Molluscan RXR Transcriptional Regulation by Retinoids in a Drosophila CNS Organ Culture System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
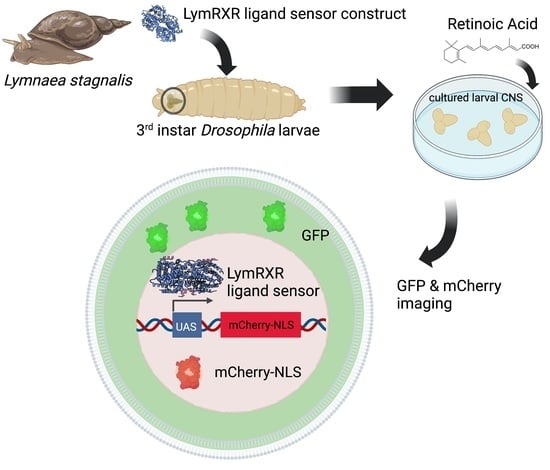
2.1. LymRXR Ligand Sensor Construct
2.2. Fly Maintenance and Genetics
2.3. Chemicals
2.4. Imaging
2.5. Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results

3.1. The LymRXR Ligand Sensor Responds to All-Trans RA in the Drosophila Larval CNS
3.2. Both All-Trans and 9-Cis Retinoid Isomers Activate LymRXR to a Similar Extent
3.3. Sensor Activation by a Vertebrate RXR Agonist
3.4. Evidence for Endogenous Retinoid Activity in the Developing CNS of Drosophila Larvae
4. Discussion
4.1. RXR and Retinoids in Lymnaea
4.2. Molluscan RXRs and Retinoid Binding
4.3. Retinoid Signaling in Drosophila
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kostrouch, Z.; Kostrouchova, M.; Love, W.; Jannini, E.; Piatigorsky, J.; Rall, J.E. Retinoic acid X receptor in the diploblast, Tripedalia cystophora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13442–13447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourguet, W.; Ruff, M.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H.; Moras, D. Crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the human nuclear receptor RXR-alpha. Nature 1995, 375, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierle, S.; Merk, D. Therapeutic modulation of retinoid X receptors—SAR and therapeutic potential of RXR ligands and recent patents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, R.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Dyck, J.A.; Stein, R.B.; Eichele, G.; Evans, R.M.; Thaller, C. 9-cis Retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell 1992, 68, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühl, R.; Krzyżosiak, A.; Niewiadomska-Cimicka, A.; Rochel, N.; Szeles, L.; Vaz, B.; Wietrzych-Schindler, M.; Álvarez, S.; Szklenar, M.; Nagy, L.; et al. 9-cis-13,14-Dihydroretinoic Acid Is an Endogenous Retinoid Acting as RXR Ligand in Mice. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, E.; Ruivo, R.; Borges, D.; Franco, J.N.; Santos, M.M.; Castro, L.F.C. Of Retinoids and Organotins: The Evolution of the Retinoid X Receptor in Metazoa. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, L.F.C.; Lima, D.; Machado, A.; Melo, C.; Hiromori, Y.; Nishikawa, J.; Nakanishi, T.; Reis-Henriques, M.A.; Santos, M.M. Imposex induction is mediated through the Retinoid X Receptor signalling pathway in the neogastropod Nucella lapillus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 85, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidli, S.; Castro, L.F.C.; Lahbib, Y.; Reis-Henriques, M.A.; El Menif, N.T.; Santos, M.M. Imposex development in Hexaplex trunculus (Gastropoda: Caenogastropoda) involves changes in the transcription levels of the retinoid X receptor (RXR). Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulianelli, S.; Primost, M.A.; Lanari, C.; Bigatti, G. RXR expression in Marine Gastropods with Different Sensitivity to Imposex Development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushitani, H.; Katsu, Y.; Kagechika, H.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Barroso, C.M.; Ohta, Y.; Shiraishi, H.; Iguchi, T.; Horiguchi, T. Characterization and comparison of transcriptional activities of the retinoid X receptors by various organotin compounds in three prosobranch gastropods; Thais clavigera, Nucella lapillus and Babylonia japonica. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmetrichuk, J.M.; Carlone, R.L.; Spencer, G.E. Retinoic acid induces neurite outgrowth and growth cone turning in invertebrate neurons. Dev. Biol. 2006, 294, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farrar, N.R.; Dmetrichuk, J.M.; Carlone, R.L.; Spencer, G.E. A Novel, Nongenomic Mechanism Underlies Retinoic Acid-Induced Growth Cone Turning. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14136–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothwell, C.M.; de Hoog, E.; Spencer, G.E. The role of retinoic acid in the formation and modulation of invertebrate central synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothwell, C.M.; Spencer, G.E. Retinoid signaling is necessary for, and promotes long-term memory formation following operant conditioning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 114, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Hoog, E.; Lukewich, M.K.; Spencer, G.E. Retinoic acid inhibits neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels. Cell Calcium 2018, 72, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoog, E.; Lukewich, M.K.; Spencer, G.E. Retinoid receptor-based signaling plays a role in voltage-dependent inhibition of invertebrate voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10076–10093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoog, E.; Spencer, G.E. Activity-dependent modulation of neuronal KV channels by retinoic acid enhances CaV channel activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Mazariegos, J.; Nadendla, E.K.; Lima, D.; Pierzchalski, K.; Jones, J.W.; Kane, M.; Nishikawa, J.-I.; Hiromori, Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Santos, M.M.; et al. A Mollusk Retinoic Acid Receptor (RAR) Ortholog Sheds Light on the Evolution of Ligand Binding. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4275–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, C.J.; Rand, C.; Mohammad, I.; Lepp, A.; Vesprini, N.; Wiebe, O.; Carlone, R.; Spencer, G.E. Expression of a retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-like protein in the embryonic and adult nervous system of a protostome species. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2015, 324, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handberg-Thorsager, M.; Ulman, V.; Tomançak, P.; Arendt, D.; Schubert, M. A Behavioral Assay to Study Effects of Retinoid Pharmacology on Nervous System Development in a Marine Annelid. In Retinoid and Rexinoid Signaling; Ray, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.S.S.; Hiromori, Y.; Kaite, Y.; Ruivo, R.; Franco, J.N.; Nakanishi, T.; Santos, M.M.; Castro, L.F.C. An Orthologue of the Retinoic Acid Receptor (RAR) Is Present in the Ecdysozoa Phylum Priapulida. Genes 2019, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouton, D.; Escriva, H.; de Mendonça, R.L.; Glineur, C.; Bertin, B.; Noël, C.; Robinson-Rechavi, M.; de Groot, A.; Cornette, J.; Laudet, V.; et al. A conserved retinoid X receptor (RXR) from the mollusk Biomphalaria glabrata transactivates transcription in the presence of retinoids. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 34, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, C.J.; Farrar, N.; Carlone, R.L.; Spencer, G.E. Developmental expression of a molluscan RXR and evidence for its novel, nongenomic role in growth cone guidance. Dev. Biol. 2010, 343, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akmammedov, A.; Geigges, M.; Paro, R. Single vector non-leaky gene expression system for Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsley, J.A.; Kim, M.J.; Wegman, L.J.; Pettus, J.M.; Johnson, W.A. Sensory mechanisms controlling the timing of larval developmental and behavioral transitions require the Drosophila DEG/ENaC subunit, Pickpocket1. Dev. Biol. 2008, 322, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hultqvist, G.; Åberg, E.; Camilloni, C.; Sundell, G.N.; Andersson, E.; Dogan, J.; Chi, C.N.; Vendruscolo, M.; Jemth, P. Emergence and evolution of an interaction between intrinsically disordered proteins. Elife 2017, 6, e16059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowickyj, S.M.; Chithalen, J.V.; Cameron, D.; Tyshenko, M.G.; Petkovich, M.; Wyatt, G.R.; Jones, G.; Walker, V.K. Locust retinoid X receptors: 9-Cis-retinoic acid in embryos from a primitive insect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9540–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Pastor, R.; Burchfiel, E.T.; Thiele, D.J. Regulation