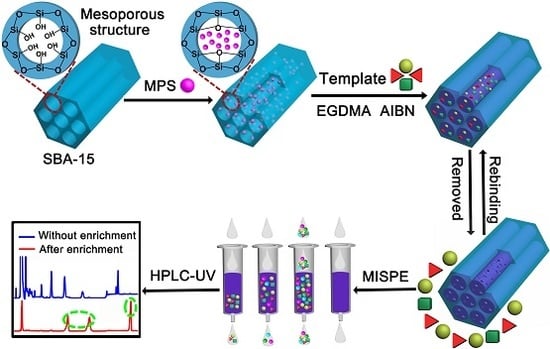
The Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on SBA-15 for Selective Separation and Determination of Panax notoginseng Saponins Simultaneously in Biological Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of SBA-15 Support and Modified SBA-15
2.3.1. Synthesis of SBA-15 Substrate
2.3.2. Preparation of Vinyl Modified SBA-15
2.4. Imprinting at the Surface of Modified SBA-15
2.5. Evaluation of the Binding Ability of SBA-15@MT-MIPs
2.6. Separation and Determination of Rb1, Rg1 and R1 in Real Samples
2.6.1. Preparation of Plasma Samples
2.6.2. Enrichment of Rb1, Rg1 and R1 from Plasma Samples by MISPE
2.6.3. Chromatographic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Optimization of Preparation Conditions of SBA-15@MT-MIPs
3.2. Characterization of SBA-15@MT-MIPs
3.3. Investigation on the Performance of SBA-15@MT-MIPs
3.3.1. Study of Binding Properties
3.3.2. Molecular Selectivity of the SBA-15@MT-MIPs
3.3.3. Reusability of SBA-15@MT-MIPs
3.4. Separation and Determination of Rb1, Rg1 and R1 in Real Samples
3.4.1. Optimization of the MISPE Protocols
3.4.2. Validation Assay
3.4.3. Application to the Determination of Trace Rb1, Rg1 and R1 in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yao, C.; Qiu, S.; Chen, M.; Pan, H.; Shi, X.; Wu, W.; Guo, D. Method development and application of offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry-fast data directed analysis for comprehensive characterization of the saponins from Xueshuantong Injection. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2016, 128, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.L.; Yang, W.Z.; Wu, W.Y.; Da, J.; Hou, J.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jin, Y.; Yang, M.; Jiang, B.H.; et al. Simultaneous quantitation of five Panax notoginseng saponins by multi heart-cutting two-dimensional liquid chromatography: Method development and application to the quality control of eight Notoginseng containing Chinese patent medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1402, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Xia, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Shi, M. Ginsenoside Rd is efficacious against acute ischemic stroke by suppressing microglial proteasome-mediated inflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Sun, G.; Luo, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Ai, Q.; Xing, N.; Sun, X. Cardioprotective effects of Notoginsenoside R1 against ischemia/reperfusion injuries by regulating oxidative stress-and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21730–21744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Wong, C.K.C.; Lai, H.C.; Wong, A.S.T. Ginsenoside-Rb1 targets chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer stem cells via simultaneous inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25897–25914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhang, H.; Cao, D.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Panax notoginseng saponins promote endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and attenuate atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Tang, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Ma, X.; Xiang, J. Antioxidative effects of Panax notoginseng saponins in brain cells. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Qu, H. Optimization of a chromatographic process for the purification of saponins in Panax notoginseng extract using a design space approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Qiao, C.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Zhao, J.; Cui, X.M.; Zhang, Q.W.; Liu, X.M.; Hu, D.J. A novel strategy with standardized reference extract qualification and single compound quantitative evaluation for quality control of Panax notoginseng used as a functional food. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1313, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, B.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, W. Cadmium accumulation in Panax notoginseng: Levels, affecting factors and the non-carcinogenic health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Guo, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; Kou, Z.; Sui, F.; Li, C.; Tang, L.; Wang, J. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH Chen: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 188, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Dong, R.; Tan, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.; Ren, X. Compatible stability study of Panax notoginseng saponin injection (Xueshuantong®) in combination with 47 different injectables. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Q.; Qu, H.; Cheng, Y. Simultaneously determination of five ginsenosides in rabbit plasma using solid-phase extraction and HPLC/MS technique after intravenous administration of ‘SHENMAI’ injection. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2007, 44, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z. Comparative study on volatile oils of four Panax genus species in southeast Asia by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ye, S.; Cheng, Y. Separation and on-line concentration of saponins from Panax notoginseng by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1109, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, C.; Shoyama, Y.; Hiroyuki, T. Pharmacokinetic study of ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 in rat by ELISA using anti-ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 monoclonal antibodies. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2006, 34, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Hu, Y.; Fang, G.; Yang, G.; Xu, Z.; Dou, L.; Chen, Z.; Fan, G. Recent developments in the field of the determination of constituents of TCMs in body fluids of animals and human. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2014, 87, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubhakar, A.; Kozak, R.P.; Reiding, K.R.; Royle, L.; Spencer, D.I.R.; Fernandes, D.L.; Wuhrer, M. Automated high-throughput permethylation for glycosylation analysis of biologics using MALDI-TOF-MS. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8562–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Peng, G. A convenient method for the determination of molecular weight cut-off of ultrafiltration membranes. