A Tight Control of Non-Canonical TGF-β Pathways and MicroRNAs Downregulates Nephronectin in Podocytes
Abstract
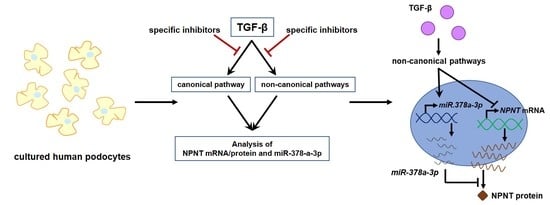
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. RNA Isolation, cDNA Transcription, and qPCR
2.3. MicroRNA Isolation, cDNA Transcription, and TaqMan PCR
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Cell Fractionation
2.6. NPNT Elisa
2.7. CHX Chase Assay
2.8. Data Analysis/Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Podocyte NPNT Is Downregulated after Stimulation with TGF-β
3.2. TGF-β-Dependent Regulation of NPNT Protein Is Mediated through Intracellular Signaling Pathways
3.3. Non-Canonical Pathways Predominantly Mediate Regulation of NPNT under Baseline Conditions
3.4. NPNT Protein Secretion Is Not Dependent on TGF-β Pathways
3.5. TGF-β-Mediated Downregulation of NPNT Is Dependent on Non-Canonical Signaling Pathways in Podocytes
3.6. Non-Canonical TGF-β Pathways Regulate NPNT-Targeting miRs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, A.; Satchell, S.C.; Neal, C.R.; McKenzie, E.A.; Tooke, J.E.; Mathieson, P.W. Glomerular endothelial glycocalyx constitutes a barrier to protein permeability. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reiser, J.; Altintas, M.M. Podocytes. F1000Research 2016, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byron, A.; Randles, M.J.; Humphries, J.D.; Mironov, A.; Hamidi, H.; Harris, S.; Mathieson, P.W.; Saleem, M.A.; Satchell, S.C.; Zent, R.; et al. Glomerular cell cross-talk influences composition and assembly of extracellular matrix. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, C.; Lennon, R. Basement Membrane Defects in Genetic Kidney Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Funk, S.D.; Lin, M.H.; Miner, J.H. Alport syndrome and Pierson syndrome: Diseases of the glomerular basement membrane. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutnam, Z.J.; Wight, T.N.; Yang, B.B. miRNAs regulate expression and function of extracellular matrix molecules. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muller-Deile, J.; Dannenberg, J.; Liu, P.; Lorenzen, J.; Nystrom, J.; Thum, T.; Schiffer, M. Identification of cell and disease specific microRNAs in glomerular pathologies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3927–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller-Deile, J.; Gellrich, F.; Schenk, H.; Schroder, P.; Nystrom, J.; Lorenzen, J.; Haller, H.; Schiffer, M. Overexpression of TGF-beta Inducible microRNA-143 in Zebrafish Leads to Impairment of the Glomerular Filtration Barrier by Targeting Proteoglycans. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, M.; Putta, S.; Wang, M.; Yuan, H.; Lanting, L.; Nair, I.; Gunn, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Shimano, H.; Todorov, I.; et al. TGF-beta activates Akt kinase through a microRNA-dependent amplifying circuit targeting PTEN. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller-Deile, J.; Dannenberg, J.; Schroder, P.; Lin, M.H.; Miner, J.H.; Chen, R.; Brasen, J.H.; Thum, T.; Nystrom, J.; Staggs, L.B.; et al. Podocytes regulate the glomerular basement membrane protein nephronectin by means of miR-378a-3p in glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Deile, J.; Sopel, N.; Ohs, A.; Rose, V.; Gröner, M.; Wrede, C.; Hegermann, J.; Daniel, C.; Amann, K.; Zahner, G.; et al. Glomerular Endothelial Cell-Derived microRNA-192 Regulates Nephronectin Expression in Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2777–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagi, R.; Ishimoto, Y.; Jao, T.M. Foreseeing the future of glomerular disease through slits: miR-NPNT axis. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 782–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiffer, M.; Mundel, P.; Shaw, A.S.; Bottinger, E.P. A novel role for the adaptor molecule CD2-associated protein in transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37004–37012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xavier, S.; Niranjan, T.; Krick, S.; Zhang, T.; Ju, W.; Shaw, A.S.; Schiffer, M.; Bottinger, E.P. TbetaRI independently activates Smad- and CD2AP-dependent pathways in podocytes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L. Regulation of Smad activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1759, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonniaud, P.; Margetts, P.J.; Kolb, M.; Schroeder, J.A.; Kapoun, A.M.; Damm, D.; Murphy, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Dugar, S.; Higgins, L.; et al. Progressive transforming growth factor beta1-induced lung fibrosis is blocked by an orally active ALK5 kinase inhibitor. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xiong, X.; Chen, Y.G. Feedback regulation of TGF-beta signaling. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopp, J.B.; Factor, V.M.; Mozes, M.; Nagy, P.; Sanderson, N.; Böttinger, E.P.; Klotman, P.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Transgenic mice with increased plasma levels of TGF-beta 1 develop progressive renal disease. Lab. Investig. 1996, 74, 991–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, S.; Ishimura, E.; Mori, K.; Fukumoto, S.; Yamano, S.; Wei, M.; Emoto, M.; Wanibuchi, H.; Inaba, M. Nephronectin expression in glomeruli of renal biopsy specimens from various kidney diseases: Nephronectin is expressed in the mesangial matrix expansion of diabetic nephropathy. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 122, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S. Pathogenic role of TGF-β in the progression of podocyte diseases. Histol. Histopathol. 2011, 26, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, T.T.