Challenging the Paradigm: Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins and Angiogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
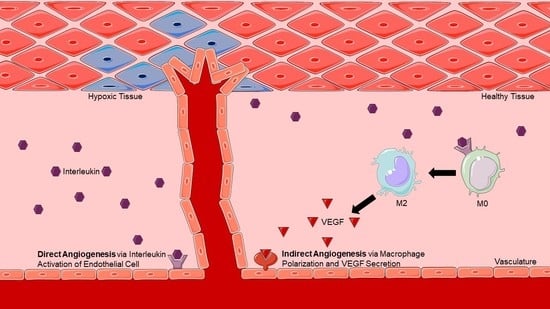
2. Direct Angiogenesis: Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelial-Induced Angiogenesis
3. Indirect Angiogenesis: Macrophage Polarization-Induced Angiogenesis
4. Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, T.L.; Domann, F.E.; Case, A.J. Limitations of oxygen delivery to cells in culture: An underappreciated problem in basic and translational research. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 113, 311–322, Erratum in Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 162, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, C.; Gerisch, A.; Chaplain, M.A.J. A novel nonlocal partial differential equation model of endothelial progenitor cell cluster formation during the early stages of vasculogenesis. J. Theor. Biol. 2022, 534, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, B.; Li, Z.; Xiao, W.; Li, G.; Ding, S.; Meng, A.; Jia, S. Sec14l3 potentiates VEGFR2 signaling to regulate zebrafish vasculogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Flores, L.; Gutiérrez, R.; González-Gómez, M.; García, M.A.P.; Carrasco, J.L.; Díaz-Flores, L., Jr.; Madrid, J.F.; Álvarez-Argüelles, H. Participation of Intussusceptive Angiogenesis in the Morphogenesis of Lobular Capillary Hemangioma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du Cheyne, C.; Smeets, M.; De Spiegelaere, W. Techniques used to assess intussusceptive angiogenesis: A systematic review. Dev. Dyn. 2021, 250, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Muñoz-Félix, J.M.; Pedrosa, A.R.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M. “Splitting the matrix”: Intussusceptive angiogenesis meets MT1-MMP. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hughes, E.D.; Saunders, T.L.; Wu, J.; Hernández Vásquez, M.N.; Makinen, T.; King, P.D. Angiogenesis depends upon EPHB4-mediated export of collagen IV from vascular endothelial cells. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e156928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, R.S.; Chen, D.S.; Ferrara, N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell 2019, 176, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adair, T.H.; Montani, J.P. Overview of Angiogenesis. In Angiogenesis; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010; Chapter 1. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53238/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Balberova, O.V.; Bykov, E.V.; Shnayder, N.A.; Petrova, M.M.; Gavrilyuk, O.A.; Kaskaeva, D.S.; Soloveva, I.A.; Petrov, K.V.; Mozheyko, E.Y.; Medvedev, G.V.; et al. The “Angiogenic Switch” and Functional Resources in Cyclic Sports Athletes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, C.; Ye, Q.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Endothelial deletion of SHP2 suppresses tumor angiogenesis and promotes vascular normalization. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, S.E.; Stabile, E.; Kinnaird, T.; Lee, C.W.; Clavijo, L.; Burnett, M.S. Janus phenomenon: The interrelated tradeoffs inherent in therapies designed to enhance collate.ral formation and those designed to inhibit atherogenesis. Circulation 2004, 109, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Cazares, D.; Chavez-Dominguez, R.; Carlos-Reyes, A.; Lopez-Camarillo, C.; Hernadez de la Cruz, O.N.; Lopez-Gonzalez, J.S. Contribution of Angiogenesis to Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, X.H.; Jin, L. Macrophage Polarization in Physiological and Pathological Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M. Angiogenesis: Where do we stand now? Circulation 2005, 111, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, G.H.; Takeda, K. Role and regulation of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jokilehto, T.; Jaakkola, P.M. The role of HIF prolyl hydroxylases in tumour growth. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, N.; Verbruggen, S.; Gijbels, M.J.; Post, M.J.; De Winther, M.P.; Donners, M.M. Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Zhang, S.X.; Wu, H.J.; Rong, X.L.; Guo, J. M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corliss, B.A.; Azimi, M.S.; Munson, J.M.; Peirce, S.M.; Murfee, W.L. Macrophages: An Inflammatory Link Between Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizzo, G.; Hilliard, B.A.; Monestier, M.; Cohen, P.L. Efficient clearance of early apoptotic cells by human macrophages requires M2c polarization and MerTK induction. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3508–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duluc, D.; Corvaisier, M.; Blanchard, S.; Catala, L.; Descamps, P.; Gamelin, E.; Ponsoda, S.; Delneste, Y.; Hebbar, M.; Jeannin, P. Interferon-gamma reverses the immunosuppressive and protumoral properties and prevents the generation of human tumor-associated macrophages. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Koch, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Jung, F.; Blocki, A. An In Vitro Model of Angiogenesis during Wound Healing Provides Insights into the Complex Role of Cells and Factors in the Inflammatory and Proliferation Phase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paukku, K.; Silvennoinen, O. STATs as critical mediators of signal transduction and transcription: Lessons learned from STAT5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, R.N. Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS): Inhibitors of the JAK/STAT pathway. Shock 2002, 17, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanada, T.; Yoshimura, A. Regulation of cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpert, O.V.; Fong, T.; Koch, A.E.; Peterson, J.D.; Waltenbaugh, C.; Tepper, R.I.; Bouck, N.P. Inhibition of angiogenesis by interleukin 4. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaji-Kegan, K.; Su, Q.; Angelini, D.J.; Johns, R.A. IL-4 is proangiogenic in the lung under hypoxic conditions. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5469–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Miyazaki, D.; Inata, K.; Uotani, R.; Miyake, H.; Sasaki, S.I.; Shimizu, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Nakamura, K. Role of IL-4 in bone marrow driven dysregulated angiogenesis and age-related macular degeneration. eLife 2020, 9, e54257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Chau, C.; Bao, J.; Tsoukas, M.M.; Chan, L.S. IL-4 dysregulates microRNAs involved in inflammation, angiogenesis and apoptosis in epidermal keratinocytes. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, M.; Harris, A.L.; Bicknell, R. Interleukin-4 is a potent mitogen for capillary endothelium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 174, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, J.; Morisaki, T.; Shono, T.; Nishie, A.; Torisu, H.; Ono, M.; Kuwano, M. Novel biological functions of interleukin-4: Formation of tube-like structures by vascular endothelial cells in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 250, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushi, J.; Ono, M.; Morikawa, W.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kuwano, M. The activity of soluble VCAM-1 in angiogenesis stimulated by IL-4 and IL-13. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, K.; Tse, H.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Ley, K. T cells in atherosclerosis. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohno, T.; Mizukami, H.; Suzuki, M.; Saga, Y.; Takei, Y.; Shimpo, M.; Matsushita, T.; Okada, T.; Hanazono, Y.; Kume, A.; et al. Interleukin-10-mediated inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth in mice bearing VEGF-producing ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5091–5094. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestre, J.S.; Mallat, Z.; Duriez, M.; Tamarat, R.; Bureau, M.F.; Scherman, D.; Duverger, N.; Branellec, D.; Tedgui, A.; Levy, B.I. Antiangiogenic effect of interleukin-10 in ischemia-induced angiogenesis in mice hindlimb. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Grötsch, B.; Luo, Y.; Knaup, K.X.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chen, X.X.; Jantsch, J.; Fillatreau, S.; Schett, G.; Bozec, A. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dace, D.S.; Khan, A.A.; Kelly, J.; Apte, R.S. Interleukin-10 promotes pathological angiogenesis by regulating macrophage response to hypoxia during development. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurier, E.B.; Dalton, D.; Dampier, W.; Raman, P.; Nassiri, S.; Ferraro, N.M.; Rajagopalan, R.; Sarmady, M.; Spiller, K.L. Transcriptome analysis of IL-10-stimulated (M2c) macrophages by next-generation sequencing. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halloran, M.M.; Haskell, C.J.; Woods, J.M.; Hosaka, S.; Koch, A.E. Interleukin-13 is an endothelial chemotaxin. Pathobiology 1997, 65, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Nitto, T.; Inoue, T.; Node, K. IL-13 attenuates vascular tube formation via JAK2-STAT6 pathway. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savetsky, I.L.; Ghanta, S.; Gardenier, J.C.; Torrisi, J.S.; García Nores, G.D.; Hespe, G.E.; Nitti, M.D.; Kataru, R.P.; Mehrara, B.J. Th2 cytokines inhibit lymphangiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.B.; Kotenko, S.V.; Yilmaz, M.; Mani, O.; Zumkehr, J.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. Regulation of T cells and cytokines by the interleukin-10 (IL-10)-family cytokines IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 and IL-26. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, G.; Dickensheets, H.; Eskdale, J.; Izotova, L.S.; Mirochnitchenko, O.V.; Peat, J.D.; Vazquez, N.; Pestka, S.; Donnelly, R.P.; Kotenko, S.V. Cloning, expression and initial characterization of interleukin-19 (IL-19), a novel homologue of human interleukin-10 (IL-10). Genes Immun. 2000, 1, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, G. Interleukin-19: Multiple roles in immune regulation and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, R.; Wallace, E.; Endesfelder, S.; Wolk, K. IL-19 and IL-20: Two novel cytokines with importance in inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autieri, M.V. IL-19 and Other IL-20 Family Member Cytokines in Vascular Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabunia, K.; Ellison, S.; Kelemen, S.; Kako, F.; Cornwell, W.D.; Rogers, T.J.; Datta, P.K.; Ouimet, M.; Moore, K.J.; Autieri, M.V. IL-19 Halts Progression of Atherosclerotic Plaque, Polarizes, and Increases Cholesterol Uptake and Efflux in Macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellison, S.; Gabunia, K.; Kelemen, S.E.; England, R.N.; Scalia, R.; Richards, J.M.; Orr, A.W.; Traylor, J.G., Jr.; Rogers, T.; Cornwell, W.; et al. Attenuation of experimental atherosclerosis by interleukin-19. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2316–2324, Erratum in Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, e1. Orr, Wayne [corrected to Orr, A Wayne]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- England, R.N.; Autieri, M.V. Anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin-19 in vascular disease. Int. J. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 253583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsing, C.H.; Li, H.