Interactive Effects of Biochar, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous on the Symbiotic Performance, Growth, and Nutrient Uptake of Soybean (Glycine max L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Samples
2.2. Biochar Material
2.3. Plant and Bacteria
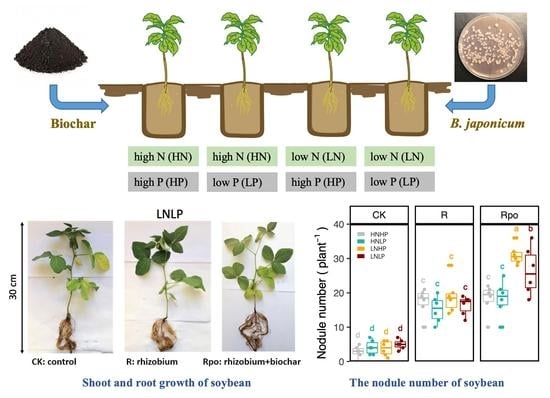
2.4. Pot Experiment
- Uninoculated control plants grown in soil with low N and low P (LNLP) and without biochar;
- Uninoculated control plants grown in soil with high N and low P (HNLP) and without biochar;
- Uninoculated control plants grown in soil with low N and high P (LNHP) and without biochar;
- Uninoculated control plants grown in soil with high N and high P (HNHP) and without biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with LNLP and without biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with HNLP and without biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with LNHP and without biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with HNHP and without biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with LNLP and with biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with HNLP and with biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with LNHP and with biochar;
- Plants inoculated with B. japonicum and grown in soil with HNHP and with biochar.
2.5. Plant and Soil Nutrient Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Biochar and Nutrient Amendments on Soybean Growth
3.2. Effects of Biochar and Nutrients on Plant Nitrogen and Phosphorous Concentrations
3.3. Effects of Biochar and Nutrients on Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorous Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, C.J.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Hipps, N.A. Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: A review. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Lima, I.; Xing, B. Characterization of designer biochar produced at different temperatures and their effects on a loamy sand. Ann. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, O.Y.; Raichle, B.; Sink, S. Impact of biochar on the water holding capacity of loamy sand soil. Intern. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2013, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.Y.; van Zwieten, L.; Meszaros, I.; Downie, A.; Joseph, S. Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Meng, J.; Liang, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Can biochar provide ammonium and nitrate to poor soils? Soil column incubation. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.; Li, Q.; Omari, R.A.; Hou, M.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Effect of biochar and irrigation on the interrelationships among soybean growth, root nodulation, plant p uptake, and soil nutrients in a sandy field. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Effect of biochar and irrigation on soybean-rhizobium symbiotic performance and soil enzymatic activity in field rhizosphere. Agronomy 2019, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Reckling, M.; Wirth, S. Biochar-based inoculum of Bradyrhizobium sp. improves plant growth and yield of lupin (Lupinus albus L.) under drought stress. Eur. J. Soil 2017, 78, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolton, M.; Meller Harel, Y.; Pasternak, Z.; Graber, E.R.; Elad, Y.; Cytryn, E. Impact of biochar application to soil on the root-associated bacterial community structure of fully developed greenhouse pepper plants. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 77, 4924–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelissen, V.; Rutting, T.; Huygen, D.; Staelens, J.; Ruysschaert, G.; Boeckx, P. Maize biochars accelerate short-term soil nitrogen dynamics in a loamy sand soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, F.Z.; Mia, S.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Abuyusuf, M.; Hossain, A.I. Synergistic effects of biochar and npk fertilizer on soybean yield in an alkaline soil. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.; El-Meihy, R.; Ali, M.; Chen, F.; Raleve, D. Interactive effects of biochar and micronutrients on faba bean growth, symbiotic performance, and soil properties. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2017, 180, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Alaylar, B.; Kistaubayeva, A.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Biochar for improving soil biological properties and mitigating salt stress in plants on salt-affected soils. Commun. Plant Soil Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietikäinen, J.; Kiikkila, O.; Fritze, H. Charcoal as a habitat for microbes and its effects on the microbial community of the underlying humus. Oikos 2000, 89, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Yamane, K.; Izumi, Y.; Daimon, H.; Motonaga, T. Continuous application of biochar inoculated with root nodule bacteria to subsoil enhances yield of soybean by the nodulation control using crack fertilization technique. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 18, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Jin, G.; Li, X.