of heat shock transcription factors and their roles in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmetrichuk, J.M.; Carlone, R.L.; Jones, T.R.B.; Vesprini, N.D.; Spencer, G.E. Detection of Endogenous Retinoids in the Molluscan CNS and Characterization of the Trophic and Tropic Actions of 9-cis Retinoic Acid on Isolated Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13014–13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesprini, N.D.; Spencer, G.E. Retinoic acid induces changes in electrical properties of adult neurons in a dose- and isomer-dependent manner. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 111, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, S.; Rothwel, C.M.; Wright, M.L.; de Hoog, E.; Walker, S.; Hudson, E.; Spencer, G.E. Extending the duration of long-term memories: Interactions between environmental darkness and retinoid signaling. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2016, 136, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo-Paysaa, F.; Marlétaz, F.; Laudet, V.; Schubert, M. Retinoic acid signaling in development: Tissue-specific functions and evolutionary origins. Genesis 2008, 46, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Créton, R.; Zwaan, G.; Dohmen, R. Specific Developmental Defects in Molluscs after Treatment with Retinoic Acid during Gastrulation. Dev. Growth Differ. 1993, 35, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietrzych, M.; Meziane, H.; Sutter, A.; Ghyselinck, N.; Chapman, P.F.; Chambon, P.; Krȩżel, W. Working memory deficits in retinoid X receptor γ-deficient mice. Learn. Mem. 2005, 12, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mounier, A.; Georgiev, D.; Nam, K.N.; Fitz, N.F.; Castranio, E.L.; Wolfe, C.M.; Cronican, A.A.; Schug, J.; Lefterov, I.; Koldamova, R. Bexarotene-Activated Retinoid X Receptors Regulate Neuronal Differentiation and Dendritic Complexity. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11862–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upreti, C.; Woodruff, C.M.; Zhang, X.-L.; Yim, M.J.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Pagano, A.M.; Rehanian, D.S.; Yin, D.; Kandel, E.R.; Stanton, P.K.; et al. Loss of retinoid X receptor gamma subunit impairs group 1 mGluR mediated electrophysiological responses and group 1 mGluR dependent behaviours. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzel, A.M.; Macrander, J.; Mane-Padros, D.; Fang, B.; Sladek, F.M.; Tarrant, A.M. Conservation of DNA and ligand binding properties of retinoid X receptor from the placozoan Trichoplax adhaerens to human. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 184, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, Q.; Xu, F.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Que, H.; Zhang, G. Functional characterization of retinoid X receptor with an emphasis on the mediation of organotin poisoning in the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Gene 2020, 753, 144780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, A.; Ruivo, R.; Fonseca, E.; Froufe, E.; Castro, L.F.C.; Santos, M.M. The retinoic acid receptor (RAR) in molluscs: Function, evolution and endocrine disruption insights. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.A.; Sturzenbecker, L.J.; Kazmer, S.; Bosakowski, T.; Huselton, C.; Allenby, G.; Speck, J.; Ratzeisen, C.; Rosenberger, M.; Lovey, A.; et al. 9-Cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXRα. Nature 1992, 355, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodeur, H.; Parisotto, M.; Chagnon, S.; Mader, S.; Bhat, P.V. Isomer-specific retinoic acid biosynthesis in HeLa cells expressing recombinant class I aldehyde dehydrogenases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2007, 1770, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesalski, H.K.; Doepner, G.; Tzimas, G.; Gamulin, V.; Schröder, H.C.; Batel, R.; Nau, H.; Müller, W.E. Modulation of myb gene expression in sponges by retinoic acid. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romert, A.; Tuvendal, P.; Simon, A.; Dencker, L.; Eriksson, U. The identification of a 9-cis retinol dehydrogenase in the mouse embryo reveals a pathway for synthesis of 9-cis retinoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charton, J.; Deprez-Poulain, R.; Hennuyer, N.; Tailleux, A.; Staels, B.; Deprez, B. Novel non-carboxylic acid retinoids: 1,2,4-Oxadiazol-5-one derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haffez, H.; Chisholm, D.R.; Valentine, R.; Pohl, E.; Redfern, C.; Whiting, A. The molecular basis of the interactions between synthetic retinoic acid analogues and the retinoic acid receptors. Med. Chem. Comm. 2017, 8, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.; de Rosny, E.; Juillan-Binard, C.; Ferrer, J.-L.; Laudet, V.; Pierce, R.J.; Pebay-Peyroula, E.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C.; Borel, F. Crystal Structure of a Novel Tetrameric Complex of Agonist-bound Ligand-binding Domain of Biomphalaria glabrata Retinoid X Receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 354, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Y.; Delaporte, C.; Moras, D.; Richards, G.; Billas, I.M.L. The ligand-binding domains of the three RXR-USP nuclear receptor types support distinct tissue and ligand specific hormonal responses in transgenic Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2009, 330, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.E.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Stewart, A.F. Heterodimerization of the Drosophila ecdysone receptor with retinoid X receptor and ultraspiracle. Nature 1993, 362, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.R.; Lai, C.Q.; Feng, X.; Parnell, L.D.; Wan, J.B.; Wang, J.D.; Li, D.; Ordovas, J.M.; Kang, J.X. Drosophila lacks C20 and C22 PUFAs. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Röller, H.; Dahm, K.H. The chemistry and biology of juvenile hormone. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1968, 24, 651–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halme, A.; Cheng, M.; Hariharan, I.K. Retinoids Regulate a Developmental Checkpoint for Tissue Regeneration in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wishart, T.M.; Rooney, T.M.; Lamont, D.J.; Wright, A.K.; Morton, A.J.; Jackson, M.; Freeman, M.R.; Gillingwater, T.H. Combining Comparative Proteomics and Molecular Genetics Uncovers Regulators of Synaptic and Axonal Stability and Degeneration In Vivo. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, W.F.; Torrecillas, A.; Fita, I.; Verdaguer, N.; Corbalán-García, S.; Gomez-Fernandez, J.C. Retinoic Acid Binds to the C2-Domain of Protein Kinase Cα. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 8774–8779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Hoog, E.; Saba Echezarreta, V.E.; Turgambayeva, A.; Foran, G.; Megaly, M.; Necakov, A.; Spencer, G.E. Molluscan RXR Transcriptional Regulation by Retinoids in a Drosophila CNS Organ Culture System. Cells 2022, 11, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162493
de Hoog E, Saba Echezarreta VE, Turgambayeva A, Foran G, Megaly M, Necakov A, Spencer GE. Molluscan RXR Transcriptional Regulation by Retinoids in a Drosophila CNS Organ Culture System. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162493
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Hoog, Eric, Victoria Elda Saba Echezarreta, Anel Turgambayeva, Gregory Foran, Marvel Megaly, Aleksandar Necakov, and Gaynor E. Spencer. 2022. "Molluscan RXR Transcriptional Regulation by Retinoids in a Drosophila CNS Organ Culture System" Cells 11, no. 16: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162493
APA Stylede Hoog, E., Saba Echezarreta, V. E., Turgambayeva, A., Foran, G., Megaly, M., Necakov, A., & Spencer, G. E. (2022). Molluscan RXR Transcriptional Regulation by Retinoids in a Drosophila CNS Organ Culture System. Cells, 11(16), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162493