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harstad, R.K.; Bowser, M.T. High-speed microdialysis-capillary electrophoresis assays for measuring branched chain amino acid uptake in 3T3-L1 cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8115–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, L.; Erny, G.L.; Santos, L.; Alves, A. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymers to the analysis and removal of personal care products: A review. Talanta 2016, 146, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and their advances toward industrial use: A review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing-synthesis, characterisation and application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cang, H.; Jin, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical sensor for 2,4-dichlorophenol determination. Polymers 2016, 8, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.A.; Rahman, S.K.A.; Hussein, M.Z.; Ibrahim, N.A. Preparation and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymer as SPE sorbent for melamine isolation. Polymers 2013, 5, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Huang, C.; Shinde, S.; Jagadeesan, K.K.; Ekstrom, S.; Fritz, E.; Sellergren, B. Catalytic formation of disulfide bonds in peptides by molecularly imprinted microgels at oil/water interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2016, 8, 30484–30491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Cai, K. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitated drug delivery via cascade pH stimuli in tumor microenvironment for tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Meng, X.; Lv, Y.; Bian, Z.; Xin, Z. Effect of impregnation solvent on Ni dispersion and catalytic properties of Ni/SBA-15 for CO methanation reaction. Fuel 2016, 165, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, D. TiO2 incorporated in magnetic mesoporous SBA-15 by a facile inner-pore hydrolysis process toward enhanced adsorption-photocatalysis performances for As(III). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Gu, X.; Shi, L.; Hong, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Du, S.; Chen, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers based on SBA-15 for selective solid-phase extraction of baicalein from plasma samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; He, H.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hong, J.; Du, S.; Chen, L.; Yuan, C. Synthesis of surface nano-molecularly imprinted polymers for sensitive baicalin detection from biological samples. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 41377–41384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Liu, D.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Novel magnetic multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers for specific separation and determination of three endocrine disrupting compounds simultaneously in environmental water samples. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56798–56808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Tan, X.; Lei, F. Selective separation and determination of glucocorticoids in cosmetics using dual-template magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and HPLC. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 504, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuis, F.; Pichon, V.; Lanza, F.; Sellergren, S.; Hennion, M.C. Optimization of the class-selective extraction of triazines from aqueous samples using a molecularly imprinted polymer by a comprehensive approach of the retention mechanism. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 999, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Huang, Y. Preparation and characterization of dual-template molecularly imprinted monolith with metal ion as pivot. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 80, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Yang, S.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer for the specific solid-phase extraction of saponins from Panax notoginseng herbal extract. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 11, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mei, X.; Xu, L.; Shen, X.; Zhu, W.; Hong, J.; Zhou, X. Development and application of novel clonazepam molecularly imprinted coatings for stir bar sorptive extraction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Peng, Y.; Du, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecularly imprinted layer-coated monodisperse spherical silica microparticles toward affinity-enrichment of isoflavonoid glycosides from Radix Puerariae. Analyst 2012, 137, 2891–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buszewski, B.; Ricanyova, J.; Gadzala-Kopciuch, R.; Szumski, M. Supramolecular recognition of estrogens via molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Weiss, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted microspheres. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8239–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, S. Synthesis of lab-in-a-pipette-tip extraction using hydrophilic nano-sized dummy molecularly imprinted polymer for purification and analysis of prednisolone. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 480, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; He, J.; Zhou, W.; Gu, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, K.; Yin, X. Innovative method for the enrichment of high-polarity bioactive molecules present at low concentrations in complex matrices. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Mdluli, P.S.; Chimuka, L. Experimental and theoretical study of molecular interactions between 2-vinyl pyridine and acidic pharmaceuticals used as multi-template molecules in molecularly imprinted polymer. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 103, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.Z.; Gu, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Du, S.; Chen, L.; Yuan, C.S. A novel molecularly imprinted method with computational simulation for the affinity isolation and knockout of baicalein fromScutellaria baicalensis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdinia, A.; Ahmadifar, M.; Aziz-Zanjani, M.O.; Jabbari, A.; Hashtroudi, M.S. Selective adsorption of 2,4-dinitrophenol on molecularly imprinted nanocomposites of mesoporous silica SBA-15/polyaniline. Analyst 2012, 137, 4368–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.R.; Chen, J.B.