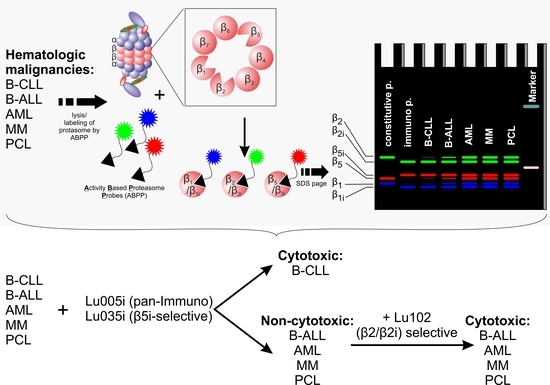
Immunoproteasome Activity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia as a Target of the Immunoproteasome-Selective Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Samples
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. CRISPR/Cas9 Knockout of PSMB5
2.4. Chemicals
2.5. Proteasome β-Subunits Profiling with Activity-Based Proteasome Probes Labelling
2.6. CTG Viability Assay
2.7. Lactate Dehydrogenase Quantification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. B-CLL Shows Exclusive Predominant Activity of the Immunoproteasome
3.2. B-CLL Is the Most Sensitive to Bortezomib and Carfilzomib
3.3. Immunoproteasome-Selective Proteasome Inhibitors Are Selectively Cytotoxic in B-CLL and Their Cytotoxicity Correlates with Immunoproteasome Activity
3.4. β2-Selective Proteasome Inhibitor Sensitizes Hematological Malignancies to β5i-Selective Immunoproteasome Inhibitor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daver, N.; Wei, A.H.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Vyas, P.; DiNardo, C.D. New directions for emerging therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: The next chapter. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstenau, M.; Eichhorst, B. Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chim, C.S.; Kumar, S.K.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Cook, G.; Richardson, P.G.; Gertz, M.A.; Giralt, S.; Mateos, M.V.; Leleu, X.; Anderson, K.C. Management of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: Novel agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond. Leukemia 2018, 32, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavralidis, A.; Brunner, A.M. Novel Therapies in the Treatment of Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2020, 15, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurnari, C.; Pagliuca, S.; Visconte, V. Deciphering the Therapeutic Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelo, D.J.; Jabbour, E.; Advani, A. Recent Advances in Managing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2020, 40, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skanland, S.S.; Mato, A.R. Overcoming resistance to targeted therapies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.N.; Sherbenou, D.W. Emerging Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, M.; Heinemeyer, W.; Jager, S.; Ullrich, T.; Bochtler, M.; Wolf, D.H.; Huber, R. The catalytic sites of 20S proteasomes and their role in subunit maturation: A mutational and crystallographic study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10976–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinemeyer, W.; Fischer, M.; Krimmer, T.; Stachon, U.; Wolf, D.H. The active sites of the eukaryotic 20 S proteasome and their involvement in subunit precursor processing. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25200–25209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Akopian, T.N.; Castillo, V.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome active sites allosterically regulate each other, suggesting a cyclical bite-chew mechanism for protein breakdown. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, A.; Besse, L.; Kraus, M.; Mendez-Lopez, M.; Bader, J.; Xin, B.T.; de Bruin, G.; Maurits, E.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Driessen, C. Proteasome Inhibition in Multiple Myeloma: Head-to-Head Comparison of Currently Available Proteasome Inhibitors. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 26, 340–351.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, M.; Bader, J.; Geurink, P.P.; Weyburne, E.S.; Mirabella, A.C.; Silzle, T.; Shabaneh, T.B.; van der Linden, W.A.; de Bruin, G.; Haile, S.R.; et al. The novel beta2-selective proteasome inhibitor LU-102 synergizes with bortezomib and carfilzomib to overcome proteasome inhibitor resistance of myeloma cells. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weyburne, E.S.; Wilkins, O.M.; Sha, Z.; Williams, D.A.; Pletnev, A.A.; de Bruin, G.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Goldberg, A.L.; Cole, M.D.; Kisselev, A.F. Inhibition of the Proteasome beta2 Site Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to beta5 Inhibitors and Suppresses Nrf1 Activation. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuazon, S.A.; Holmberg, L.A.; Nadeem, O.; Richardson, P.G. A clinical perspective on plasma cell leukemia; current status and future directions. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahler, J.C.; Ruiz, S.; Niemer, I.; Calvert, L.R.; Andreeff, M.; Keating, M.; Faderl, S.; McConkey, D.J. Effects of the proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, on apoptosis in isolated lymphocytes obtained from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4570–4577. [Google Scholar]