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yu, J. Phosphorus and magnesium interactively modulate the elongation and directional growth of primary roots in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3841–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zeng, R.; Liao, H. Improving crop nutrient efficiency through root architecture modifications. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2016, 58, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Jabborova, D.; Wirth, S.; Alam, P.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Interactive effects of nutrients and Bradyrhizobium japonicum on the growth and root architecture of soybean (Glycine max L.). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niste, M.; Vidican, R.; Rotar, I.; Stoian, V.; Pop, R.; Miclea, R. Plant nutrition affected by soil salinity and response of rhizobium regarding the nutrients accumulation. Proenviron. Promediu 2014, 7, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Paliya, S.; Tikle, A.N.; Thomas, T. Efficacy of micronutrients in influencing growth behavior of rhizobium of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L. [Millsp.]). Orient J. Chem. 2014, 30, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Shen, S.H.; Jing, Y.X. Effects of rhizobia inoculation and nitrogen fertilization on photosynthetic physiology of soybean. Photosynthetica 2006, 44, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri-Janagard, M.; Raei, Y.; Gasemi-Golezani, G.; Aliasgarzad, N. Influence of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on soybean yield at different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus. Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2012, 3, 544–549. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, S.; Rosanoff, A.; Yang, G.; Sun, X. Magnesium fertilizer-induced increase of symbiotic microorganisms improves forage growth and quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3253–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.G.; Pérez-Fernández, M.A.; Morcillo, R.J.L.; Kleinert, A.; Hills, P.; Brand, D.J.; Steenkamp, E.T.; Valentine, A.J. Roots and nodules response differently to P starvation in the Mediterranean-type legume Virgilia divaricata. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojon, A.; Nacry, P.; Davidian, J.C. Root uptake regulation: A central process for NPS homeostasis in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egamberdiyeva, D.; Qarshieva, D.; Davranov, K. Growth and yield of soybean inoculated with Bradyrhizobium spp. in calcareous soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 4, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, S.E.; Rojas-Pierce, M.; Yan, X.; Blair, M.W.; Pedraza, F.; Munoz, F.; Tohme, J.; Lynch, J.P. Quantitative trait loci for root architecture traits correlated with phosphorus acquisition in common bean. Crop. Sci. 2006, 46, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, S.; Schulze, J.; Tran, L.P. Comparative analysis of the symbiotic efficiency of Medicago truncatula and Medicago sativa under phosphorus deficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 4, 5198–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, I.; He, L.; Ullah, S.; Quan, Z.; Wei, S.; Iqbal, W.; Munsif, F.; Shah, T.; Xuan, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Biochar addition coupled with nitrogen fertilization impacts on soil quality, crop productivity, and nitrogen uptake under double-cropping system. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.-C.; Guo, W.-Y.; Liang, J.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Hao, X.-Y.; Hou, A.-F.; Zong, X.-X.; Leng, T.-R.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wang, Q.-Y.; et al. Effects of multiple N, P, and K fertilizer combinations on adzuki bean (Vigna angularis) yield in a semi-arid region of northeastern China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majeed, A.; Mehdi, S.M.; Niaz, A.; Mahmood, A.; Haq, E.U.; Ahmad, N.; Javid, S.; Mehmood, A. Influence of P-enriched compost application on economics and P use efficiency of a maize–wheat rotation system. Crop. J. 2018, 6, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Sasaki, Y.; Katahira, M.; Singh, D. Cow Manure application cuts chemical phosphorus fertilizer need in silage rice in Japan. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erro, J.; Urrutia, O.; Baigorri, R.; Fuentes, M.; Zamarreño, A.M.; Garcia-Mina, J.M. Incorporation of humic-derived active molecules into compound NPK granulated fertilizers: Main technical difficulties and potential solutions. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2016, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Ma, H.; Reckling, M.; Jakhongir, A.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Response of soybean to hydrochar-based rhizobium inoculation in loamy sandy soil. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shareef, T.M.E.; Zhao, B.W.; Filonchyk, M. Characterization of biochars derived from maize straw and corn cob and effects of their amendment on maize growth and loess soil properties. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 3678–3686. [Google Scholar]