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-Beta as a Master Regulator of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.A.; O’Hare, M.J.; Reiser, J.; Coward, R.J.; Inward, C.D.; Farren, T.; Xing, C.Y.; Ni, L.; Mathieson, P.W.; Mundel, P. A conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating nephrin and podocin expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daehn, I.; Casalena, G.; Zhang, T.; Shi, S.; Fenninger, F.; Barasch, N.; Yu, L.; D’Agati, V.; Schlondorff, D.; Kriz, W.; et al. Endothelial mitochondrial oxidative stress determines podocyte depletion in segmental glomerulosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenberger, R.; Schmidt, A.; Linton, J.; Wang, D.; Backus, C.; Denda, S.; Muller, U.; Reichardt, L.F. Identification and characterization of a novel extracellular matrix protein nephronectin that is associated with integrin alpha8beta1 in the embryonic kidney. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinck, A.P.; Mueller, T.D.; Springer, T.A. Structural Biology and Evolution of the TGF-β Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a022103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Shi-wen, X.; Eastwood, M.; Black, C.M.; Denton, C.P.; Leask, A.; Abraham, D.J. Contribution of activin receptor-like kinase 5 (transforming growth factor beta receptor type I) signaling to the fibrotic phenotype of scleroderma fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, B.; Umelo, I.A.; Bellier, J.; Castronovo, V.; Turtoi, A. Stromal Modulators of TGF-β in Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, K.; Corbley, M.J.; Sun, L.; Friedman, J.E.; Shan, F.; Papadatos, J.L.; Costa, D.; Lutterodt, F.; Sweigard, H.; Bowes, S.; et al. SM16, an orally active TGF-beta type I receptor inhibitor prevents myofibroblast induction and vascular fibrosis in the rat carotid injury model. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz, M.A.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J.; Bayon, Y.; Pfahl, M.; Piedrafita, F.J. Retinoid-related molecules induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis through activation of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8504–8512. [Google Scholar]
- La Ferla-Bruhl, K.; Westhoff, M.A.; Karl, S.; Kasperczyk, H.; Zwacka, R.M.; Debatin, K.M.; Fulda, S. NF-kappaB-independent sensitization of glioblastoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis by proteasome inhibition. Oncogene 2007, 26, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.W.; Yakymovych, I.; Jia, M.; Yakymovych, M.; Souchelnytskyi, S. Phosphorylation of eEF1A1 at Ser300 by TβR-I results in inhibition of mRNA translation. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome inhibitors: Valuable new tools for cell biologists. Trends Cell Biol. 1998, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazono, A.; Yamada, A.; Morimura, N.; Takami, M.; Suzuki, D.; Kobayashi, M.; Tezuka, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kamijo, R. TGF-beta suppresses POEM expression through ERK1/2 and JNK in osteoblasts. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5321–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsukasaki, M.; Yamada, A.; Yoshimura, K.; Miyazono, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Takami, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Morimura, N.; Kamijo, R. Nephronectin expression is regulated by SMAD signaling in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.; Agrawal, A.; Bhushan, R.; Chavalmane, A.K.; Kalathur, R.K.; Takahashi, T.; Kondaiah, P. Expression profiling of genes regulated by TGF-beta: Differential regulation in normal and tumour cells. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Z.; Dickens, M.; Raingeaud, J.; Davis, R.J.; Greenberg, M.E. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 1995, 270, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hébert, M.C.; Zhang, Y.E. TGF-beta receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent TGF-beta responses. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freud, G.E.; Stern, M.C.; Watson, H.; Durrer, D. Activation of the hypertrophic right ventricle in the dog. Cardiovasc. Res. 1975, 9, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakin, A.V.; Rinehart, C.; Tomlinson, A.K.; Arteaga, C.L. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for TGFbeta-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J. Cell. Sci. 2002, 115, 3193–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funaba, M.; Zimmerman, C.M.; Mathews, L.S. Modulation of Smad2-mediated signaling by extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41361–41368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Caestecker, M.P.; Parks, W.T.; Frank, C.J.; Castagnino, P.; Bottaro, D.P.; Roberts, A.B.; Lechleider, R.J. Smad2 transduces common signals from receptor serine-threonine and tyrosine kinases. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sopel, N.; Ohs, A.; Schiffer, M.; Müller-Deile, J. A Tight Control of Non-Canonical TGF-β Pathways and MicroRNAs Downregulates Nephronectin in Podocytes. Cells 2022, 11, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010149
Sopel N, Ohs A, Schiffer M, Müller-Deile J. A Tight Control of Non-Canonical TGF-β Pathways and MicroRNAs Downregulates Nephronectin in Podocytes. Cells. 2022; 11(1):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSopel, Nina, Alexandra Ohs, Mario Schiffer, and Janina Müller-Deile. 2022. "A Tight Control of Non-Canonical TGF-β Pathways and MicroRNAs Downregulates Nephronectin in Podocytes" Cells 11, no. 1: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010149
APA StyleSopel, N., Ohs, A., Schiffer, M., & Müller-Deile, J. (2022). A Tight Control of Non-Canonical TGF-β Pathways and MicroRNAs Downregulates Nephronectin in Podocytes. Cells, 11(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010149