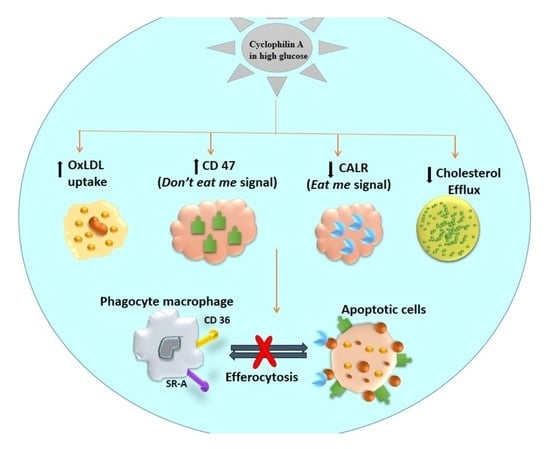
Cyclophilin A Impairs Efferocytosis and Accelerates Atherosclerosis by Overexpressing CD 47 and Down-Regulating Calreticulin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Culture Model
2.2. In Vitro Efferocytosis Assays
2.3. Flow Cytometry Assay
2.4. Confocal Microscopy Assay
2.5. Cholesterol Efflux Culture Assays Using Cholesterol Efflux Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
2.6. In Vitro Silencing of Cyclophilin A Gene
2.7. Gene-Expression Analysis of ABCA1 mRNA by RT-PCR
2.8. Protein Sample Preparation for LC/MS/MS Analysis In Vitro
2.9. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
2.10. Data Analysis and Bioinformatics
2.11. Quantification of CD 47 by Confocal Microscopy
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. In Vivo Study Model
2.14. ORO Staining
2.15. Histological Analysis
2.16. Immunohistochemistry
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Assay
3.1.1. Cyclophilin A Impairs Efferocytosis of Apoptotic Macrophages
3.1.2. Cyclophilin A Reduces Cholesterol Efflux of Macrophages
3.1.3. Cyclophilin A Decreases ABCA1 Expression and ABCA1-mediated Cholesterol Efflux from Macrophage-Derived Foam Cells
3.1.4. CD 47 Is Overexpressed in Cyclophilin A-Primed Macrophages
3.1.5. Cyclophilin A Increases Expression of CD 47 and Reduces Expression of Eat-Me Signal, Calreticulin
3.2. In Vivo Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cyp A | Cyclophilin A |
| CD 47 | Cluster of Differentiation 47 |
| ABCA1-ATP | ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| NG | Normal Glucose |
| HFD | High Fat Diet |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| HG | High Glucose |
| HCASMC | Human coronary artery smooth muscle cells |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NZW | New Zealand White Rabbit |
| CALR | Calreticulin |
| C1QB | Complement C1q B Chain |
| ANXA1 | Annexin-A1 |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
References
- Tian-Tian, Z.; Jun-Feng, Z.; Heng, G. Functions of cyclophilin A in atherosclerosis. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2013, 18, e118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, S.; Vinitha, A.; Kartha, C.C. Cyclophilin A enhances macrophage differentiation and lipid uptake in high glucose conditions: A cellular mechanism for accelerated macro vascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, K.; Nigro, P.; Berk, B.C. Oxidative stress and vascular smooth muscle cell growth: A mechanistic linkage by cyclophilin A. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anandan, V.; Thankayyan Retnabai, S.K.; Jaleel, A.; Thulaseedharan, T.; Mullasari, A.; Pillai, M.R.; Kartha, C.C.; Ramachandran, S. Cyclophilin A induces macrophage apoptosis and enhances atherosclerotic lesions in high-fat diet-fed hyperglycemic rabbits. FASEB BioAdvances 2021, 3, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, K.S.; Lorenz, U. Engulfment of apoptotic cells: Signals for a good meal. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, K.S. Find-me and eat-me signals in apoptotic cell clearance: Progress and conundrums. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Weissman, I.L.; Leeper, N.J. The role of efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2017, 135, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Vré, E.A.; Ait-Oufella, H.; Tedgui, A.; Mallat, Z. Apoptotic cell death and efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, S.; Venugopal, A.; Kutty, V.R.; Vinitha, A.; Divya, G.; Chitrasree, V.; Mullassari, A.; Pratapchandran, N.; Santosh, K.; Pillai, M.R. Plasma level of cyclophilin A is increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and suggests presence of vascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kojima, Y.; Downing, K.; Kundu, R.; Miller, C.; Dewey, F.; Lancero, H.; Raaz, U.; Perisic, L.; Hedin, U.; Schadt, E. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B regulates efferocytosis and atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 124, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinet, W.; Schrijvers, D.M.; De Meyer, G.R. Necrotic cell death in atherosclerosis. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, Y.; Volkmer, J.-P.; McKenna, K.; Civelek, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Miller, C.L.; Direnzo, D.; Nanda, V.; Ye, J.; Connolly, A.J. CD 47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis. Nature 2016, 536, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramji, D.P.; Davies, T.S. Cytokines in atherosclerosis: Key players in all stages of disease and promising therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurdagul Jr, A.; Doran, A.C.; Cai, B.; Fredman, G.; Tabas, I.A. Mechanisms and consequences of defective efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M. Cyclophilin A: A key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.-G.; Melaragno, M.G.; Liao, D.-F.; Yan, C.; Haendeler, J.; Suh, Y.-A.; Lambeth, J.D.; Berk, B.C. Cyclophilin A is a secreted growth factor induced by oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, J.; Jin, Z.-G.; Meoli, D.F.; Matoba, T.; Berk, B.C. Cyclophilin A is secreted by a vesicular pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerterp, M.; Murphy, A.J.; Wang, M.; Pagler, T.A.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Kappus, M.S.; Gorman, D.J.; Nagareddy, P.R.; Zhu, X.; Abramowicz, S. Deficiency of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in macrophages increases inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, J.F.; Lawn, R.M.; Garvin, M.R.; Wade, D.P. ABCA1 is the cAMP-inducible apolipoprotein receptor that mediates cholesterol secretion from macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34508–34511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Silver, D.L.; Costet, P.; Tall, A.R. Specific binding of ApoA-I, enhanced cholesterol efflux, and altered plasma membrane morphology in cells expressing ABC1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33053–33058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Barrera, G.C.; Nakamura, K.; Baldán, Á.; Tarr, P.; Fishbein, M.C.; Frank, J.; Francone, O.L.; Edwards, P.A. ABCG1 has a critical role in mediating cholesterol efflux to HDL and preventing cellular lipid accumulation. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Lan, D.; Chen, W.; Matsuura, F.; Tall, A.R. ATP-binding cassette transporters G1 and G4 mediate cellular cholesterol efflux to high-density lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9774–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khera, A.V.; Cuchel, M.; De La Llera-Moya, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Burke, M.F.; Jafri, K.; French, B.C.; Phillips, J.A.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Wilensky, R.L. Cholesterol efflux capacity, high-density lipoprotein function, and atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohatgi, A.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D.; Givens, E.G.; Ayers, C.R.; Wedin, K.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Rader, D.R.; de Lemos, J.A. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and incident cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shea, S.; Stein, J.H.; Jorgensen, N.W.; McClelland, R.L.; Tascau, L.; Shrager, S.; Heinecke, J.W.; Yvan-Charvet, L.; Tall, A.R. Cholesterol mass efflux capacity, incident cardiovascular disease, and progression of carotid plaque: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Jiang, H.; Song, W.; Riezman, H.; Tontonoz, P.; Weston, T.A.; Guagliardo, P.; Kim, P.H.; Jung, R.; Heizer, P. Cultured macrophages transfer surplus cholesterol into adjacent cells in the absence of serum or high-density lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10476–10483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankman, L.S.; Gomez, D.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Salmon, M.; Alencar, G.F.; Haskins, R.M.; Swiatlowska, P.; Newman, A.A.; Greene, E.S.; Straub, A.C. KLF4-dependent phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells has a key role in atherosclerotic plaque pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vengrenyuk, Y.; Nishi, H.; Long, X.; Ouimet, M.; Savji, N.; Martinez, F.O.; Cassella, C.P.; Moore, K.J.; Ramsey, S.A.; Miano, J.M. Cholesterol loading reprograms the microRNA-143/145–myocardin axis to convert aortic smooth muscle cells to a dysfunctional macrophage-like phenotype. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerterp, M.; Tall, A.R. A new pathway of macrophage cholesterol efflux. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11853–11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.P.; Weissman, I.L.; Majeti, R. The CD 47–SIRPα pathway in cancer immune evasion and potential therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, S.; Jamieson, C.H.; Pang, W.W.; Park, C.Y.; Chao, M.P.; Majeti, R.; Traver, D.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD 47 is upregulated on circulating hematopoietic stem cells and leukemia cells to avoid phagocytosis. Cell 2009, 138, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thorp, E.; Li, G.; Seimon, T.A.; Kuriakose, G.; Ron, D.; Tabas, I. Reduced apoptosis and plaque necrosis in advanced atherosclerotic lesions of Apoe−/− and Ldlr−/− mice lacking CHOP. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Païdassi, H.; Tacnet-Delorme, P.; Verneret, M.; Gaboriaud, C.; Houen, G.; Duus, K.; Ling, W.L.; Arlaud, G.J.; Frachet, P. Investigations on the C1q–calreticulin–phosphatidylserine interactions yield new insights into apoptotic cell recognition. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.; Atreya, C. Identification of simian cyclophilin A as a calreticulin-binding protein in yeast two-hybrid screen and demonstration of cyclophilin A interaction with calreticulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 25, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksh, S.; Burns, K.; Andrin, C.; Michalak, M. Interaction of calreticulin with protein disulfide isomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 31338–31344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anandan, V.; Thulaseedharan, T.; Suresh Kumar, A.; Chandran Latha, K.; Revikumar, A.; Mullasari, A.; Kartha, C.C.; Jaleel, A.; Ramachandran, S. Cyclophilin A Impairs Efferocytosis and Accelerates Atherosclerosis by Overexpressing CD 47 and Down-Regulating Calreticulin. Cells 2021, 10, 3598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123598
Anandan V, Thulaseedharan T, Suresh Kumar A, Chandran Latha K, Revikumar A, Mullasari A, Kartha CC, Jaleel A, Ramachandran S. Cyclophilin A Impairs Efferocytosis and Accelerates Atherosclerosis by Overexpressing CD 47 and Down-Regulating Calreticulin. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123598
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnandan, Vinitha, Thushara Thulaseedharan, Aishwarya Suresh Kumar, Karthika Chandran Latha, Amjesh Revikumar, Ajit Mullasari, Chandrasekharan C. Kartha, Abdul Jaleel, and Surya Ramachandran. 2021. "Cyclophilin A Impairs Efferocytosis and Accelerates Atherosclerosis by Overexpressing CD 47 and Down-Regulating Calreticulin" Cells 10, no. 12: 3598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123598
APA StyleAnandan, V., Thulaseedharan, T., Suresh Kumar, A., Chandran Latha, K., Revikumar, A., Mullasari, A., Kartha, C. C., Jaleel, A., & Ramachandran, S. (2021). Cyclophilin A Impairs Efferocytosis and Accelerates Atherosclerosis by Overexpressing CD 47 and Down-Regulating Calreticulin. Cells, 10(12), 3598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123598