- Lamothe, B.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; Gandhi, V. Carfilzomib Triggers Cell Death in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia by Inducing Proapoptotic and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Responses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4712–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almond, J.B.; Snowden, R.T.; Hunter, A.; Dinsdale, D.; Cain, K.; Cohen, G.M. Proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis of B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells involves cytochrome c release and caspase activation, accompanied by formation of an approximately 700 kDa Apaf-1 containing apoptosome complex. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.V.; Hertlein, E.; Lu, Y.; Sass, E.J.; Lapalombella, R.; Chen, T.L.; Davis, M.E.; Woyach, J.A.; Lehman, A.; Jarjoura, D.; et al. The proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib functions independently of p53 to induce cytotoxicity and an atypical NF-kappaB response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2406–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Rhyasen, G.; Bolanos, L.; Rasch, C.; Varney, M.; Wunderlich, M.; Goyama, S.; Jansen, G.; Cloos, J.; Rigolino, C.; et al. Cytotoxic effects of bortezomib in myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia depend on autophagy-mediated lysosomal degradation of TRAF6 and repression of PSMA1. Blood 2012, 120, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapnes, C.; Doskeland, A.P.; Hatfield, K.; Ersvaer, E.; Ryningen, A.; Lorens, J.B.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Bruserud, O. The proteasome inhibitors bortezomib and PR-171 have antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects on primary human acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 136, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Inukai, T.; Imamura, T.; Yano, M.; Tomoyasu, C.; Lucas, D.M.; Nemoto, A.; Sato, H.; Huang, M.; Abe, M.; et al. Anti-leukemic activity of bortezomib and carfilzomib on B-cell precursor ALL cell lines. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faderl, S.; Rai, K.; Gribben, J.; Byrd, J.C.; Flinn, I.W.; O’Brien, S.; Sheng, S.; Esseltine, D.L.; Keating, M.J. Phase II study of single-agent bortezomib for the treatment of patients with fludarabine-refractory B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2006, 107, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.T.; Flynn, J.M.; Jones, J.A.; Andritsos, L.A.; Maddocks, K.J.; Sass, E.J.; Lucas, M.S.; Chase, W.; Waymer, S.; Ling, Y.; et al. Phase I dose escalation trial of the novel proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib in patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wartman, L.D.; Fiala, M.A.; Fletcher, T.; Hawkins, E.R.; Cashen, A.; DiPersio, J.F.; Jacoby, M.A.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.E.; Pusic, I.; Uy, G.L.; et al. A phase I study of carfilzomib for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarlo, C.; Buccisano, F.; Maurillo, L.; Cefalo, M.; Di Caprio, L.; Cicconi, L.; Ditto, C.; Ottaviani, L.; Di Veroli, A.; Del Principe, M.I.; et al. Phase II Study of Bortezomib as a Single Agent in Patients with Previously Untreated or Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia Ineligible for Intensive Therapy. Leuk. Res. Treatment. 2013, 2013, 705714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Takahama, Y.; Kasahara, M.; Tanaka, K. The immunoproteasome and thymoproteasome: Functions, evolution and human disease. Nat. Immunol 2018, 19, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewerth, D.; Kaspers, G.J.; Assaraf, Y.G.; van Meerloo, J.; Kirk, C.J.; Anderl, J.; Blank, J.L.; van de Ven, P.M.; Zweegman, S.; Jansen, G.; et al. Interferon-gamma-induced upregulation of immunoproteasome subunit assembly overcomes bortezomib resistance in human hematological cell lines. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verbrugge, S.E.; Scheper, R.J.; Lems, W.F.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Jansen, G. Proteasome inhibitors as experimental therapeutics of autoimmune diseases. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raule, M.; Cerruti, F.; Benaroudj, N.; Migotti, R.; Kikuchi, J.; Bachi, A.; Navon, A.; Dittmar, G.; Cascio, P. PA28alphabeta reduces size and increases hydrophilicity of 20S immunoproteasome peptide products. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tubio-Santamaria, N.; Ebstein, F.; Heidel, F.H.; Kruger, E. Immunoproteasome Function in Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis. Cells 2021, 10, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, D.J.; Orlowski, R.Z. The immunoproteasome as a target in hematologic malignancies. Semin. Hematol. 2012, 49, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Bruin, G.; Xin, B.T.; Kraus, M.; van der Stelt, M.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kisselev, A.F.; Driessen, C.; Florea, B.I.; Overkleeft, H.S. A Set of Activity-Based Probes to Visualize Human (Immuno)proteasome Activities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 4199–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, G.; Huber, E.M.; Xin, B.T.; van Rooden, E.J.; Al-Ayed, K.; Kim, K.B.; Kisselev, A.F.; Driessen, C.; van der Stelt, M.; van der Marel, G.A.; et al. Structure-based design of beta1i or beta5i specific inhibitors of human immunoproteasomes. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6197–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeussler, M.; Schonig, K.; Eckert, H.; Eschstruth, A.; Mianne, J.; Renaud, J.B.; Schneider-Maunoury, S.; Shkumatava, A.; Teboul, L.; Kent, J.; et al. Evaluation of off-target and on-target scoring algorithms and integration into the guide RNA selection tool CRISPOR. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.E.; Canver, M.C.; Orkin, S.H. Generation of genomic deletions in mammalian cell lines via CRISPR/Cas9. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 95, e52118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, K.; Thomaschewski, M.; Benten, D.; Fehse, B. RGB marking with lentiviral vectors for multicolor clonal cell tracking. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, C.; Berger, T.; Groettrup, M.; Basler, M. Immunoproteasome Inhibition Impairs T and B Cell Activation by Restraining ERK Signaling and Proteostasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome inhibitors: From research tools to drug candidates. Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisselev, A.F.; van der Linden, W.A.; Overkleeft, H.S. Proteasome inhibitors: An expanding army attacking a unique target. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackburn, C.; Gigstad, K.M.; Hales, P.; Garcia, K.; Jones, M.; Bruzzese, F.J.; Barrett, C.; Liu, J.X.; Soucy, T.A.; Sappal, D.S.; et al. Characterization of a new series of non-covalent proteasome inhibitors with exquisite potency and selectivity for the 20S beta5-subunit. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demo, S.D.; Kirk, C.J.; Aujay, M.A.; Buchholz, T.J.; Dajee, M.; Ho, M.N.; Jiang, J.; Laidig, G.J.; Lewis, E.R.; Parlati, F.; et al. Antitumor activity of PR-171, a novel irreversible inhibitor of the proteasome. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6383–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Screen, M.; Britton, M.; Downey, S.L.; Verdoes, M.; Voges, M.J.; Blom, A.E.; Geurink, P.P.; Risseeuw, M.D.; Florea, B.I.; van der Linden, W.A.; et al. Nature of pharmacophore influences active site specificity of proteasome inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40125–40134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, E.M.; Basler, M.; Schwab, R.; Heinemeyer, W.; Kirk, C.J.; Groettrup, M.; Groll, M. Immuno- and constitutive proteasome crystal structures reveal differences in substrate and inhibitor specificity. Cell 2012, 148, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, B.T.; de Bruin, G.; Huber, E.M.; Besse, A.; Florea, B.I.; Filippov, D.V.; van der Marel, G.A.; Kisselev, A.F.; van der Stelt, M.; Driessen, C.; et al. Structure-Based Design of beta5c Selective Inhibitors of Human Constitutive Proteasomes. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7177–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey-Kopyscinski, S.; Daily, E.W.; Gautier, M.; Bhatt, A.; Florea, B.I.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Richardson, P.G.; Driessen, C.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kisselev, A.F. An inhibitor of proteasome beta2 sites sensitizes myeloma cells to immunoproteasome inhibitors. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurink, P.P.; van der Linden, W.A.; Mirabella, A.C.; Gallastegui, N.; de Bruin, G.; Blom, A.E.; Voges, M.J.; Mock, E.D.; Florea, B.I.; van der Marel, G.A.; et al. Incorporation of non-natural amino acids improves cell permeability and potency of specific inhibitors of proteasome trypsin-like sites. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niewerth, D.; Franke, N.E.; Jansen, G.; Assaraf, Y.G.; van Meerloo, J.; Kirk, C.J.; Degenhardt, J.; Anderl, J.; Schimmer, A.D.; Zweegman, S.; et al. Higher ratio immune versus constitutive proteasome level as novel indicator of sensitivity of pediatric acute leukemia cells to proteasome inhibitors. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, T.W.; Downey-Kopyscinski, S.L.; Fields, J.L.; Rahme, G.J.; Colley, W.C.; Israel, M.A.; Maksimenko, A.V.; Fiering, S.N.; Kisselev, A.F. Activity of immunoproteasome inhibitor ONX-0914 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia expressing MLL-AF4 fusion protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, L.; Besse, A.; Kraus, M.; Maurits, E.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Bornhauser, B.; Bourquin, J.P.; Driessen, C. High Immunoproteasome Activity and sXBP1 in Pediatric Precursor B-ALL Predicts Sensitivity towards Proteasome Inhibitors. Cells 2021, 10, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heink, S.; Ludwig, D.