PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Identification of PBK/TOPK
3. General Features of PBK/TOPK
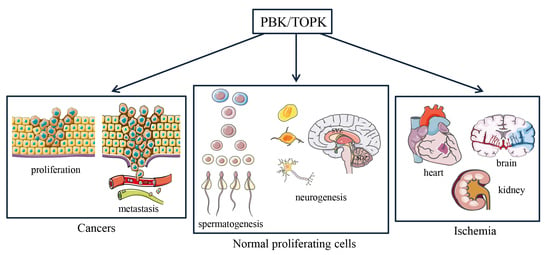
4. PBK/TOPK Function in Mitotic Progression and Tumor Cellular Proliferation
5. PBK/TOPK as Diagnostic/Prognostic Indicator and Therapeutic Targets in Tumors
6. Involvement of PBK/TOPK in Myocardial, Renal and Cerebral Ischemia
7. Research of PBK/TOPK Inhibitors
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abe, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Kito, K.; Ueda, N. Cloning and expression of a novel MAPKK-like protein kinase, lymphokine-activated killer T-cell-originated protein kinase, specifically expressed in the testis and activated lymphoid cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21525–21531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaudet, S.; Branton, D.; Lue, R.A. Characterization of PDZ-binding kinase, a mitotic kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5167–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, Y.; Park, J.H.; Miyamoto, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Kato, T.; Iwasa, A.; Okabe, S.; Imai, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. T-LAK Cell-Originated Protein Kinase (TOPK) as a Prognostic Factor and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 6110–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, C.; Senba, M.; Mori, N. Mitotic kinase PBK/TOPK as a therapeutic target for adult Tcell leukemia/lymphoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herbert, K.J.; Thomas, M.A.; Remko, P.; Giacomo, P.; Geoff, S.H. T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK): An emerging target for cancer-specific therapeutics. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Tao, Z.; Gao, L.; Yan, F.; Gao, Z.; Liu, X.; Ji, X.; Luo, Y. Ischemic postconditioning relieves cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury through activating T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase/protein kinase B pathway in rats. Stroke 2014, 45, 2417–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.; Ye, N.; Dai, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Y. The Protective Role of the TOPK/PBK Pathway in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion and H(2)O(2)-Induced Injury in H9C2 Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yao, S.; Wang, T.; Yuan, S. Remote ischemic postconditioning protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by activation of T-LAK-cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK)/PTEN/Akt signaling pathway mediated anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, R.A.; Marfatia, S.M.; Branton, D.; Chishti, A.H. Cloning and characterization of hdlg: The human homologue of the Drosophila discs large tumor suppressor binds to protein 4.1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9818–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsumine, A.; Ogai, A.; Senda, T.; Okumura, N.; Satoh, K.; Baeg, G.H.; Kawahara, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Okada, M.; Toyoshima, K.; et al. Binding of APC to the human homolog of the Drosophila discs large tumor suppressor protein. Science 1996, 272, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Jin, K.; Shao, B. The Prognostic Value of Serum Cytokines in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Xu, L.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shi, C.H.; Qiao, S.B.; Ma, Z.Q.; Yuan, J.S. Snapshot: Implications for mTOR in Aging-related Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, F.X.; Jiang, L.D.; Han, F.; Degos, V.; Chen, S.D.; Su, H. Increased Inflammatory Response in Old Mice is Associated with More Severe Neuronal Injury at the Acute Stage of Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fujibuchi, T.; Abe, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Ueda, N.; Shigemoto, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kito, K. Expression and phosphorylation of TOPK during spermatogenesis. Dev. Growth Differ. 2005, 47, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, J.D.; Garcia, A.D.; Nakano, I.; Livingstone, M.; Norris, B.; Polakiewicz, R.; Wexler, E.M.; Sofroniew, M.V.; Kornblum, H.I.; Geschwind, D.H. PBK/TOPK, a proliferating neural progenitor-specific mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10773–10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown-Clay, J.D.; Shenoy, D.N.; Timofeeva, O.; Kallakury, B.V.; Nandi, A.K.; Banerjee, P.P. PBK/TOPK enhances aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer via beta-catenin-TCF/LEF-mediated matrix metalloproteinases production and invasion. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15594–15609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.H.; Liang, Y.X.; He, H.