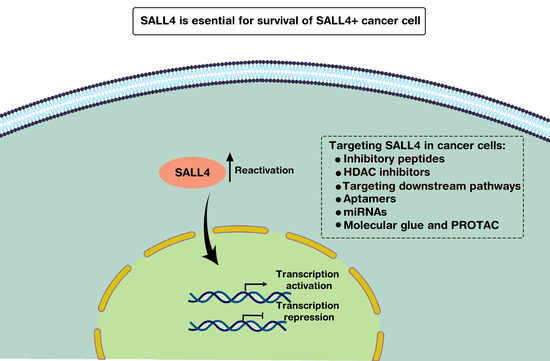
SALL4: An Intriguing Therapeutic Target in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanisms Leading to Aberrant Activation of SALL4 in Cancer
3. SALL4 Is Aberrantly Activated in Many Types of Cancers
3.1. SALL4 and Hematologic Malignancies
3.2. SALL4 and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.3. SALL4 and Colorectal Cancer
3.4. SALL4 and Breast Cancer
3.5. SALL4 and Lung Cancer
4. SALL4 as a Potential Therapeutic Target
4.1. Approach 1: Target SALL4 Function, the SALL4 Inhibitors
4.1.1. Targeting the Interaction of SALL4 with NuRD Complex
4.1.2. Inhibition of HDACs
4.2. Approach 2: Targeting SALL4 Downstream Pathways; Repurposing Oxidative Phosphorylation Drugs to Inhibit SALL4 Positive Cells
4.3. Approach 3: Modulating SALL4 Abundancy
4.3.1. Nucleic Acid-Based Therapy
4.3.2. SALL4 Degraders
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elling, U.; Klasen, C.; Eisenberger, T.; Anlag, K.; Treier, M. Murine inner cell mass-derived lineages depend on Sall4 function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16319–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.Q.; Anderson, A.; Kawakami, H.; Kim, J.; Barrett, J.; Kawakami, Y. Normal embryonic development and neonatal digit regeneration in mice overexpressing a stem cell factor, Sall4. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlhase, J.; Chitayat, D.; Kotzot, D.; Ceylaner, S.; Froster, U.G.; Fuchs, S.; Montgomery, T.; Rösler, B. SALL4 mutations in Okihiro syndrome (Duane-radial ray syndrome), acro-renal-ocular syndrome, and related disorders. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 26, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.B.R. SALL4 as a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator in normal and leukemic hematopoiesis. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miettinen, M.; Wang, Z.; McCue, P.A.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Rys, J.; Biernat, W.; Lasota, J.; Lee, Y.-S. SALL4 expression in germ cell and non-germ cell tumors: A systematic immunohistochemical study of 3215 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolè, L.; Sanavia, T.; Veronese, N.; Cappellesso, R.; Luchini, C.; Dabrilli, P.; Fassina, A. Oncofetal gene SALL4 and prognosis in cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22968–22979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kühnlein, R.P.; Frommer, G.; Friedrich, M.; Gonzalez-Gaitan, M.; Weber, A.; Wagner-Bernholz, J.F.; Gehring, W.J.; Jäckle, H.; Schuh, R. spalt encodes an evolutionarily conserved zinc finger protein of novel structure which provides homeotic gene function in the head and tail region of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatetsu, H.; Kong, N.R.; Chong, G.; Amabile, G.; Tenen, D.G.; Chai, L. SALL4, the missing link between stem cells, development and cancer. Gene 2016, 584, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweetman, D.; Smith, T.; Farrell, E.R.; Chantry, A.; Munsterberg, A. The conserved glutamine-rich region of chick csal1 and csal3 mediates protein interactions with other spalt family members. Implications for Townes-Brocks syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6560–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Yang, F.; Ren, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Dai, W. Identification of the nuclear localization signal of SALL4B, a stem cell transcription factor. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bard, J.D.; Gelebart, P.; Amin, H.M.; Young, L.C.; Ma, Y.; Lai, R. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is a transcriptional factor regulating the gene expression of SALL4. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Yoshihashi, K.; Suzuki, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Mutoh, H.; Maeda, S.; Yamagata, Y.; Seto, Y.; Aburatani, H.; Hatakeyama, M. CDX1 confers intestinal phenotype on gastric epithelial cells via induction of stemness-associated reprogramming factors SALL4 and KLF5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20584–20589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.Y.; Tam, W.L.; Zhang, J.; Ang, H.S.; Jia, H.; Lipovich, L.; Ng, H.H.; Wei, C.L.; Sung, W.K.; Robson, P.; et al. Sall4 regulates distinct transcription circuitries in different blastocyst-derived stem cell lineages. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Böhm, J.; Sustmann, C.; Wilhelm, C.; Kohlhase, J. SALL4 is directly activated by TCF/LEF in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Qian, J.; Yao, D.M.; Qian, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.Z.; Chai, H.Y.; Ma, J.C.; Deng, Z.Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Aberrant hypomethylation of SALL4 gene in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gao, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.C.; Kwon, J.; Qi, J.; Tian, X.; Stein, A.; Liu, Y.V.; Kong, N.R.; et al. Targeting an Inducible SALL4-Mediated Cancer Vulnerability with Sequential Therapy. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 6018–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Liu, Y.V.; Gao, C.; Bassal, M.A.; Jones, A.I.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Pseudogene-mediated DNA demethylation leads to oncogene activation. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Kwon, J.; Fabiani, E.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.V.; Follo, M.Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Gao, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Demethylation and Up-Regulation of an Oncogene after Hypomethylating Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1998–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Yu, R.; Yin, H.; Sun, T.; Sun, C.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Z. SALL4 suppresses PTEN expression to promote glioma cell proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 135, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Jeong, H.W.; Kong, N.; Yang, Y.; Carroll, J.; Luo, H.R.; Silberstein, L.E.; Yupoma; Chai, L. Stem cell factor SALL4 represses the transcriptions of PTEN and SALL1 through an epigenetic repressor complex. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.R.; Bassal, M.A.; Tan, H.K.; Kurland, J.V.; Yong, K.J.; Young, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Lee, J.D.; Liu, Y.; et al. Zinc Finger Protein SALL4 Functions through an AT-Rich Motif to Regulate Gene Expression. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.L.; Li, F.; Yeo, J.Z.; Yong, K.J.; Bassal, M.A.; Ng, G.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Leong, C.Y.; Tan, H.K.; Wu, C.S.; et al. New High-Throughput Screening Identifies Compounds That Reduce Viability Specifically in Liver Cancer Cells That Express High Levels of SALL4 by Inhibiting Oxidative Phosphorylation. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1615–1629.e1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Chai, L.; Fowles, T.C.; Alipio, Z.; Xu, D.; Fink, L.M.; Ward, D.C.; Ma, Y. Genome-wide analysis reveals Sall4 to be a major regulator of pluripotency in murine-embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19756–19761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Gao, C.; Chai, L.; Ma, Y. A novel SALL4/OCT4 transcriptional feedback network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, W.; Ni, L.; Liu, B.; Wei, Y.; Lv, Y.; Qiang, S.; Dong, J.; Liu, X. Upregulation of SALL4 by EGFR activation regulates the stemness of CD44-positive lung cancer. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, S.; Lu, J.; He, J.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Ritz, J.; Silberstein, L.E.; Chai, L. Aberrant expression of SALL4 in acute B cell lymphoblastic leukemia: Mechanism, function, and implication for a potential novel therapeutic target. Exp. Hematol. 2014, 42, 307–316.e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.-C.; Qian, J.; Lin, J.; Qian, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.-Z.; Chai, H.-Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Qian, Z. Aberrant hypomethylation of SALL4 gene is associated with intermediate and poor karyotypes in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, A.Y.; Fan, C.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, S.; Yu, D.; Huang, Z.; Liu, F.; et al. MicroRNA-33b Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis by Targeting HMGA2, SALL4 and Twist1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, T.; Song, Y.; Chai, L.; Li, Y. Low-expression of microRNA-107 inhibits cell apoptosis in glioma by upregulation of SALL4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sauer, M.A.; Hussein, S.G.; Yang, J.; Tenen, D.G.; Chai, L. SALL4 and microRNA: The Role of Let-7. Genes 2021, 12, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, F.; Mao, X.; Li, W.; Chen, H. Effect of SALL4 on the Proliferation, Invasion and Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820980074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Kong, J. High expression of SALL4 is associated with poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Killian, T.; Gatto, L. Exploiting the DepMap cancer dependency data using the depmap R package. F1000Research 2021, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Kong, N.R.; Ma, Y.; Amin, H.M.; Lai, R.; Chai, L. Differential expression of the novel oncogene, SALL4, in lymphoma, plasma