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Kruger, E. IFN-gamma-induced immune adaptation of the proteasome system is an accelerated and transient response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9241–9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groettrup, M.; Standera, S.; Stohwasser, R.; Kloetzel, P.M. The subunits MECL-1 and LMP2 are mutually required for incorporation into the 20S proteasome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8970–8975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Javitt, A.; Barnea, E.; Kramer, M.P.; Wolf-Levy, H.; Levin, Y.; Admon, A.; Merbl, Y. Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Alter the Immunopeptidome Landscape by Modulation of HLA-B Expression. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, A.M.; Koop, A.L.; Teoh, C.Y.; Ermak, G.; Grune, T.; Davies, K.J. The immunoproteasome, the 20S proteasome and the PA28alphabeta proteasome regulator are oxidative-stress-adaptive proteolytic complexes. Biochem. J. 2010, 432, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wulaningsih, W.; Holmberg, L.; Garmo, H.; Malmstrom, H.; Lambe, M.; Hammar, N.; Walldius, G.; Jungner, I.; Ng, T.; Van Hemelrijck, M. Serum lactate dehydrogenase and survival following cancer diagnosis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimazal, F.; Sperr, W.R.; Kundi, M.; Vales, A.; Fonatsch, C.; Thalhammer-Scherrer, R.; Schwarzinger, I.; Valent, P. Prognostic significance of serial determinations of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the follow-up of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germing, U.; Hildebrandt, B.; Pfeilstocker, M.; Nosslinger, T.; Valent, P.; Fonatsch, C.; Lubbert, M.; Haase, D.; Steidl, C.; Krieger, O.; et al. Refinement of the international prognostic scoring system (IPSS) by including LDH as an additional prognostic variable to improve risk assessment in patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Leukemia 2005, 19, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, W.; Li, H.; Lv, R.; Liu, W.; Yi, S.; Li, Z.; Qiu, L. Prognostic Significance of Serum LDH in B Cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A Single-Institution Study of 829 Cases in China. Blood 2016, 128, 5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, M.; Lindstrom, M.M.; LaStant, J.J.; Bradshaw, J.M.; Owens, T.D.; Schmidt, C.; Maurits, E.; Tsu, C.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kirk, C.J.; et al. Co-inhibition of immunoproteasome subunits LMP2 and LMP7 is required to block autoimmunity. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e46512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Shao, J.; He, R.; Xi, J.; Zhuang, R.; Zhang, J. Immunoproteasome-selective inhibitors: The future of autoimmune diseases? Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanderson, M.P.; Friese-Hamim, M.; Walter-Bausch, G.; Busch, M.; Gaus, S.; Musil, D.; Rohdich, F.; Zanelli, U.; Downey-Kopyscinski, S.L.; Mitsiades, C.S.; et al. M3258 Is a Selective Inhibitor of the Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (beta5i) Delivering Efficacy in Multiple Myeloma Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloot, W.; Glaser, N.; Hansen, A.; Hellmann, J.; Jaeckel, S.; Johannes, S.; Knippel, A.; Lai, V.; Onidi, M. Improved nonclinical safety profile of a novel, highly selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 (M3258). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 429, 115695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| AML | B-ALL | B-CLL | MM | PCL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nr of patients | 16 | 3 | 17 | 6 | 5 |
| Male-females (%) | 62–38% | 33–67% | 65–35% | 50–50% | 20–80% |
| Age (median; min–max) | 64 (32–84) | 35 (28–38) | 69 (54–81) | 74 (56–84) | 60 (51–69) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Besse, A.; Kraus, M.; Mendez-Lopez, M.; Maurits, E.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Driessen, C.; Besse, L. Immunoproteasome Activity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia as a Target of the Immunoproteasome-Selective Inhibitors. Cells 2022, 11, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050838
Besse A, Kraus M, Mendez-Lopez M, Maurits E, Overkleeft HS, Driessen C, Besse L. Immunoproteasome Activity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia as a Target of the Immunoproteasome-Selective Inhibitors. Cells. 2022; 11(5):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050838
Chicago/Turabian StyleBesse, Andrej, Marianne Kraus, Max Mendez-Lopez, Elmer Maurits, Herman S. Overkleeft, Christoph Driessen, and Lenka Besse. 2022. "Immunoproteasome Activity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia as a Target of the Immunoproteasome-Selective Inhibitors" Cells 11, no. 5: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050838
APA StyleBesse, A., Kraus, M., Mendez-Lopez, M., Maurits, E., Overkleeft, H. S., Driessen, C., & Besse, L. (2022). Immunoproteasome Activity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia as a Target of the Immunoproteasome-Selective Inhibitors. Cells, 11(5), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050838