Silane Cross-Linked Sulfonted Poly(Ether Ketone/Ether Benzimidazole)s for Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
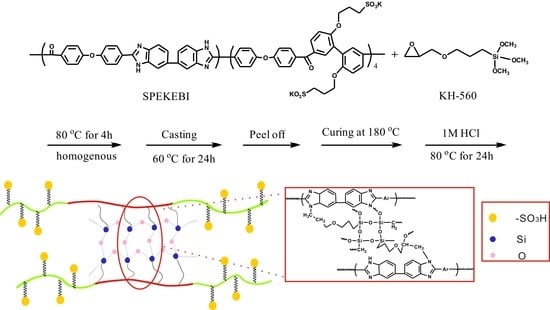
2.2. Synthesis of SPEKEBI Polymer
2.3. Preparation of the SPEKEBI-x-SiO2 Membranes
2.4. Characterization and Measurements
2.4.1. Instruments Characterization
2.4.2. Water Uptake and Swelling Ratio Measurements
2.4.3. Ion Exchange Capacity and Oxidative Stability
2.4.4. Membrane-Electrode Assembly and Single Fuel Cell Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of SPEKEBI-x-SiO2
3.2. Thermal Stability
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Oxidative Stability
3.5. Ion Exchange Capacity, Water Uptake and Swelling Ratio
3.6. Proton Conductivity
3.7. Methanol Permeability and Selectivity
3.8. Single Fuel Cell Performance
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ran, J.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Guiver, M.D.; Jiang, Z. Nanostructured ion-exchange membranes for fuel cells: Recent advances and perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5280–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B. Water soluble polymers as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Polymers 2012, 4, 913–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, B.; Jannasch, P. Proton-conducting aromatic polymers carrying hypersulfonated side chains for fuel cell applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Guiver, M.D. Ion transport by nanochannels in ion-containing aromatic copolymers. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2175–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Fu, Y.; Manthiram, A. Novel blend membranes based on acid-base interactions for fuel cells. Polymers 2012, 4, 1627–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Ying, L.; Fang, J.; Du, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Guo, X.; Yin, J. Preparation of covalently cross-linked sulfonated polybenzimidazole membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Jana, T.; Modestra, J.A.; Naresh, K.A.; Mohan, S.V. Highly efficient sulfonated polybenzimidazole as a proton exchange membrane for microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 317, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.; Liu, H.; Lee, M.H. Alternating copolymer of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone-benzimidazole)s (SPEEK-BI) bearing acid and base moieties. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Lee, Y.M.; Guiver, M.D. Densely sulfophenylated segmented copoly(arylene ether sulfone) proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4901–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hong, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, C.; Na, H. Property enhancement effects of side-chain-type naphthalene-based sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) on Nafion composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32227–32236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elabd, Y.A.; Hickner, M.A. Block copolymers for fuel cells. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Yang, H.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Proton-conducting membranes based on side-chain-type sulfonated poly(ether ketone/ether benzimidazole)s via one-pot condensation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 465, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzd, A.S.; Trfimchuk, E.S.; Nikonorova, N.I.; Nesterova, E.A.; Meshkov, I.B.; Gallyamov, M.O.; Khokhlov, A.R. Novel polyolefin/silicon dioxide/H3PO4 composite membranes with spatially heterogeneous structure for phosphoric acid fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4132–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Chakrabarty, T.; Shahi, V.K. Highly charged and stable cross-linked 4,4′-bis(4-aminophenoxy)biphenyl-3,3′-disulfonic acid (BAPBDS)-sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) polymer electrolyte membranes impervious to methanol. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8036–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Cai, Y.B.; Xu, S. Phosphoric acid-doped cross-linked sulfonated poly(imide-benzimidazole) for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 501, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Ma, W.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Na, H. Silane-cross-linked polybenzimidazole with improved conductivity for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Geng, L.; Fu, Y.; Dai, X.; Qi, B.; Lv, C. In situ sol-gel route to novel sulfonated polyimide SiO2 hybrid proton-exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Shao, K.