cell myeloma, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Kong, N.R.; Li, A.; Tatetu, H.; Ueno, S.; Yang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, Y.; Kao, G.S.; et al. SALL4 is a key transcription regulator in normal human hematopoiesis. Transfusion 2013, 53, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.D.; Wu, F.; Ye, X.; Sharon, D.; Hitt, M.; McMullen, T.P.; Hegazy, S.A.; Gelebart, P.; Yang, J.; et al. The expression and oncogenic effects of the embryonic stem cell marker SALL4 in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ma, Y.; Kong, N.; Alipio, Z.; Gao, C.; Krause, D.S.; Silberstein, L.E.; Chai, L. Dissecting the role of SALL4, a newly identified stem cell factor, in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1211–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Zhou, D.; Shen, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q. Overexpression of the novel oncogene SALL4 and activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2009, 194, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Z.; Ning, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tong, C.; Chai, L.; et al. Stem cell factor SALL4, a potential prognostic marker for myelodysplastic syndromes. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Cui, W.; Yang, J.; Qu, J.; Di, C.; Amin, H.M.; Lai, R.; Ritz, J.; Krause, D.S.; Chai, L. SALL4, a novel oncogene, is constitutively expressed in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and induces AML in transgenic mice. Blood 2006, 108, 2726–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Gao, C.; Lu, J.; Tatetsu, H.; Williams, D.A.; Müller, L.U.; Cui, W.; Chai, L. Leukemic survival factor SALL4 contributes to defective DNA damage repair. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6087–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dimri, G.P.; Martinez, J.L.; Jacobs, J.J.; Keblusek, P.; Itahana, K.; Van Lohuizen, M.; Campisi, J.; Wazer, D.E.; Band, V. The Bmi-1 oncogene induces telomerase activity and immortalizes human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4736–4745. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Andrews, L.G.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Loss of the human polycomb group protein BMI1 promotes cancer-specific cell death. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4370–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Chai, L.; Liu, F.; Fink, L.M.; Lin, P.; Silberstein, L.E.; Amin, H.M.; Ward, D.C.; Ma, Y. Bmi-1 is a target gene for SALL4 in hematopoietic and leukemic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10494–10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Chai, L.; Gao, C.; Fowles, T.C.; Alipio, Z.; Dang, H.; Xu, D.; Fink, L.M.; Ward, D.C.; Ma, Y. SALL4 is a key regulator of survival and apoptosis in human leukemic cells. Blood 2008, 112, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Q.; Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, L.; Li, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. The differential expression pattern of the BMI-1, SALL4 and ABCA3 genes in myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell Int. 2012, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Lu, J.; Jeong, H.W.; Liu, B.H.; Tang, P.; Yao, X.; Neuberg, D.; Huang, G.; et al. A SALL4/MLL/HOXA9 pathway in murine and human myeloid leukemogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4195–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Leung, L.H.; Cooney, A.J.; Chen, C.; Rosengart, T.K.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J. Knockdown of SALL4 Protein Enhances All-trans Retinoic Acid-induced Cellular Differentiation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10599–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.W.; Cui, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; He, J.; Li, A.; Song, D.; Guo, Y.; Liu, B.H.; Chai, L. SALL4, a stem cell factor, affects the side population by regulation of the ATP-binding cassette drug transport genes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohadi, F.; Rahgozar, S.; Ghodousi, E.S. Sal-Like Protein 4 Transcription Factor: A Significant Diagnostic Biomarker Involved in Childhood ALL Resistance and Relapse. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hupfeld, T.; Chapuy, B.; Schrader, V.; Beutler, M.; Veltkamp, C.; Koch, R.; Cameron, S.; Aung, T.; Haase, D.; Larosee, P.; et al. Tyrosinekinase inhibition facilitates cooperation of transcription factor SALL4 and ABC transporter A3 towards intrinsic CML cell drug resistance. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Kohashi, K.; Yoshizumi, T.; Okumura, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Shimokawa, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Aishima, S.; Maehara, Y.; Oda, Y. Coexpression of SALL4 with HDAC1 and/or HDAC2 is associated with underexpression of PTEN and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 64, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.X.; Wang, J.L.; Guo, X.J.; He, C.C.; Ying, X.; Ma, J.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Q. Serum SALL4 is a novel prognosis biomarker with tumor recurrence and poor survival of patients in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 262385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, F.; Han, X.; Yao, S.K.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, H.C. Importance of SALL4 in the development and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Venkatramani, R.; Gomulia, E.; Shillingford, N.; Wang, L. The diagnostic and prognostic value of SALL4 in hepatoblastoma. Histopathology 2016, 69, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakaboski, E.; Jares, A.; Ma, Y. Stem cell gene SALL4 in aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma: A cancer stem cell-specific target? Hepatology 2014, 60, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yong, K.J.; Gao, C.; Lim, J.S.; Yan, B.; Yang, H.; Dimitrov, T.; Kawasaki, A.; Ong, C.W.; Wong, K.F.; Lee, S.; et al. Oncofetal gene SALL4 in aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2266–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikawa, T.; Kamiya, A.; Zeniya, M.; Chikada, H.; Hyuck, A.D.; Yamazaki, Y.; Wauthier, E.; Tajiri, H.; Miller, L.D.; Wang, X.W.; et al. Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4), a stem cell biomarker in liver cancers. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.S.; Yamashita, T.; Kondo, M.; Nio, K.; Hayashi, T.; Hara, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Hayashi, T.; Oishi, N.; et al. The transcription factor SALL4 regulates stemness of EpCAM-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- YYanagihara, N.; Kobayashi, D.; Kuribayashi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Watanabe, N. Significance of SALL4 as a drug-resistant factor in lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G. Association between quantitative parameters of CEUS and Sall4/Wnt/β-catenin signaling in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3339–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pantier, R.; Chhatbar, K.; Quante, T.; Skourti-Stathaki, K.; Cholewa-Waclaw, J.; Alston, G.; Alexander-Howden, B.; Lee, H.Y.; Cook, A.G.; Spruijt, C.G.; et al. SALL4 controls cell fate in response to DNA base composition. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Aishima, S.; Kohashi, K.; Okumura, Y.; Wang, H.; Hida, T.; Kotoh, K.; Shirabe, K.; Maehara, Y.; Takayanagi, R.; et al. Spalt-like transcription factor 4 immunopositivity is associated with epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression in combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Histopathology 2016, 68, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mani, S.K.; Diab, A.; Lefrancois, L.; Fares, N.; Merle, P.; Andrisani, O. DNA demethylation induces SALL4 gene re-expression in subgroups of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with Hepatitis B or C virus infection. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puccini, A.; Lenz, H.J. Colorectal cancer in 2017: Practice-changing updates in the adjuvant and metastatic setting. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Song, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; et al. Expression and clinical significance of SALL4 and β-catenin in colorectal cancer. J. Mol. Histol. 2016, 47, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.K.; Liu, C.; Fan, X.X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L. Spalt-like transcription factor 4 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2017, 20, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardalan Khales, S.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Abdollahi, A.; Raeisossadati, R.; Tousi, M.F.; Forghanifard, M.M. SALL4 as a new biomarker for early colorectal cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Sun, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Qian, H. MiR-3622a-3p acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by reducing stemness features and EMT through targeting spalt-like transcription factor 4. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Deng, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, P.; Wu, K.