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, C.L.; Chuang, S.S.; Lan, K.M.; Chang, M.S. The distribution of interleukin-19 in healthy and neoplastic tissue. Cytokine 2008, 44, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabunia, K.; Autieri, M.V. Interleukin-19 can enhance angiogenesis by Macrophage Polarization. Macrophage (Houst) 2015, 2, e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Gabunia, K.; Kelemen, S.E.; Panetti, T.S.; Autieri, M.V. The anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 19 is expressed by and angiogenic for human endothelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konrad, R.J.; Higgs, R.E.; Rodgers, G.H.; Ming, W.; Qian, Y.W.; Bivi, N.; Mack, J.K.; Siegel, R.W.; Nickoloff, B.J. Assessment and Clinical Relevance of Serum IL-19 Levels in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis Using a Sensitive and Specific Novel Immunoassay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azuma, Y.T.; Matsuo, Y.; Kuwamura, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Murphy, A.J.; Nakajima, H.; Karow, M.; Takeuchi, T. Interleukin-19 protects mice from innate-mediated colonic inflammation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Camarillo, G.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Granados, J.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K. Expression of interleukin (IL)-19 and IL-24 in inflammatory bowel disease patients: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Fu, T.; Gao, W.; Liu, H. Correlation of serum levels of HIF-1α and IL-19 with the disease progression of COPD: A retrospective study. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 3791–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, J.; Gabunia, K.; Kelemen, S.E.; Kako, F.; Choi, E.T.; Autieri, M.V. Interleukin-19 increases angiogenesis in ischemic hind limbs by direct effects on both endothelial cells and macrophage polarization. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 79, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kako, F.; Gabunia, K.; Ray, M.; Kelemen, S.E.; England, R.N.; Kako, B.; Scalia, R.G.; Autieri, M.V. Interleukin-19 induces angiogenesis in the absence of hypoxia by direct and indirect immune mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C931–C941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vrakas, C.N.; Herman, A.B.; Ray, M.; Kelemen, S.E.; Scalia, R.; Autieri, M.V. RNA stability protein ILF3 mediates cytokine-induced angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 3304–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Moriyama, M.; Miyake, K.; Nakashima, H.; Tanaka, A.; Maehara, T.; Iizuka-Koga, M.; Tsuboi, H.; Hayashida, J.N.; Ishiguro, N.; et al. Interleukin-33 produced by M2 macrophages and other immune cells contributes to Th2 immune reaction of IgG4-related disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirchandani, A.S.; Salmond, R.J.; Liew, F.Y. Interleukin-33 and the function of innate lymphoid cells. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Shi, L.; Mu, R.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Jia, R.; Yang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and interleukin 33 form a regulatory circuit to perpetuate the inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.M. Role of IL-33 in inflammation and disease. J. Inflamm. (Lond) 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, H.R.; Kewin, P.; Li, Y.; Mu, R.; Fraser, A.R.; Pitman, N.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; McKenzie, A.N.; McInnes, I.B.; et al. IL-33 exacerbates antigen-induced arthritis by activating mast cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10913–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Huang, T. Anti-IL-33 antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, H.J.; Min, J.K.; Pyun, B.J.; Maeng, Y.S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kwon, Y.G. Interleukin-33 induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production. Blood 2009, 114, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Stolarski, B.; Kewin, P.; Murphy, G.; Corrigan, C.J.; Ying, S.; Pitman, N.; Mirchandani, A.; Rana, B.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. IL-33 amplifies the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vailhé, B.; Vittet, D.; Feige, J.J. In vitro models of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Lab. Investig. 2001, 81, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Cytokine | Macrophage Phenotype Induced | Direct Angiogenic Potential |
|---|---|---|
| IL-4 | M2a [19,20] | Controversial [33,34,35,36,37] |
| IL-10 | M2c [19,20] | Controversial [40,41,42,43] |
| IL-13 | M2a [19,30] | Controversial [37,45,46,47] |
| IL-19 | M2a [57,63] | Yes [58,63,64,65] |
| IL-33 | M2a [19,74] | Yes [73] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peluzzo, A.M.; Autieri, M.V. Challenging the Paradigm: Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins and Angiogenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030587
Peluzzo AM, Autieri MV. Challenging the Paradigm: Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins and Angiogenesis. Cells. 2022; 11(3):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030587
Chicago/Turabian StylePeluzzo, Amanda M., and Michael V. Autieri. 2022. "Challenging the Paradigm: Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins and Angiogenesis" Cells 11, no. 3: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030587
APA StylePeluzzo, A. M., & Autieri, M. V. (2022). Challenging the Paradigm: Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins and Angiogenesis. Cells, 11(3), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030587