- Win, M.; Nakasathien, S.; Sarobol, E. Effects of phosphorus on seed oil and protein contents and phosphorus use efficiency in some soybean varieties. Kasetsart J. Nat. Sci. 2010, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yeboah, E.; Gideon, A.; Patrick, O.; Ben, A.; Agyeman, K.O.A. Method of biochar application affects growth, yield and nutrient uptake of cowpea. Open Agric. 2020, 5, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusif, S.A.; Muhammad, I.; Hayatu, N.G.; Sauwa, M.M.; Tafinta, I.Y.; Mohammed, M.A.; Lukman, S.A.; Abubakar, G.A.; Hussain, A.M. Effects of biochar and rhizobium inoculation on nodulation and growth of groundnut in Sokoto State, Nigeria. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Jiang, H.; Tian, J.; Zhao, J.; Liao, H. Rhizobia: Enhance acquisition of phosphorus from different sources by soybean plants. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halwani, M.; Reckling, M.; Egamberdieva, D.; Omari, R.A.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D.; Bachinger, J.; Bloch, R. Soybean nodulation response to cropping interval and inoculation in european cropping systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 638452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Li, L.; Ma, H.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Soil amendment with different maize biochars improves chickpea growth under different moisture levels by improving symbiotic performance with Mesorhizobium ciceri and soil biochemical properties to varying degrees. Front. Microb. 2019, 10, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Kong, L.; Shan, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhang, H.; Xie, F.; Ao, X. Effect of biochar on grain yield and leaf photosynthetic physiology of soybean cultivars with different phosphorus efficiencies. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reibe, K.; Roß, C.L.; Ellmer, F. Hydro-/Biochar application to sandy soils: Impact on yield components and nutrients of spring wheat in pots. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 61, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.M.D.; Babar, A. Impacts of plant growth promoters and plant growth regulators on rainfed agriculture. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Part 2; Agronomy Monographs 9; Page, A.L., Ed.; ASA, SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Dumroese, R.K. Interaction of biochar type and rhizobia inoculation increases the growth and biological nitrogen fixation of Robinia pseudoacacia Seedlings. Forests 2020, 11, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Alidousta, D.; Yng, X.; Isoda, A. Effects of bamboo biochar on soybean root nodulation in multi-elements contaminated soils. Ecotox Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, S.; van Groenigen, J.W.; van de Voorde, T.F.J.; Oram, N.J.; Bezemer, T.M.; Mommer, L.; Jeffery, S. Biochar application rate affects biological nitrogen fixation in red clover conditional on potassium availability. Agricult. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.; Behrendt, U.; Abd-Allah, E.F.; Berg, G. Biochar treatment resulted in a combined effect on soybean growth promotion and a shift in plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quilliam, R.S.; Glanville, H.C.; Wade, S.C.; Jones, D.L. Life in the ‘charosphere’—Does biochar in agricultural soil provide a significant habitat for microorganisms? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Yan, X.; Rubio, G.; Beebe, S.E.; Blair, M.W.; Lynch, J.P. Genetic mapping of basal root gravitropism and phosphorus acquisition efficiency in common bean. Funct. Plant. Biol. 2004, 31, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, S.; Tran, L.S.P. Phosphorus homeostasis in legume nodules as an adaptive strategy to phosphorus deficiency. Plant Sci. 2015, 239, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, G.W. Nutritional constraints on root nodule bacteria affecting symbiotic nitrogen fixation: A review. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2001, 41, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bucio, J.; Hernández-Abreu, E.; Sánchez-Calderón, L.; Nieto-Jacobo, M.F.; Simpson, J.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Phosphate availability alters architecture and causes changes in hormone sensitivity in the Arabidopsis root system. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Duvall, M.; Sohi, S.P. Localisation of nitrate in the rhizosphere of biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, F.; Naveed, M.; Bashir, M.A.; Asif, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Alkahtani, J.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Elshikh, M.S. Formulation of biochar-based phosphorus fertilizer and its impact on both soil properties and chickpea growth performance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Geoderma 2013, 206, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramírez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouas, S.; Labidi, N.; Debez, A.; Abdelly, C. Effect of P on nodule formation and N fixation in bean. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Hedley, M.; Camps Arbestain, M.; Kirschbaum, M.U.F. Can biochar increase the bioavailability of phosphorus? J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 16, 268–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Ro, K.S.; Sun, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Libra, J.A.; Xing, B. New evidence for high sorption capacity of hydrochar for hydrophobic organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13274–13282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Alaylar, B.; Zoghi, Z.; Kistaubayeva, A.; Ma, H.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S. Biochar amendments improve licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fish.) growth and nutrient uptake through altering the root system and soil enzyme activities in loamy sand under salt stress. Plants 2021, 10, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, F.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, K.; Bian, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Drosos, M.; Joseph, S.; Pan, G. Could biochar amendment be a tool to improve soil availability and plant uptake of phosphorus? A meta-analysis of published experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34108–34120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Ajaz, M.M.; Rizwan, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Arshad, M.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, N.; Qureshi, M.A. Effect of biochar and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on growth and phosphorus uptake by maize in an Aridisol. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, L.; Qin, H.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y. Fertilizer nitrogen uptake by rice increased by biochar application. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduah, J.O.; Nartey, E.K.; Abekoe, M.K.; Breuning-Madsen, H.; Andersen, M.N. Phosphorus retention and availability in three contrasting soils amended with rice husk and corn cob biochar at varying pyrolysis temperatures. Geoderma 2019, 341, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.; Kim, H.; Chen, J.; Kim, Y. Effects of biochar addition on nitrogen leaching and soil structure following fertilizer application to rice paddy soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, T.; Cao, T.; Yang, T.; Meng, J.; Chen, W. Effects of biochar application on nitrogen leaching, ammonia volatilization and nitrogen use efficiency in two distinct soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Characteristics | Maize Biochar |
|---|---|
| DM (% FM) | 92.85 |
| Ash (% DM) | 18.42 |
| TOC (% DM) | 75.47 |
| N (% DM) | 1.80 |
| C/N ratio | 41.93 |
| pH value | 9.89 |
| Ca (g (kg DM)−1) | 9.26 |
| Fe (g (kg DM)−1) | 11.40 |
| Mg (g (kg DM)−1) | 4.91 |
| K (g (kg DM)−1) | 32.26 |
| P (g (kg DM)−1) | 5.26 |
| Treatment | Nutrient Concentrations |
|---|---|
| high N and high P (HNHP) | NH4NO3—3000 µmol/L, KH2PO4—250 µmol/L |
| high N and low P (HNLP) | NH4NO3—3000 µmol/L, KH2PO4—50 µmol/L |
| low N and high P (LNHP) | NH4NO3—300 µmol/L, KH2PO4—250 µmol/L |
| low N and low P (LNLP) | NH4NO3—300 µmol/L, KH2PO4—50 µmol/L |
| Interaction Effects | Shoot Biomass | Root Biomass | Nodule Number | Plant N | Plant P | Soil N | Soil P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculation × N supply | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | *** | ns |
| Inoculation × P supply | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| N input × P supply | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ** |
| Inoculation × N supply × P supply | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egamberdieva, D.; Ma, H.; Reckling, M.; Omari, R.A.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Interactive Effects of Biochar, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous on the Symbiotic Performance, Growth, and Nutrient Uptake of Soybean (Glycine max L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010027
Egamberdieva D, Ma H, Reckling M, Omari RA, Wirth S, Bellingrath-Kimura SD. Interactive Effects of Biochar, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous on the Symbiotic Performance, Growth, and Nutrient Uptake of Soybean (Glycine max L.). Agronomy. 2022; 12(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgamberdieva, Dilfuza, Hua Ma, Moritz Reckling, Richard Ansong Omari, Stephan Wirth, and Sonoko D. Bellingrath-Kimura. 2022. "Interactive Effects of Biochar, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous on the Symbiotic Performance, Growth, and Nutrient Uptake of Soybean (Glycine max L.)" Agronomy 12, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010027
APA StyleEgamberdieva, D., Ma, H., Reckling, M., Omari, R. A., Wirth, S., & Bellingrath-Kimura, S. D. (2022). Interactive Effects of Biochar, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous on the Symbiotic Performance, Growth, and Nutrient Uptake of Soybean (Glycine max L.). Agronomy, 12(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010027