The Ubiquitin Ligase RNF138 Cooperates with CtIP to Stimulate Resection of Complex DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Human G1-Phase Cells
Abstract
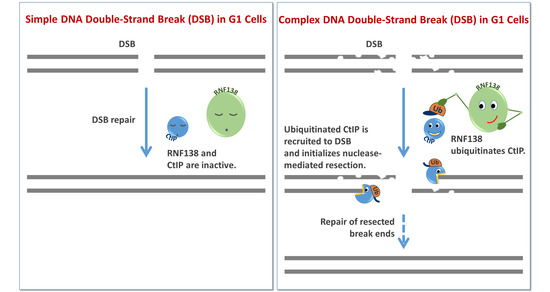
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Cell Culture, Transfection, and Clonogenic Survival Assay
2.2. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting
2.3. Irradiation
2.4. Immunostaining and Confocal Microscopy
2.5. EdU Labeling
2.6. Cell-Cycle Specific DSB-Repair Kinetics
2.7. Immunoprecipitation (IP) and Pull down (PD)
2.8. Western-Blot Analysis and Ligand-Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. BRCA1 and RIF1 Play No Major Role in Regulating Resection of Complex DSBs in G1 Cells
3.2. The E3 Ubiquitin Ligases RNF8 and RNF138 Are Required for Radiation-Dependent Ubiquitination in G1 Cells
3.3. RNF138 Is Involved in Resection of Complex DSBs in G1-Phase Cells
3.4. RNF138 Is Essential for DSB Recruitment of the Resection Factor CtIP in G1-Phase Cells
3.5. RNF138 Interacts with CtIP and Is Required for CtIP’s Ubiquitination in G1-Phase Cells
3.6. Removal of Ku80 in the Context of DSB Resection Does Not Require RNF138 in G1-Phase Cells
3.7. RNF138 Deficiency Diminishes DSB Repair and Survival of Heavy-Ion Irradiated Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mladenov, E.; Magin, S.; Soni, A.; Iliakis, G. DNA double-strand break repair as determinant of cellular radiosensitivity to killing and target in radiation therapy. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipler, A.; Iliakis, G. DNA double-strand-break complexity levels and their possible contributions to the probability for error-prone processing and repair pathway choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7589–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, R.; Panday, A.; Elango, R.; Willis, N.A. DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic mammalian cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, P.; Anderson, J.A.; Harper, J.V.; Hill, M.A.; Botchway, S.W.; Parker, A.W.; O’Neill, P. The dynamics of Ku70/80 and DNA-PKcs at DSBs induced by ionizing radiation is dependent on the complexity of damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10821–10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, A.A.; Jeggo, P.A. The repair and signaling responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Adv. Genet. 2013, 82, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipler, A.; Mladenova, V.; Soni, A.; Nikolov, V.; Saha, J.; Mladenov, E.; Iliakis, G. Chromosome thripsis by DNA double strand break clusters causes enhanced cell lethality, chromosomal translocations and 53BP1-recruitment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7673–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hada, M.; Georgakilas, A.G. Formation of clustered DNA damage after high-LET irradiation: A review. J. Radiat. Res. 2008, 49, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.F. Radiation Mutagenesis: The Initial DNA Lesions Responsible. Radiat. Res. 1995, 142, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, T.; Ilicic, K.; Greubel, C.; Girst, S.; Reindl, J.; Sammer, M.; Schwarz, B.; Siebenwirth, C.; Walsh, D.W.M.; Schmid, T.E.; et al. DNA damage interactions on both nanometer and micrometer scale determine overall cellular damage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psonka-Antonczyk, K.; Elsasser, T.; Gudowska-Nowak, E.; Taucher-Scholz, G. Distribution of double-strand breaks induced by ionizing radiation at the level of single DNA molecules examined by atomic force microscopy. Radiat. Res. 2009, 172, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickoloff, J.A.; Sharma, N.; Taylor, L. Clustered DNA Double-Strand Breaks: Biological Effects and Relevance to Cancer Radiotherapy. Genes 2020, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaithamby, A.; Chen, D.J. Mechanism of cluster DNA damage repair in response to high-atomic number and energy particles radiation. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, B.; Dubiak-Szepietowska, M.; Janiel, E.; Schmidt, A.; Durante, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G. Differential Repair Protein Recruitment at Sites of Clustered and Isolated DNA Double-Strand Breaks Produced by High-Energy Heavy Ions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, B.; Splinter, J.; Taucher-Scholz, G. Positional Stability of Damaged Chromatin Domains along Radiation Tracks in Mammalian Cells. Radiat. Res. 2009, 171, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorat, Y.; Brunner, C.U.; Schanz, S.; Jakob, B.; Taucher-Scholz, G.; Rube, C.E. Nanoscale analysis of clustered DNA damage after high-LET irradiation by quantitative electron microscopy-the heavy burden to repair. DNA Repair 2015, 28, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorat, Y.; Reindl, J.; Isermann, A.; Rube, C.; Friedl, A.A.; Rube, C.E. Focused Ion Microbeam Irradiation Induces Clustering of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Heterochromatin Visualized by Nanoscale-Resolution Electron Microscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasino, F.; Friedrich, T.; Scholz, U.; Taucher-Scholz, G.; Durante, M.; Scholz, M. A DNA double-strand break kinetic rejoining model based on the local effect model. Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povirk, L.F. Processing of damaged DNA ends for double-strand break repair in mammalian cells. ISRN Mol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 345805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbeck, N.B.; Ringel, O.; Herrlitz, M.; Jakob, B.; Durante, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G. DNA end resection is needed for the repair of complex lesions in G1-phase human cells. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, H.; Fujisawa, H.; Nakajima, N.I.; Hirakawa, H.; Jeggo, P.A.; Okayasu, R.; Fujimori, A. The complexity of DNA double strand breaks is a critical factor enhancing end-resection. DNA Repair 2013, 12, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbeck, N.B.; Topsch, J.; Scholz, M.; Kraft-Weyrather, W.; Durante, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G. Efficient Rejoining of DNA Double-Strand Breaks despite Increased Cell-Killing Effectiveness following Spread-Out Bragg Peak Carbon-Ion Irradiation. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, J.S.; Durante, M. Charged particle therapy--optimization, challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano-Diaz, C.; Orthwein, A.; Fradet-Turcotte, A.; Xing, M.; Young, J.T.; Tkac, J.; Cook, M.A.; Rosebrock, A.P.; Munro, M.; Canny, M.D.; et al. A cell cycle-dependent regulatory circuit composed of 53BP1-RIF1 and BRCA1-CtIP controls DNA repair pathway choice. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, A.; Kocher, S.; Volquardsen, J.; Petersen, C.; Borgmann, K.; Dikomey, E.; Rothkamm, K.; Mansour, W.Y. Impaired 53BP1/RIF1 DSB mediated end-protection stimulates CtIP-dependent end resection and switches the repair to PARP1-dependent end joining in G1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57679–57693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Fong, K.W.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. RIF1 counteracts BRCA1-mediated end resection during DNA repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11135–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertman, P.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Mailand, N. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifiers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmels, S.F.; Sartori, A.A. Controlling DNA-End Resection: An Emerging Task for Ubiquitin and SUMO. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolas, N.K.; Chapman, J.R.; Nakada, S.; Ylanko, J.; Chahwan, R.; Sweeney, F.D.; Panier, S.; Mendez, M.; Wildenhain, J.; Thomson, T.M.; et al. Orchestration of the DNA-damage response by the RNF8 ubiquitin ligase. Science 2007, 318, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailand, N.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Faustrup, H.; Melander, F.; Bartek, J.; Lukas, C.; Lukas, J. RNF8 Ubiquitylates Histones at DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Promotes Assembly of Repair Proteins. Cell 2007, 131, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquila, L.; Atanassov, B.S. Regulation of Histone Ubiquitination in Response to DNA Double Strand Breaks. Cells 2020, 9, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, I.H.; Gagne, J.P.; Genois, M.M.; Strickfaden, H.; McDonald, D.; Xu, Z.; Poirier, G.G.; Masson, J.Y.; Hendzel, M.J. The RNF138 E3 ligase displaces Ku to promote DNA end resection and regulate DNA repair pathway choice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.K.; Galanty, Y.; Sczaniecka-Clift, M.; Coates, J.; Jhujh, S.; Demir, M.; Cornwell, M.; Beli, P.; Jackson, S.P. Systematic E2 screening reveals a UBE2D-RNF138-CtIP axis promoting DNA repair. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Chen, J. The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.M.; Strickfaden, H.; Lee, B.L.; Spyracopoulos, L.; Hendzel, M.J. RYBP Is a K63-Ubiquitin-Chain-Binding Protein that Inhibits Homologous Recombination Repair. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggiolu, G.; Pomorski, M.; Claverie, G.; Berthet, G.; Mer-Calfati, C.; Saada, S.; Deves, G.; Simon, M.; Seznec, H.; Barberet, P. Single alpha-particle irradiation permits real-time visualization of RNF8 accumulation at DNA damaged sites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannone, S.M.; Roy, S.; Chan, D.W.; Murphy, M.B.; Huang, S.; Campisi, J.; Chen, D.J. Werner syndrome protein is regulated and phosphorylated by DNA-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38242–38248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riballo, E.; Kuhne, M.; Rief, N.; Doherty, A.; Smith, G.C.; Recio, M.J.; Reis, C.; Dahm, K.; Fricke, A.; Krempler, A.; et al. A pathway of double-strand break rejoining dependent upon ATM, Artemis, and proteins locating to gamma-H2AX foci. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue-Sawano, A.; Kurokawa, H.; Morimura, T.; Hanyu, A.; Hama, H.; Osawa, H.; Kashiwagi, S.; Fukami, K.; Miyata, T.; Miyoshi, H.; et al. Visualizing spatiotemporal dynamics of multicellular cell-cycle progression. Cell 2008, 132, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Guo, C.; Fournier, C.; Wilma, K. The influence of fractionation on cell survival and premature differentiation after carbon ion irradiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2008, 49, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, A.; Wiedemann, J.; Adrian, J.A.; Dornhecker, M.; Zipf, A.; Kraft-Weyrather, W.; Kraft, G.; Richter, S.; Teuscher, N.; Fournier, C. α-Irradiation setup for primary human cell cultures. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, B.; Scholz, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G. Biological imaging of heavy charged-particle tracks. Radiat. Res. 2003, 159, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, S.; Coates, J.; Jackson, S.P. A new method for high-resolution imaging of Ku foci to decipher mechanisms of DNA double-strand break repair. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbrich, M.; Shibata, A.; Beucher, A.; Fisher, A.; Ensminger, M.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Barton, O.; Jeggo, P.A. gammaH2AX foci analysis for monitoring DNA double-strand break repair: Strengths, limitations and optimization. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raderschall, E.; Golub, E.I.; Haaf, T. Nuclear foci of mammalian recombination proteins are located at single-stranded DNA regions formed after DNA damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landberg, G.; Erlanson, M.; Roos, G.; Tan, E.M.; Casiano, C.A. Nuclear autoantigen p330d/CENP-F: A marker for cell proliferation in human malignancies. Cytometry 1996, 25, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panier, S.; Boulton, S.J. Double-strand break repair: 53BP1 comes into focus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Boom, J.; Wolf, M.; Weimann, L.; Schulze, N.; Li, F.; Kaschani, F.; Riemer, A.; Zierhut, C.; Kaiser, M.; Iliakis, G.; et al. VCP/p97 Extracts Sterically Trapped Ku70/80 Rings from DNA in Double-Strand Break Repair. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehs, R.; Steinlage, M.; Barton, O.; Juhasz, S.; Kunzel, J.; Spies, J.; Shibata, A.; Jeggo, P.A.; Löbrich, M. DNA Double-Strand Break Resection Occurs during Non-homologous End Joining in G1 but Is Distinct from Resection during Homologous Recombination. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 671–684, e675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Conrad, S.; Birraux, J.; Geuting, V.; Barton, O.; Ismail, A.; Kakarougkas, A.; Meek, K.; Taucher-Scholz, G.; Löbrich, M.; et al. Factors determining DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. Embo J. 2011, 30, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, J.; Lukas, C. Molecular biology. Shielding broken DNA for a quick fix. Science 2013, 339, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Garcia, A.; Lopez-Saavedra, A.; Huertas, P. BRCA1 accelerates CtIP-mediated DNA-end resection. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isozaki, T.; Fujita, M.; Yamada, S.; Imadome, K.; Shoji, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Nakayama, F.; Imai, T.; Matsubara, H. Effects of carbon ion irradiation and X-ray irradiation on the ubiquitylated protein accumulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowsheen, S.; Aziz, K.; Aziz, A.; Deng, M.; Qin, B.; Luo, K.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Yu, J.; et al. L3MBTL2 orchestrates ubiquitin signalling by dictating the sequential recruitment of RNF8 and RNF168 after DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorslund, T.; Ripplinger, A.; Hoffmann, S.; Wild, T.; Uckelmann, M.; Villumsen, B.; Narita, T.; Sixma, T.K.; Choudhary, C.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; et al. Histone H1 couples initiation and amplification of ubiquitin signalling after DNA damage. Nature 2015, 527, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, M.; Mantiero, D.; Lucchini, G.; Longhese, M.P. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sae2 protein promotes resection and bridging of double strand break ends. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38631–38638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimatsu, N.; Mukherjee, B.; Deland, K.; Kurimasa, A.; Bolderson, E.; Khanna, K.K.; Burma, S. Exo1 plays a major role in DNA end resection in humans and influences double-strand break repair and damage signaling decisions. DNA Repair 2012, 11, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Averbeck, N.B.; Barent, C.; Jakob, B.; Syzonenko, T.; Durante, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G. The Ubiquitin Ligase RNF138 Cooperates with CtIP to Stimulate Resection of Complex DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Human G1-Phase Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162561
Averbeck NB, Barent C, Jakob B, Syzonenko T, Durante M, Taucher-Scholz G. The Ubiquitin Ligase RNF138 Cooperates with CtIP to Stimulate Resection of Complex DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Human G1-Phase Cells. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162561
Chicago/Turabian StyleAverbeck, Nicole B., Carina Barent, Burkhard Jakob, Tatyana Syzonenko, Marco Durante, and Gisela Taucher-Scholz. 2022. "The Ubiquitin Ligase RNF138 Cooperates with CtIP to Stimulate Resection of Complex DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Human G1-Phase Cells" Cells 11, no. 16: 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162561
APA StyleAverbeck, N. B., Barent, C., Jakob, B., Syzonenko, T., Durante, M., & Taucher-Scholz, G. (2022). The Ubiquitin Ligase RNF138 Cooperates with CtIP to Stimulate Resection of Complex DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Human G1-Phase Cells. Cells, 11(16), 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162561