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Deng, M.; Gao, J.; et al. Inhibition of SALL4 suppresses carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer via regulating Gli1 expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10092–10101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesari, A.; Rajab, S.; Rezaei, M.; Basam, M.; Golmohamadi, S.; Ghasemi, F. Knockdown of Sal-like 4 expression by siRNA induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 11531–11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kuribayshi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, N. SALL4 is essential for cancer cell proliferation and is overexpressed at early clinical stages in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Xiao, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Shi, G.; Zhou, H.; Geng, J.; Ning, X.; Wu, J.; et al. High cytoplasmic expression of SALL4 predicts a malignant phenotype and poor prognosis of breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Neoplasma 2015, 62, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Z.; Ye, Y.Y.; Xu, F.; Niu, R.J.; Zhang, H.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.B.; Han, B.S. Knockdown of SALL4 inhibits the proliferation and reverses the resistance of MCF-7/ADR cells to doxorubicin hydrochloride. BMC Mol. Biol. 2016, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Itou, J.; Sato, F.; Toi, M. SALL4—KHDRBS3 network enhances stemness by modulating CD44 splicing in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, J.; Tanaka, S.; Li, W.; Iida, A.; Sehara-Fujisawa, A.; Sato, F.; Toi, M. The Sal-like 4—Integrin α6β1 network promotes cell migration for metastasis via activation of focal adhesion dynamics in basal-like breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, J.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Toi, M. Sal-like 4 (SALL4) suppresses CDH1 expression and maintains cell dispersion in basal-Like breast cancer. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3115–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, A.K.; Wang, C.; Zeng, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Wei, J.; Huang, G.; Mo, B.; Luo, M.; Mo, B. Expression and clinical significance of SALL4 and LGR5 in patients with lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3629–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kuribayashi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, N. Overexpression of SALL4 in lung cancer and its importance in cell proliferation. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimoto, M.; Sumiyoshi, S.; Yoshizawa, A.; Sonobe, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Moriyoshi, K.; Kido, A.; Tanaka, C.; Koyanagi, I.; Date, H.; et al. SALL4 immunohistochemistry in non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Histopathology 2014, 64, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, X.; You, Q.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Ou, J. Knockdown of SALL4 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human lung cancer cells in vivo and in vitro. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, K.J.; Li, A.; Ou, W.B.; Hong, C.K.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F.; Tatetsu, H.; Yan, B.; Qi, L.; Fletcher, J.A.; et al. Targeting SALL4 by entinostat in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75425–75440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, G.; Liu, C.T. Knockdown of SALL4 overcomes cisplatin-resistance through AKT/mTOR signaling in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 634–641. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Xu, L.; Bi, W.; Ou, W.-B. SALL4 Oncogenic Function in Cancers: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.-M.; Dong, J.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Cheng, X.-D.; Zhang, W.-D.; Qin, J.-J. PROTAC: An Effective Targeted Protein Degradation Strategy for Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 692574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Dimitrov, T.; Yong, K.J.; Tatetsu, H.; Jeong, H.W.; Luo, H.R.; Bradner, J.E.; Tenen, D.G.; Chai, L. Targeting transcription factor SALL4 in acute myeloid leukemia by interrupting its interaction with an epigenetic complex. Blood 2013, 121, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.H.; Jobichen, C.; Chia, C.S.B.; Chan, T.H.M.; Tang, J.P.; Chung, T.X.Y.; Li, J.; Poulsen, A.; Hung, A.W.; Koh-Stenta, X.; et al. Targeting cancer addiction for SALL4 by shifting its transcriptome with a pharmacologic peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7119–E7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shchepina, L.A.; Pletjushkina, O.Y.; Avetisyan, A.V.; Bakeeva, L.E.; Fetisova, E.K.; Izyumov, D.S.; Saprunova, V.B.; Vyssokikh, M.Y.; Chernyak, B.V.; Skulachev, V.P.J.O. Oligomycin, inhibitor of the F0 part of H+-ATP-synthase, suppresses the TNF-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8149–8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porporato, P.E.; Filigheddu, N.; Pedro, J.M.B.