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Lu, J.M.; Chen, G.; Lin, Z.Y.; Fu, X.; Ling, X.H.; Han, Z.D.; et al. Overexpression of PDZ-binding kinase confers malignant phenotype in prostate cancer via the regulation of E2F1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Abe, Y.; Fujibuchi, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Kito, K.; Ueda, N.; Shigemoto, K.; Gyo, K. Characterization of a MAPKK-like protein kinase TOPK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 325, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuryev, A.; Wennogle, L.P. Novel raf kinase protein-protein interactions found by an exhaustive yeast two-hybrid analysis. Genomics 2003, 81, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, F.; Zykova, T.; Kim, M.O.; Cho, Y.Y.; Bode, A.M.; Peng, C.; Ma, W.; Carper, A.; Langfald, A.; et al. T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK) phosphorylation of MKP1 protein prevents solar ultraviolet light-induced inflammation through inhibition of the p38 protein signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29601–29609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Nishidate, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Katagiri, T. Critical roles of T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase in cytokinesis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, S.; Simard, C.; Lemieux, R. Regulation of growth-related genes by interleukin-6 in murine myeloma cells. Cytokine 2002, 20, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.K.; Rapoport, A.P. Expression of PDZ-binding kinase (PBK) is regulated by cell cycle-specific transcription factors E2F and CREB/ATF. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Zhao, X.F.; Fang, H.B.; Minkove, S.; Poss, D.E.; Rapoport, A.P. c-Myc and E2F1 drive PBK/TOPK expression in high-grade malignant lymphomas. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.R.; Gangula, N.R.; Kavela, S.; Pandey, V.; Maddika, S. TOPK and PTEN participate in CHFR mediated mitotic checkpoint. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 2511–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yan, W.; Sun, H.; Xue, P.; Fan, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, J.; Shao, C.; et al. Phosphorylation of TOPK at Y74, Y272 by Src increases the stability of TOPK and promotes tumorigenesis of colon. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24483–24494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizkallah, R.; Batsomboon, P.; Dudley, G.B.; Hurt, M.M. Identification of the oncogenic kinase TOPK/PBK as a master mitotic regulator of C2H2 zinc finger proteins. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukukawa, C.; Ueda, K.; Nishidate, T.; Katagiri, T.; Nakamura, Y. Critical roles of LGN/GPSM2 phosphorylation by PBK/TOPK in cell division of breast cancer cells. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2010, 49, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Kagawa-Miki, L.; Ueda, N.; Shigemoto, K.; Yasukawa, M.; Kito, K. A mitotic kinase TOPK enhances Cdk1/cyclin B1-dependent phosphorylation of PRC1 and promotes cytokinesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.K.; Ford, T.; Fleksher, D.; Neuman, B.; Rapoport, A.P. Attenuation of DNA damage checkpoint by PBK, a novel mitotic kinase, involves protein-protein interaction with tumor suppressor p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Eichberg, D.; Liu, Z.; Fang, H.B.; Rapoport, A.P. PBK/TOPK interacts with the DBD domain of tumor suppressor p53 and modulates expression of transcriptional targets including p21. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5464–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Lin, M.L.; Nishidate, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Katagiri, T. PDZ-binding kinase/T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase, a putative cancer/testis antigen with an oncogenic activity in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9186–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayllon, V.; O’Connor, R. PBK/TOPK promotes tumour cell proliferation through p38 MAPK activity and regulation of the DNA damage response. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L. T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase is essential for the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2013, 31, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Bai, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zou, D.; Qu, S.; Tian, G.; Song, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF21) protects mouse liver against D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via activating Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 403, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, B.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, N.; Xu, X.; Zhi, C.; Mei, J.; Yan, Z.; et al. PBK/TOPK expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: Its correlation and prognostic significance with Ki67 and p53 expression. Histopathology 2013, 63, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Qi, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhi, C.; Wan, L.; Shen, H. PBK/TOPK expression correlates with mutant p53 and affects patients’ prognosis and cell proliferation and viability in lung adenocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Zykova, T.A.; Kang, B.S.; Wang, Z.; Ebeling, M.C.; Abe, Y.; Ma, W.Y.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Bidirectional signals transduced by TOPK-ERK interaction increase tumorigenesis of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, T.A.; Zhu, F.; Lu, C.; Higgins, L.; Tatsumi, Y.; Abe, Y.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Lymphokine-activated killer T-cell-originated protein kinase phosphorylation of histone H2AX prevents arsenite-induced apoptosis in RPMI7951 melanoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6884–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.M.; Zhu, F.