Treatment with Bacterial Biologics Promotes Healthy Aging and Traumatic Brain Injury Responses in Adult Drosophila, Modeling the Gut–Brain Axis and Inflammation Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Drosophila Stocks and Culturing Conditions
2.2. IAB and LGG Media Preparations and Longevity Studies
2.3. Negative Geotaxis Response
2.4. Western Analysis
2.5. Traumatic Brain Injury
2.6. Mortality Indexes
2.7. Quantitative PCR
2.8. Receptor Activation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Negative Geotaxis Response
3.2. Longevity Profiles
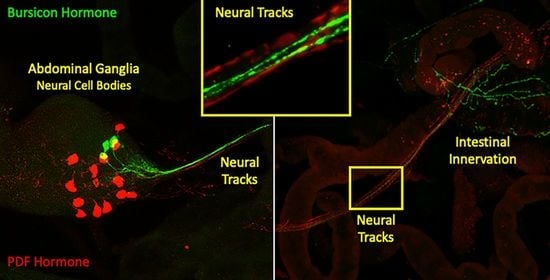
3.3. Neural Aggregate Changes Due to Aging
3.4. Neural Function Following Trauma
3.5. Aging Profiles Following Trauma
3.6. Conserved Aging and Trauma Responses
3.7. Basal Immune Profiles
3.8. Impact of Biologics on Behavior and Longevity
3.9. Mild and Severe Trauma Responses
3.10. In Vitro Receptor Interactions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, S.; Ligoxygakis, P. Beyond host defense: Deregulation of Drosophila immunity and age-dependent neurodegeneration. Front. Immunol 2020, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Karpac, J.; Tran, S.L.; Jasper, H. PGRP-SC2 promotes gut immune homeostasis to limit commensal dysbiosis and extend lifespan. Cell 2014, 156, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Prakash, S. Longevity extension in Drosophila through gut-brain communication. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.; Cumming, R.C.; Lindmo, K.; Galaviz, V.; Cheng, S.; Rusten, T.E.; Finley, K.D. Genetic modifiers of the drosophila blue cheese gene link defects in lysosomal transport with decreased life span and altered ubiquitinated-protein profiles. Genetics 2007, 176, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 335–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Prakash, S. A novel synbiotic delays Alzheimer’s disease onset via combinatorial gut-brain-axis signaling in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.; Cumming, R.C.; Brech, A.; Isakson, P.; Schubert, D.R.; Finley, K.D. Promoting basal levels of autophagy in the nervous system enhances longevity and oxidant resistance in adult Drosophila. Autophagy 2008, 4, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, B.J.; Isakson, P.; Lewerenz, J.; Sanchez, H.; Kotzebue, R.W.; Cumming, R.C.; Harris, G.L.; Nezis, I.P.; Schubert, D.R.; Simonsen, A.; et al. p62, Ref(2)P and ubiquitinated proteins are conserved markers of neuronal aging, aggregate formation and progressive autophagic defects. Autophagy 2011, 7, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barekat, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Mauntz, R.E.; Kotzebue, R.W.; Molina, B.; El-Mecharrafie, N.; Conner, C.J.; Garza, S.; Melkani, G.C.; Joiner, W.J.; et al. Using Drosophila as an integrated model to study mild repetitive traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ratliff, E.P.; Molina, B.; El-Mecharrafie, N.; Mastroianni, J.; Kotzebue, R.W.; Achal, M.; Mauntz, R.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Barekat, A.; et al. Aging and intermittent fasting impact on transcriptional regulation and physiological responses of adult Drosophila neuronal and muscle tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratliff, E.P.; Kotzebue, R.W.; Molina, B.; Mauntz, R.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Barekat, A.; El-Mecharrafie, N.; Garza, S.; Gurney, M.A.; Achal, M.; et al. Assessing basal and acute autophagic responses in the adult Drosophila nervous system: The impact of gender, genetics and diet on endogenous pathway profiles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, E.P.; Mauntz, R.E.; Kotzebue, R.W.; Gonzalez, A.; Achal, M.; Barekat, A.; Finley, K.A.; Sparhawk, J.M.; Robinson, J.E.; Herr, D.R.; et al. Aging and autophagic function influences the progressive decline of adult Drosophila behaviors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.; Currais, A.; Prior, M.; Fischer, W.; Chiruta, C.; Ratliff, E.; Daugherty, D.; Dargusch, R.; Finley, K.; Esparza-Molto, P.B.; et al. The mitochondrial ATP synthase is a shared drug target for aging and dementia. Aging Cell 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepchia, D.; Currais, A.; Dargusch, R.; Finley, K.; Schubert, D.; Maher, P. Geroprotective effects of Alzheimer’s disease drug candidates. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 3269–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenberger, R.J.; Chtarbanova, S.; Rimkus, S.A.; Fischer, J.A.; Kaur, G.; Seppala, J.M.; Swanson, L.C.; Zajac, J.E.; Ganetzky, B.; Wassarman, D.A. Death following traumatic brain injury in Drosophila is associated with intestinal barrier dysfunction. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schubert, D.; Currais, A.; Goldberg, J.; Finley, K.; Petrascheck, M.; Maher, P. Geroneuroprotectors: Effective geroprotectors for the brain. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, L.A.; Stearns-Yoder, K.A.; Hoffberg, A.S.; Penzenik, M.E.; Starosta, A.J.; Hernandez, T.D.; Hadidi, D.A.; Lowry, C.A. Growing literature but limited evidence: A systematic review regarding prebiotic and probiotic interventions for those with traumatic brain injury and/or posttraumatic stress disorder. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, L.; Rodela, S.; Abian, J.; Claria, J.; Esmatjes, E. F2 isoprostane is already increased at the onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus: Effect of glycemic control. Metabolism 2004, 53, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatsenko, I.; Boquete, J.P.; Lemaitre, B. Microbiota-derived lactate activates production of reactive oxygen species by the intestinal NADPH oxidase nox and shortens Drosophila lifespan. Immunity 2018, 49, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Sun, H.; Yang, W.; Gao, M.; Xu, H. Impact of Probiotic Combination in InR([E19])/TM2 Drosophila melanogaster on longevity, related gene expression, and intestinal microbiota: A preliminary study. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.; Mishra, S.K.; Pant, H.C. Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 2011, 572634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishna, G.; Beitchman, J.A.; Bromberg, C.E.; Currier Thomas, T. Approaches to monitor circuit disruption after traumatic brain injury: Frontiers in preclinical research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Prakash, S. A novel polyphenolic prebiotic and probiotic formulation have synergistic effects on the gut microbiota influencing Drosophila melanogaster physiology. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Luan, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chang, X.; Snijders, A.M.; Mao, J.H.; Secombe, J.; Dan, Z.; Chen, J.H.; et al. Drosophila histone demethylase KDM5 regulates social behavior through immune control and gut microbiota maintenance. Cell. Host. Microbe. 2019, 25, 537–552 e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Tan, F.H.; Lau, S.A.; Jaafar, M.H.; Chung, F.Y.; Azzam, G.; Liong, M.T.; Li, Y. Lactic acid bacteria feeding reversed the malformed eye structures and ameliorated gut microbiota profiles of Drosophila melanogaster Alzheimer’s disease model. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzi, A.; Frohlich, E.E.; Holzer, P. Gut microbiota and the neuroendocrine system. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, M.W.; Pandya, J.D.; Shear, D.A. Gut microbiota as a therapeutic target to ameliorate the biochemical, neuroanatomical, and behavioral effects of traumatic brain injuries. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, V.; Giron, M.C. Microbiome-gut-brain axis and toll-like receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dus, M.; Lai, J.S.; Gunapala, K.M.; Min, S.; Tayler, T.D.; Hergarden, A.C.; Geraud, E.; Joseph, C.M.; Suh, G.S. Nutrient sensor in the brain directs the action of the brain-gut axis in Drosophila. Neuron 2015, 87, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elder, G.A.; Ehrlich, M.E.; Gandy, S. Relationship of traumatic brain injury to chronic mental health problems and dementia in military veterans. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 707, 134294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Kanel, R.; Hepp, U.; Kraemer, B.; Traber, R.; Keel, M.; Mica, L.; Schnyder, U. Evidence for low-grade systemic proinflammatory activity in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breit, S.; Kupferberg, A.; Rogler, G.; Hasler, G. Vagus nerve as modulator of the brain-gut axis in psychiatric and inflammatory disorders. Front. Psychiatr. 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Kuo, W.W.; Ho, T.J.; Day, C.H.; Pai, P.Y.; Chung, L.C.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, H.F.; Liao, P.H.; et al. Multi-strain probiotics inhibit cardiac myopathies and autophagy to prevent heart injury in high-fat diet-fed rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasozi, K.I.; Bukenya, A.; Eze, E.D.; Kasolo, J.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Ssempijja, F.; Suubo, J.; Tamale, A.; Echoru, I.; Ntulume, I.; et al. Low concentrations of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (Yoba((R))) are safe in male Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirani, E.; Milajerdi, A.; Mirzaei, H.; Jamilian, H.; Mansournia, M.A.; Hallajzadeh, J.; Ghaderi, A. The effects of probiotic supplementation on mental health, biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with psychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, D. Inflammatory bowel diseases and brain-gut axis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Llorente, C.; Munoz, S.; Gil, A. Role of Toll-like receptors in the development of immunotolerance mediated by probiotics. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, T.; Takagi, A.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nagaoka, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Yokokura, T.; Yoshikai, Y. Lipoteichoic acids from Lactobacillus strains elicit strong tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducing activities in macrophages through Toll-like receptor 2. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, N.M.; Wang, J.; Redmond, H.P.; Wang, J.H. Current knowledge and future directions of TLR and NOD signaling in sepsis. Mil. Med. Res. 2015, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayisoglu, O.; Weiss, F.; Niklas, C.; Pierotti, I.; Pompaiah, M.; Wallaschek, N.; Germer, C.T.; Wiegering, A.; Bartfeld, S. Location-specific cell identity rather than exposure to GI microbiota defines many innate immune signalling cascades in the gut epithelium. Gut 2021, 70, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, S.; Iqbal, U.; Sebastian, M.; Pasinetti, G.M. Gut microbiota mediated allostasis prevents stress-induced neuroinflammatory risk factors of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 168, 147–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, A.; Cumming, R.C.; Finley, K.D. Linking lysosomal trafficking defects with changes in aging and stress response in Drosophila. Autophagy 2007, 3, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katzenberger, R.J.; Ganetzky, B.; Wassarman, D.A. The gut reaction to traumatic brain injury. Fly (Austin) 2015, 9, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVey Neufeld, K.A.; Strain, C.R.; Pusceddu, M.M.; Waworuntu, R.V.; Manurung, S.; Gross, G.M.; Malone, G.; Hoban, A.E.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG soluble mediators ameliorate early life stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity and changes in spinal cord gene expression. Neuronal. Signal. 2020, 4, NS20200007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianda, D.; Agustina, R.; Setiawan, E.A.; Manikam, N.R.M. Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function in children and adolescents: A systematic review of randomised trials. Benef. Microbes. 2019, 10, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenberger, R.J.; Loewen, C.A.; Wassarman, D.R.; Petersen, A.J.; Ganetzky, B.; Wassarman, D.A. A Drosophila model of closed head traumatic brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4152–E4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Chang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H.; Xu, C. Lactobacillus bulgaricus or lactobacillus rhamnosus suppresses nf-kappab signaling pathway and protects against AFB(1)-induced hepatitis: A novel potential preventive strategy for aflatoxicosis? Toxins 2019, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Su, F.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, T.; Hu, Q.; Yu, X.Q. Pattern recognition receptors in Drosophila immune responses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 102, 103468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenberger, R.J.; Ganetzky, B.; Wassarman, D.A. Age and diet affect genetically separable secondary injuries that cause acute mortality following traumatic brain injury in Drosophila. G3 (Bethesda) 2016, 6, 4151–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKernan, D.P.; Gaszner, G.; Quigley, E.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Altered peripheral toll-like receptor responses in the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deleemans, J.M.; Chleilat, F.; Reimer, R.A.; Henning, J.W.; Baydoun, M.; Piedalue, K.A.; McLennan, A.; Carlson, L.E. The chemo-gut study: Investigating the long-term effects of chemotherapy on gut microbiota, metabolic, immune, psychological and cognitive parameters in young adult cancer survivors; study protocol. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVey Neufeld, K.A.; O’Mahony, S.M.; Hoban, A.E.; Waworuntu, R.V.; Berg, B.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Neurobehavioural effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG alone and in combination with prebiotics polydextrose and galactooligosaccharide in male rats exposed to early-life stress. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| TLR/NOD | Negative Control | IAB Powder | Fold | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor | Average # | Std Dev | Average # | Std Dev | Induction * |
| hTLR2 | 0.052 | 0.001 | 2.521 | 0.025 | 48.5 |
| hTLR3 | 0.127 | 0.002 | 0.535 | 0.014 | 4.2 |
| hTLR4 | 0.163 | 0.027 | 1.877 | 0.076 | 11.5 |
| hTLR5 | 0.066 | 0.001 | 0.173 | 0.003 | 2.6 |
| hTLR7 | 0.095 | 0.002 | 0.119 | 0.014 | 1.3 |
| hTLR8 | 0.110 | 0.003 | 0.125 | 0.001 | 1.1 |
| hTLR9 | 0.156 | 0.011 | 0.204 | 0.003 | 1.3 |
| NOD1 | 0.070 | 0.002 | 0.107 | 0.000 | 1.5 |
| NOD2 | 0.073 | 0.001 | 1.649 | 0.046 | 22.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molina, B.; Mastroianni, J.; Suarez, E.; Soni, B.; Forsberg, E.; Finley, K. Treatment with Bacterial Biologics Promotes Healthy Aging and Traumatic Brain Injury Responses in Adult Drosophila, Modeling the Gut–Brain Axis and Inflammation Responses. Cells 2021, 10, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040900
Molina B, Mastroianni J, Suarez E, Soni B, Forsberg E, Finley K. Treatment with Bacterial Biologics Promotes Healthy Aging and Traumatic Brain Injury Responses in Adult Drosophila, Modeling the Gut–Brain Axis and Inflammation Responses. Cells. 2021; 10(4):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040900
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolina, Brandon, Jessica Mastroianni, Ema Suarez, Brijinder Soni, Erica Forsberg, and Kim Finley. 2021. "Treatment with Bacterial Biologics Promotes Healthy Aging and Traumatic Brain Injury Responses in Adult Drosophila, Modeling the Gut–Brain Axis and Inflammation Responses" Cells 10, no. 4: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040900
APA StyleMolina, B., Mastroianni, J., Suarez, E., Soni, B., Forsberg, E., & Finley, K. (2021). Treatment with Bacterial Biologics Promotes Healthy Aging and Traumatic Brain Injury Responses in Adult Drosophila, Modeling the Gut–Brain Axis and Inflammation Responses. Cells, 10(4), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040900