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Lin, H.; Li, M.; Na, H. Hybrid proton conducting membranes based on sulfonated cross-linked polysiloxane network for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5803–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.C.; Meyer, M.; Sabine, D.V.; Habas, J.P.; Clément, S.; Naoufal, D.; Mehdi, A. A facile synthesis of proton-conducting organic-inorganic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabu, H.; Matsui, J.; Hara, M.; Nagano, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Nagao, Y. Proton conductivities of lamellae-forming bioinspired block copolymer thin films containing silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 9484–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.P.; Shukla, G.; Manohar, M.; Shahi, V.K. Graphene oxide based nanohybrid proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications: An overview. Adv. Colloid Interface 2017, 240, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ublekov, F.; Penchev, H.; Georgiev, V.; Radev, I.; Sinigersky, V. Protonated montmorillonite as a highly effective proton-conductivity enhancer in p-PBI membranes for PEM fuel cells. Mater. Lett. 2014, 135, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced proton conductivity of proton exchange membranes by incorporating sulfonated metal-organic frameworks. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Novel aromatic proton-exchange polyelectrolytes via polyacylation of pre-sulfonated monomers. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13996–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, L.A.; Parbhoo, B.; Leadley, S.R. Development of a methodology for XPS curve-fitting of the Si 2p core level of siloxane materials. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Song, M.; Yi, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M. A Durable alternative for proton-exchange membranes: Sulfonated poly(benzoxazole thioether sulfone)s. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, P.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Parnian, M.J. Study of hydrogen crossover and proton conductivity of self-humidifying nanocomposite proton exchange membrane based on sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone). Energy 2016, 94, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, J.; Kou, P. Poly(oxyalkylene) diamine-functionalized carbon nanotube/perfluorosulfonated polymer composites: Synthesis, water state, and conductivity. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5756–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhao, C.; Ma, W.; Shao, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Na, H. Novel hybrid polymer electrolyte membranes prepared by a silane-cross-linking technique for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, C.H.; Woo, J.J.; Wu, D.; Yun, S.H.; Seo, S.J.; Xu, T.W.; Moon, S.H. Hydrogen bonding: A channel for protons to transfer through acid-base pairs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 12265–12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Huang, C.H.; Woo, J.J.; Wu, D.; Yun, S.H.; Seo, S.J.; Xu, T.W.; Moon, S.H. Modifying a proton conductive membrane by embedding a “barrier”. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 13121–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Membranes | IEC | Water Uptake (%) | Swelling Ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoratical | Practical | 30 °C | 80 °C | 30 °C | 80 °C | |
| SPEKEBI-2.5-SiO2 | 2.30 | 2.21 | 42.8 | 159.2 | 8.9 | 44.8 |
| SPEKEBI-5.0-SiO2 | 2.24 | 2.09 | 37.7 | 128.0 | 6.4 | 31.8 |
| SPEKEBI-7.5-SiO2 | 2.18 | 1.99 | 37.0 | 118.9 | 5.0 | 29.0 |
| SPEKEBI-10-SiO2 | 2.12 | 1.82 | 30.8 | 106.3 | 4.8 | 28.6 |
| Membranes | б (mS cm−1) | PMeOH | Selectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 80 °C | (×10−7 cm2 s−1) | (×10−4 S s cm−3) | |
| SPEKEBI | 136 | 233 | 8.62 | 15.8 |
| SPEKEBI-2.5-SiO2 | 131 | 204 | 7.91 | 16.6 |
| SPEKEBI-5.0-SiO2 | 118 | 231 | 6.54 | 18.0 |
| SPEKEBI-7.5-SiO2 | 129 | 244 | 5.81 | 22.2 |
| SPEKEBI-10-SiO2 | 83 | 153 | 4.22 | 19.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Z.; Cui, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Silane Cross-Linked Sulfonted Poly(Ether Ketone/Ether Benzimidazole)s for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120631
Yao Z, Cui M, Zhang Z, Wu L, Xu T. Silane Cross-Linked Sulfonted Poly(Ether Ketone/Ether Benzimidazole)s for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120631
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Zilu, Mengbing Cui, Zhenghui Zhang, Liang Wu, and Tongwen Xu. 2017. "Silane Cross-Linked Sulfonted Poly(Ether Ketone/Ether Benzimidazole)s for Fuel Cell Applications" Polymers 9, no. 12: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120631
APA StyleYao, Z., Cui, M., Zhang, Z., Wu, L., & Xu, T. (2017). Silane Cross-Linked Sulfonted Poly(Ether Ketone/Ether Benzimidazole)s for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers, 9(12), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120631