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, H.G.; Zykova, T.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. T-lymphokine-activated killer cell-originated protein kinase functions as a positive regulator of c-Jun-NH2-kinase 1 signaling and H-Ras-induced cell transformation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5186–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zykova, T.A.; Zhu, F.; Vakorina, T.I.; Zhang, J.; Higgins, L.A.; Urusova, D.V.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK) phosphorylation of Prx1 at Ser-32 prevents UVB-induced apoptosis in RPMI7951 melanoma cells through the regulation of Prx1 peroxidase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29138–29146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.R.; Lee, K.W.; Dong, Z.; Lee, K.B.; Oh, S.M. Requirement of T-lymphokine-activated killer cell-originated protein kinase for TRAIL resistance of human HeLa cervical cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, D.S.; Choi, H.J.; Hahm, D.H.; Oh, S.M. Phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha at serine 32 by T-lymphokine-activated killer cell-originated protein kinase is essential for chemoresistance against doxorubicin in cervical cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Won, H.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Oh, S.M. Activation of TOPK by lipopolysaccharide promotes induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase through NF-kappaB activity in leukemia cells. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons-Evelyn, M.; Bailey-Dell, K.; Toretsky, J.A.; Ross, D.D.; Fenton, R.; Kalvakolanu, D.; Rapoport, A.P. PBK/TOPK is a novel mitotic kinase which is upregulated in Burkitt’s lymphoma and other highly proliferative malignant cells. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2001, 27, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yan, Q.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. PBK/TOPK in the differential diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma from hepatocellular carcinoma and its involvement in prognosis of human cholangiocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Hung, J.J.; Chou, T.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Lu, P.J.; Cheng, H.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.L.; Chen, K.Y.; et al. Overexpression of T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase predicts poor prognosis in patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Jan, Y.H.; Yang, B.M.; Lu, P.J.; Cheng, H.C.; Huang, M.S.; Yang, C.J.; Hsiao, M.; et al. TOPK/PBK promotes cell migration via modulation of the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway and is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Dalela, D.; Rath, S.K.; Goel, M.M.; Bhatt, M.L. Expression of PDZ-binding kinase/T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (PBK/TOPK) in human urinary bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, M. Functional analysis of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma primary tumorassociated gene interaction network. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 4975–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, T.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, H.T.; Yen, H.H.; Sung, W.W.; Chen, C.J. Cytoplasmic, nuclear, and total PBK/TOPK expression is associated with prognosis in colorectal cancer patients: A retrospective analysis based on immunohistochemistry stain of tissue microarrays. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Akai, T.; Hayashi, T.; Tomita, T.; Nagai, S.; Kuroda, S. Novel biomarker, phosphorylated T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (p-TOPK) can predict outcome in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuropathology 2018, 38, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruthika, B.S.; Jain, R.; Arivazhagan, A.; Bharath, R.D.; Yasha, T.C.; Kondaiah, P.; Santosh, V. Transcriptome profiling reveals PDZ binding kinase as a novel biomarker in peritumoral brain zone of glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlobec, I.; Molinari, F.; Kovac, M.; Bihl, M.P.; Altermatt, H.J.; Diebold, J.; Frick, H.; Germer, M.; Horcic, M.; Montani, M.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of TOPK stratified by KRAS and BRAF gene alterations in sporadic, hereditary and metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Lei, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Sheng, W.; Lin, P.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Shen, H. Expression of PBK/TOPK in cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8059–8064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A.; Tidwell, M.; Karp, J.; Rapoport, A.P. Protein expression of PDZ-binding kinase is up-regulated in hematologic malignancies and strongly down-regulated during terminal differentiation of HL-60 leukemic cells. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2004, 32, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Tao, Z.; Yan, F.