unusual large hysteresis in the phase-transition behavior of aqueous solution of syndiotactic poly(N-n-propylacrylamide). J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 4575–4583. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, W. The Evolution of Silicon Wafer Cleaning Technology. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W. ImageJ 1.50b; National Institute of Health: Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Available online: http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- Provencher, S.W. A constrained regularization method for inverting data represented by linear algebraic or integral equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. Contin: A general purpose constrained regularization program for inverting noisy linear algebraic and integral equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, D.E. Analysis of macromolecular polydispersity in intensity correlation spectroscopy: The method of cumulants. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 4814–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, P.; Kulshreshtha, S. Modification to the cumulant analysis of polydispersity in quasielastic light scattering data. J. Polym. Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.H.; Urquidi, J.; Singh, S.; Robinson, G.W. Thermal offset viscosities of liquid H2O, D2O, and T2O. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, B.J.; Pecora, R. Dynamic light scattering; John Wiley & sons, Inc.: Mineola, New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Reufer, M.; Díaz-Leyva, P.; Lynch, I.; Scheffold, F. Temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropyl-acrylamide) microgel particles: A light scattering study. Eur. Phys. J. E. Soft Matter 2009, 28, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndt, I.; Richtering, W. Doubly temperature sensitive core-shell microgels. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 8780–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, B.; Hu, Z. Phase behavior of thermally responsive microgel colloids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 408304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, N.C.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Snowden, M.J.; Leharne, S.A.; Griffiths, P.C.; Winnington, A.L. Calorimetric investigation of the influence of cross-linker concentration on the volume phase transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) colloidal microgels. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3202–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillermo, A.; Addad, J.P.C.; Bazile, J.P.; Duracher, D.; Elaïssari, A.; Pichot, C. NMR investigations into heterogeneous structures of thermosensitive microgel particles. J. Polym. Sci.: Part B: Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, H.; Richtering, W. Influence of cross-linker density on rheological properties of temperature-sensitive microgel suspensions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2000, 278, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pelton, R.H.; Hamielec, A.E.; Woods, D.R.; McPhee, W. The kinetics of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex formation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1994, 272, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pelton, R. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels at the air-water interface. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8032–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magonov, S.; Elings, V.; Whangbo, M.H. Phase imaging and stiffness in tapping-mode atomic force microscopy. Surf. Sci. Lett. 1997, 375, L385–L391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. The incidence of light upon a transparent sphere of dimensions comparable with the wavelength. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A; 1910; 84, pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, G.R.; Alsted, T.; Richtering, W.; Pedersen, J.S. Synthesis and characterization of nanogels of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) by a combination of light and small-angle X-ray scattering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3108–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndt, I. Structure of Multi-Temperature Sensitive Core-Shell Microgels. Ph.D. Thesis, Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, Kiel, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, M.; Kokufuta, E. On the temperature-responsive polymers and gels based on N-propylacrylamides and N-propylmethacrylamides. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8649–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inomata, H.; Goto, S.; Saito, S. Phase transition of N-substituted acrylamide gels. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 4887–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Yekta, A.; Winnik, M.A. Surface characterization and dissociation properties of carboxylic acid core-shell latex particle by potentiometric and conductometric titration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 176, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Kubota, K. Thermal response of poly(N-n-propylacrylamide). Polym. J. 1999, 31, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertle, Y.; Zeiser, M.; Hasenöhrl, C.; Busch, P.; Hellweg, T. Responsive p(NIPAM-co-NtBAM) microgels: Flory-Rehner description of the swelling behavior. Coll. Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellweg, T.; Dewhurst, C.D.; Brückner, E.; Kratz, K.; Eimer, W. Colloidal crystals made of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2000, 278, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arleth, L.; Xia, X.; Hjelm, R.P.; Wu, J.; Hu, Z. Volume transition and internal structures of small poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, S.; Au-yeung, S.C.F.; Jiang, S. Volume phase transition of spherical microgel particles. Die Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1996, 240, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.W.; Napper, D.H. Coil-to-globule type transitions and swelling of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly(acrylamide) at latex interfaces in alcohol-water mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 177, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelenmeyer, S.; Deike, I.; Rosenfeldt, S.; Norhausen, C.; Dingenouts, N.; Ballauff, M.; Narayanan, T.; Lindner, P. Small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering studies of the volume phase transition in thermosensitive core-shell colloids. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 10471–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Tsubota, M.; Ikeda, I. Fourier transform IR spectroscopic study on phase transitions of copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and alkyl acrylates in water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2003, 281, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Nessen, K.; Karg, M.; Hellweg, T. Thermoresponsive poly-(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) microgels: Tailoring particle size by interfacial tension control. Polymer 2013, 54, 5499–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Fujishige, S.; Ando, I. Solution properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in water. Polym. J. 1990, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiktopulo, E.I.; Uversky, V.N.; Lushchik, V.B.; Klenin, S.I.; Bychkova, V.E.; Ptitsyn, O.B. “Domain” coil-globule transition in homopolymers. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 7519–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netopilik, M.; Bohdanecky, M.; Chytry, V.; Ulbrich, K. Cloud point of poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) solutions in water: Is it really a point? Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1997, 18, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Kubota, K. Solution properties and thermal behavior of poly(N-n-propylacrylamide) in water. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7828–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancik, A.L.; Brauns, E.B. A simple asymmetric lineshape for fitting infrared absorption spectra. Vib. Spectrosc. 2008, 47, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Iwai, K. Thermo-responsive behavior and microenvironments of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles as studied by fluorescent label method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanasundaram, K.; Thomas, J.K. Environmental effects on vibronic band intensities in pyrene monomer fluorescence and their application in studies of micellar systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 2039–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankasem, S.; Thomas, J.K.; Snowden, M.J.; Vincent, B. Photophysical studies of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel structures. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3023–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, N.; Gardebrecht, S.; Swanson, L. Fluorescence investigations of “smart” microgel systems. J. Fluoresc. 1998, 8, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, C.; Vollrath, A.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. A fluorescent thermometer based on a pyrene-labeled thermoresponsive polymer. Sensors 2010, 10, 7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hara, K.; Ware, W.R. Influence of solvent perturbation on the radiative transition probability from the 1B1u state of pyrene. Chem. Phys. 1980, 51, 6–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnik, F.M.; Ringsdorf, H.; Venzmer, J. Interactions of surfactants with hydrophobically-modified poly(N-isopropylacrylamides). 1. Fluorescence probe studies. Langmuir 1991, 7, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Microgel | /nm | /nm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NNPAM | 467 ± 83 | 790 ± 71 | 0.59 |
| NIPAM | 461 ± 90 | 776 ± 79 | 0.59 |
| NIPMAM | 769 ± 90 | 786 ± 89 | 0.98 |
| Microgel | /nm | /% | σ/nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NNPAM | 1.73 | 300 | 5.2 | 20 |
| NIPAM | 1.77 | 284 | 6.8 | 16 |
| NIPMAM | 1.35 | 464 | 5.6 | 67 |
| Microgel | /nm | /nm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NNPAM | |||
| NIPAM | |||
| NIPMAM |
| Microgel | VPTT/C | /C |
|---|---|---|
| NNPAM | 22.1 ± 0.1 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| NIPAM | 33.0 ± 0.1 | 3.12 ± 0.01 |
| NIPMAM | 43.2 ± 0.1 | 2.70 ± 0.01 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wedel, B.; Hertle, Y.; Wrede, O.; Bookhold, J.; Hellweg, T. Smart Homopolymer Microgels: Influence of the Monomer Structure on the Particle Properties. Polymers 2016, 8, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040162
Wedel B, Hertle Y, Wrede O, Bookhold J, Hellweg T. Smart Homopolymer Microgels: Influence of the Monomer Structure on the Particle Properties. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040162
Chicago/Turabian StyleWedel, Bastian, Yvonne Hertle, Oliver Wrede, Johannes Bookhold, and Thomas Hellweg. 2016. "Smart Homopolymer Microgels: Influence of the Monomer Structure on the Particle Properties" Polymers 8, no. 4: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040162
APA StyleWedel, B., Hertle, Y., Wrede, O., Bookhold, J., & Hellweg, T. (2016). Smart Homopolymer Microgels: Influence of the Monomer Structure on the Particle Properties. Polymers, 8(4), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040162