Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Hydroxyl Groups on Three-Phase Wettability in Oil-Water-Graphite Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
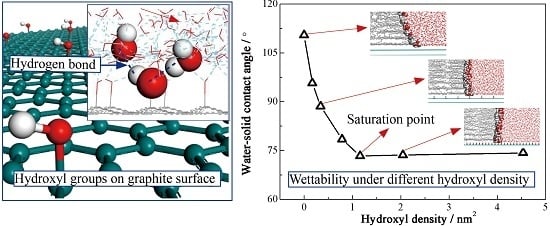
3.1. Molecular Configuration and Microscopic Contact Angle
3.2. Adsorption Properties of Water Molecules
3.3. Number of Hydrogen Bonds
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Lü, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, J.; Huang, X. A review of the recent advances in design of corrugated plate packs applied for oil-water separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 53, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Wei, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired design of a superoleophobic and low adhesive water/solid interface. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Xia, H.; Kim, E.; Sun, H.B. Recent developments in superhydrophobic surfaces with unique structural and functional properties. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11217–11231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D. Superoleophobic and Superhydrophilic Fabric Filters for Rapid Water-Oil Separation. U.S. Patent 8,695,810, 15 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Tu, W.; Wee, K.H.; Bai, R. Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 2, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijke, M.I.J.V.; Sorbie, K.S. The relation between interfacial tensions and wettability in three-phase systems: Consequences for pore occupancy and relative permeability. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2002, 33, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- And, J.R.G.; Kalko, S.G.; Fischbarg, J. Wall−water interface. A molecular dynamics study. Langmuir 1996, 12, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Bai, B. Diffusion of gas molecules on multilayer graphene surfaces: Dependence on the number of graphene layers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 116, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wen, B.; Bai, B. Application of nanoporous graphene membranes in natural gas processing: Molecular simulations of CH4/CO2, CH4/H2S and CH4/N2 separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 138, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Bai, B. Gas diffusion on graphene surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 3894–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.-I.; Lee, Y.-S. The enhanced thermal and mechanical properties of graphite foams with a higher crystallinity and apparent density. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 696, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir, P. Thermal Stability of Fully Lithiated Graphite. In Graphite: Properties, Occurrences and Uses; Campbell, Q.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 299–318. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.S.; Kawai, M.; Akagi, K.; Tsuneyuki, S. Interaction of condensed water molecules with hydroxyl and hydrogen groups on Si(001). Surf. Sci. 2005, 587, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, F.S.; Puddu, V.; Berry, R.J.; Varshney, V.; Patwardhan, S.V.; Perry, C.C.; Heinz, H. Force field and a surface model database for silica to simulate interfacial properties in atomic resolution. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Rahimi, M.; Müller-plathe, F. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Silica Nanoparticle in Oligomeric Poly(methyl methacrylate): A Model System for Studying the Interphase Thickness in a Polymer–Nanocomposite via Different Properties. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 8680–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Kurnia, K.A.; Sousa, F.L.; Silva, N.J.; Silva, J.A.; Coutinho, J.A.; Freire, M.G. Contact angles and wettability of ionic liquids on polar and non-polar surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phy. 2015, 17, 31653. [Google Scholar]
- Verdaguer, A.; Sacha, G.M.; Bluhm, H.; Salmeron, M. Molecular structure of water at interfaces: Wetting at the nanometer scale. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1478–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, M.; Xue, Q.; Jing, N.; Ling, C.; Zhang, T.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, J. Influence of chemical functionalization on the CO2/N2 separation performance of porous graphene membranes. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Maroo, S.C.; Wang, E.N. Wettability of graphene. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.J.; Wang, Q.H.; Lin, S.; Park, K.C.; Jin, Z.; Strano, M.S.; Blankschtein, D. Breakdown in the wetting transparency of graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 176101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werder, T.; Walther, J.H.; Jaffe, R.L.; Halicioglu, T.; Koumoutsakos, P. On the water−carbon interaction for use in molecular dynamics simulations of graphite and carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, M.; Allan, N.L.; Cosgrove, T.; George, N. Wetting of water and water_ethanol droplets on a non-polar surface: A molecular dynamics study. Langmuir 2002, 18, 10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, A.W.; Gast, A.P. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1967; pp. 1–808. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, D.; Zheng, Y.; Rao, D.N. Line tension-based modification of young's equation for rock/oil/brine systems. Soc. Petrol. Eng. 2009, 702–712. [Google Scholar]
- Eslami, H.; Heydari, N. Hydrogen bonding in water nanoconfined between graphene surfaces: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Müller-Plathe, F. Molecular dynamics simulation of water influence on local structure of nanoconfined polyamide-6,6. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9720–9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Heath, J.R. Graphene visualizes the first water adlayers on mica at ambient conditions. Science 2010, 329, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakala, M.; Nygård, K.; Manninen, S.; Huotari, S.; Buslaps, T.; Nilsson, A.; Pettersson, L.G.; Hämäläinen, K. Correlation of hydrogen bond lengths and angles in liquid water based on compton scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Sun, C.; Bai, B. Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Hydroxyl Groups on Three-Phase Wettability in Oil-Water-Graphite Systems. Polymers 2017, 9, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080370
Zheng W, Sun C, Bai B. Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Hydroxyl Groups on Three-Phase Wettability in Oil-Water-Graphite Systems. Polymers. 2017; 9(8):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080370
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Wenxiu, Chengzhen Sun, and Bofeng Bai. 2017. "Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Hydroxyl Groups on Three-Phase Wettability in Oil-Water-Graphite Systems" Polymers 9, no. 8: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080370
APA StyleZheng, W., Sun, C., & Bai, B. (2017). Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Hydroxyl Groups on Three-Phase Wettability in Oil-Water-Graphite Systems. Polymers, 9(8), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080370