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Min, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Activation of T-LAK-cell-originated protein kinase-mediated antioxidation protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4411–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2012, 43, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Murakami, K.; Bando, Y.; Yoshida, S. Interferon regulatory factor 7 participates in the M1-like microglial polarization switch. Glia 2015, 63, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Zhao, H.; Tao, Z.; Wang, R.; Fan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ji, X. TOPK Promotes Microglia/Macrophage Polarization towards M2 Phenotype via Inhibition of HDAC1 and HDAC2 Activity after Transient Cerebral Ischemia. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, N.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, B.H.; Bode, A.M.; Lee, H.J.; Heo, Y.S.; Boardman, L.; Limburg, P.; Lee, H.J.; Dong, Z. Coffee phenolic phytochemicals suppress colon cancer metastasis by targeting MEK and TOPK. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.J.; Li, Y.; Reddy, K.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, M.O.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Novel TOPK inhibitor HI-TOPK-032 effectively suppresses colon cancer growth. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joel, M.; Mughal, A.A.; Grieg, Z.; Murrell, W.; Palmero, S.; Mikkelsen, B.; Fjerdingstad, H.B.; Sandberg, C.J.; Behnan, J.; Glover, J.C.; et al. Targeting PBK/TOPK decreases growth and survival of glioma initiating cells in vitro and attenuates tumor growth in vivo. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, Y.; Park, J.H.; Miyamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Hisada, S.; Alachkar, H.; Nakamura, Y. TOPK inhibitor induces complete tumor regression in xenograft models of human cancer through inhibition of cytokinesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 259ra145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Sutherland, B.W.; Anantha, M.; Pallaoro, A.; Bally, M.B. Liposomal OTS964, a TOPK inhibitor: A simple method to estimate OTS964 association with liposomes that relies on enhanced OTS964 fluorescence when bound to albumin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirovano, G.; Roberts, S.; Brand, C.; Donabedian, P.L.; Mason, C.; de Souza, P.D.; Higgins, G.S.; Reiner, T. [(18)F]FE-OTS964: A Small Molecule Targeting TOPK for In Vivo PET Imaging in a Glioblastoma Xenograft Model. Mol. Imag. Biol. 2019, 21, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.; Reddy, K.; Chen, H.; Yao, K.; Wang, K.; Roh, E.; Zykova, T.; Ma, W.; et al. ADA-07 Suppresses Solar Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Carcinogenesis by Directly Inhibiting TOPK. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dou, X.; Wei, J.; Sun, A.; Shao, G.; Childress, C.; Yang, W.; Lin, Q. PBK/TOPK mediates geranylgeranylation signaling for breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Y.; Xue, H.; Wu, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z. MicroRNA-216b-3p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell growth via regulating PDZ binding kinase/T-LAK-cell-originated protein kinase. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4822–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.F.; Gao, T.T.; Shi, Y.J.; Lei, Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Feng, Q.; Chen, Z.J.; Yu, L.T. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 1-phenyl phenanthridin-6(5H)-one derivatives as anti-tumor agents targeting TOPK. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ye, L.; Yin, S.; Zhao, C.; Yan, M.; Liu, X.; Cui, J.; Hu, H. Glycyrol exerts potent therapeutic effect on lung cancer via directly inactivating T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Hu, Q.; Hu, X.; Lei, Q.; Feng, Z.; Yu, X.; Peng, C.; Song, X.; He, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Novel selective TOPK inhibitor SKLB-C05 inhibits colorectal carcinoma growth and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 445, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirubakaran, P.; Karthikeyan, M.; Singh Kh, D.; Nagamani, S.; Premkumar, K. In silico structural and functional analysis of the human TOPK protein by structure modeling and molecular dynamics studies. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Venkat, P.; Chopp, M.; Zacharek, A.; Shen, Y.; Liang, L.L.; Landschoot-Ward, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Jiang, R.C.; Chen, J.L. Deficiency of tPA Exacerbates White Matter Damage, Neuroinflammation, Glymphatic Dysfunction and Cognitive Dysfunction in Aging Mice. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, K.J.; Puliyadi, R.; Prevo, R.; Rodriguez-Berriguete, G.; Ryan, A.; Ramadan, K.; Higgins, G.S. Targeting TOPK sensitises tumour cells to radiation-induced damage by enhancing replication stress. Cell Death Differ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y. PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention. Cells 2021, 10, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020371
Han Z, Li L, Huang Y, Zhao H, Luo Y. PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention. Cells. 2021; 10(2):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020371
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Ziping, Lingzhi Li, Yuyou Huang, Haiping Zhao, and Yumin Luo. 2021. "PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention" Cells 10, no. 2: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020371
APA StyleHan, Z., Li, L., Huang, Y., Zhao, H., & Luo, Y. (2021). PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention. Cells, 10(2), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020371