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.Q.; Lu, G.H. Analysis of different parts and tissues of Panax notoginseng by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2014, 34, 634–637. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zhong, G.; Liu, Z.; Meng, M.; Liu, F.; Ni, L. Facile synthesis of novel photoresponsive mesoporous molecularly imprinted polymers for photo-regulated selective separation of bisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, J.; Zhu, H.; Pan, G.; Qiu, F.; Meng, M.; Yao, J.; Yuan, D. Graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymers with double recognition abilities: The combination of covalent boronic acid and traditional non-covalent monomers. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yan, H.; Shen, S.; Bai, L.; Liu, H.; Qiao, F. Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted melamine-urea-formaldehyde monolithic resin prepared in water for selective recognition of plant growth regulators. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 943, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, H.; Su, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, K.; Huang, L. Molecularly imprinted coated graphene oxide solid-phase extraction monolithic capillary column for selective extraction and sensitive determination of phloxine B in coffee bean. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 865, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S. Application of hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymers using K2Ti4O9 coupled with SPE-HPLC for the determination of celecoxib in human urine samples: Optimization by central composite design (CCD). Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3200–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhao, W.; Zhai, M.; Wei, F.; Cai, Z.; Sheng, N.; Hu, Q. Molecularly imprinted layer-coated silica nanoparticles for selective solid-phase extraction of bisphenol a from chemical cleansing and cosmetics samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 658, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, G.; Wei, F.; Yang, J.; Hu, Q. Determination of melamine in powdered milk by molecularly imprinted stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with HPLC. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, R.; Zhou, L.; Xie, L.; Hao, K.; Rao, T.; Wang, Q.; Ye, W.; Fu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Development of a systematic approach to rapid classification and identification of notoginsenosides and metabolites in rat feces based on liquid chromatography coupled triple time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 867, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, N.; Liu, M.; Yang, D.; Huang, Y.; Niu, X.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Ma, G.; Dou, D. Quantitative LC-MS/MS analysis of seven ginsenosides and three aconitum alkaloids in Shen-Fu decoction. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S. Profiling and multivariate statistical analysis of Panax ginseng based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2015, 107, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Polymer | Functional Monomer | Molar Ratio a | Solvents | Q (µmol·g−1) | IF b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-1 | 4-VP | 1:4:16 | ethanol | 75.51 | 1.74 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-2 | MAA | 1:4:16 | ethanol | 81.30 | 1.46 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-3 | AM | 1:4:16 | ethanol | 108.9 | 2.11 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-4 | AM | 1:3:12 | ethanol | 68.71 | 1.02 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-5 | AM | 1:5:20 | ethanol | 93.00 | 2.03 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-6 | AM | 1:6:24 | ethanol | 94.50 | 2.07 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-7 | AM | 1:4:16 | tetrahydrofuran | 31.57 | 1.82 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs-8 | AM | 1:4:16 | ethanol-acetonitrile (2:3) | 93.22 | 1.04 |
| Sample | SBET (m2·g−1) | VT (cm3·g−1) | DP (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | 631.7 | 1.128 | 68.79 |
| SBA-15-MPS | 436.9 | 0.7433 | 64.52 |
| SBA-15@MT-MIPs | 140.2 | 0.1018 | 34.28 |
| Compounds | Linear Range (ng·mL−1) | R2 | LOD (ng·mL−1) | LOQ (ng·mL−1) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 2.3–19.8 | 0.996 | 0.63 | 2.1 | 2.5 |
| Rg1 | 3.7–47.3 | 0.995 | 0.75 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| Rb1 | 3.2–44.5 | 0.995 | 0.69 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
| Compounds | Concentration Taken (ng·mL−1) | Found (ng·mL−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 104.3 | 4.2 |
| 5.0 | 5.1 | 101.4 | 4.0 | |
| 10.0 | 9.9 | 99.0 | 3.8 | |
| Rg1 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 95.0 | 3.7 |
| 8.0 | 7.5 | 93.4 | 3.6 | |
| 16.0 | 15.2 | 95.0 | 3.3 | |
| Rb1 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 94.3 | 3.6 |
| 7.0 | 6.6 | 94.3 | 3.3 | |
| 14.0 | 13.5 | 96.4 | 3.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Yao, D.; Wang, C.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Hou, S.; Chen, L.; Yuan, C.-S. The Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on SBA-15 for Selective Separation and Determination of Panax notoginseng Saponins Simultaneously in Biological Samples. Polymers 2017, 9, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120653
Sun C, Wang J, Huang J, Yao D, Wang C-Z, Zhang L, Hou S, Chen L, Yuan C-S. The Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on SBA-15 for Selective Separation and Determination of Panax notoginseng Saponins Simultaneously in Biological Samples. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120653
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chenghong, Jinhua Wang, Jiaojiao Huang, Dandan Yao, Chong-Zhi Wang, Lei Zhang, Shuying Hou, Lina Chen, and Chun-Su Yuan. 2017. "The Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on SBA-15 for Selective Separation and Determination of Panax notoginseng Saponins Simultaneously in Biological Samples" Polymers 9, no. 12: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120653
APA StyleSun, C., Wang, J., Huang, J., Yao, D., Wang, C. -Z., Zhang, L., Hou, S., Chen, L., & Yuan, C. -S. (2017). The Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on SBA-15 for Selective Separation and Determination of Panax notoginseng Saponins Simultaneously in Biological Samples. Polymers, 9(12), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120653