-S.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, J.; Menezes, M.R.; Cao, S.; Hagan, J.P. The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, B.; Wang, W.; Meng, X.-X.; Du, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Zhou, B.-H.; Fu, Z.-H. Let-7 inhibits self-renewal of hepatocellular cancer stem-like cells through regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Wnt signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.; Li, J.; Che, G.J.T.C.R. Prognostic value of let-7 in lung cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 6354–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Qiu, D.; Deng, J.; Jiao, X.; Yang, R.; Sun, Z.; Wan, X.; Li, J. Methylation-induced downregulation and tumor-suppressive role of microRNA-98 in glioma through targeting Sal-like protein 4. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Zou, B.; Liu, L.; Cui, K.; Gao, J.; Yuan, S.; Cong, N. MicroRNA-98 acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting SALL4. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74059–74073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Xing, X.; Jiang, C.; Guo, H.; Guan, Y. MiRNA-98 inhibits ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting SALL4. Minerva Med. 2021, 112, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.M.; Shi, X.L.; Xing, K.L.; Zhou, H.X.; Lu, L.L.; Wu, W.Z. miR-296-5p suppresses stem cell potency of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating Brg1/Sall4 axis. Cell. Signal. 2020, 72, 109650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Y. MicroRNA-16 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells by targeting Sal-like protein 4. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.P.; Zhang, N.N.; Ren, X.Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. miR-103/miR-195/miR-15b Regulate SALL4 and Inhibit Proliferation and Migration in Glioma. Molecules 2018, 23, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, B.; Li, M.; Ji, F.; Nie, Y. MicroRNA-219 exerts a tumor suppressive role in glioma via targeting Sal-like protein 4. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 6213–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hesari, A.; Anoshiravani, A.A.; Talebi, S.; Noruzi, S.; Mohammadi, R.; Salarinia, R.; Zare, R.; Ghasemi, F. Knockdown of sal-like 4 expression by small interfering RNA induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9392–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Hushmandi, K.; Rahmani Moghadam, E.; Zarrin, V.; Hosseinzadeh Kashani, S.; Bokaie, S.; Najafi, M.; Tavakol, S.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Nabavi, N.; et al. Progress in Delivery of siRNA-Based Therapeutics Employing Nano-Vehicles for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Xiang, J. Aptamers, the Nucleic Acid Antibodies, in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, Q.L.; Petzold, G.; Bunker, R.D.; Renneville, A.; Słabicki, M.; Liddicoat, B.J.; Abdulrahman, W.; Mikkelsen, T.; Ebert, B.L.; Thomä, N.H. Defining the human C2H2 zinc finger degrome targeted by thalidomide analogs through CRBN. Science 2018, 362, eaat0572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donovan, K.A.; An, J.; Nowak, R.P.; Yuan, J.C.; Fink, E.C.; Berry, B.C.; Ebert, B.L.; Fischer, E.S. Thalidomide promotes degradation of SALL4, a transcription factor implicated in Duane Radial Ray syndrome. ELife 2018, 7, e38430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneiro, M.; De Vita, E.; Conole, D.; Kounde, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tate, E.J.P.i.m.c. PROTACs, molecular glues and bifunctionals from bench to bedside: Unlocking the clinical potential of catalytic drugs. Prog. Med. Chem. 2021, 60, 67–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moein, S.; Tenen, D.G.; Amabile, G.; Chai, L. SALL4: An Intriguing Therapeutic Target in Cancer Treatment. Cells 2022, 11, 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162601
Moein S, Tenen DG, Amabile G, Chai L. SALL4: An Intriguing Therapeutic Target in Cancer Treatment. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoein, Shiva, Daniel G. Tenen, Giovanni Amabile, and Li Chai. 2022. "SALL4: An Intriguing Therapeutic Target in Cancer Treatment" Cells 11, no. 16: 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162601
APA StyleMoein, S., Tenen, D. G., Amabile, G., & Chai, L. (2022). SALL4: An Intriguing Therapeutic Target in Cancer Treatment. Cells, 11(16), 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162601