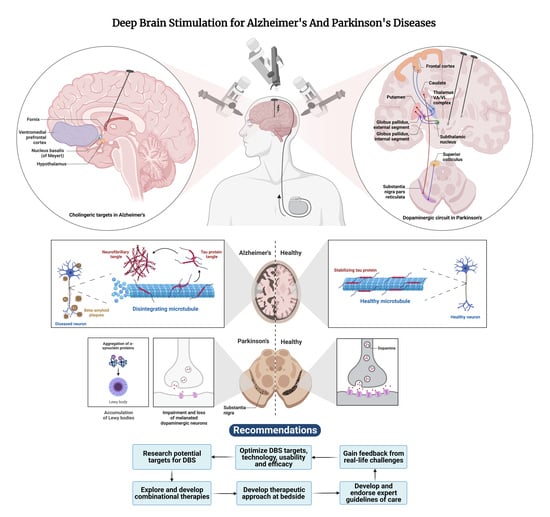
Deep Brain Stimulation beyond the Clinic: Navigating the Future of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Deep Brain Stimulation
3.1. History of DBS
3.2. Current Treatment Plans
3.3. Patient Screening
3.4. Procedure and Mechanism of Action
4. DBS in Parkinson’s Disease
4.1. Pathology of PD
4.2. Current Treatments for PD
4.3. Use of DBS in the Treatment of PD
4.4. Mechanisms of Action of DBS on PD
4.5. Criteria for Successful Treatment of DBS in PD
4.6. Parameters for DBS use in PD
4.7. Effect of Age on the Effectiveness of DBS on PD
4.8. Adverse Effects of DBS in PD
5. DBS in Alzheimer’s Disease
5.1. Pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease
5.2. Current Therapeutics in AD
5.3. Use of DBS Treatment in AD
5.4. Mechanisms of Action of DBS in AD
5.5. Criteria for Successful Applications of DBS in AD
5.6. The Effect of Age on the Effectiveness of DBS in AD
5.7. Adverse Effects of DBS in AD
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichols, E.; Szoeke, C.E.I.; Vollset, S.E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Aichour, M.T.E.; Akinyemi, R.O.; Alahdab, F.; Asgedom, S.W.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.V.F.; Loures, C.D.M.G.; Alves, L.C.V.; de Souza, L.C.; Borges, K.B.G.; Carvalho, M.D.G. Alzheimer’s disease: Risk factors and potentially protective measures. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumtaz, S.; Rana, J.N.; Choi, E.H.; Han, I. Microwave Radiation and the Brain: Mechanisms, Current Status, and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, P.T.; Head, E.; Schmitt, F.A.; Davis, P.R.; Neltner, J.H.; Jicha, G.A.; Abner, E.L.; Smith, C.D.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Kryscio, R.J.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease is not “brain aging”: Neuropathological, genetic, and epidemiological human studies. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twelves, D.; Perkins, K.S.; Counsell, C. Systematic review of incidence studies of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamarre, A.; Meissner, W.G. Epidemiology, environmental risk factors and genetics of Parkinson’s disease. La Presse Médicale 2017, 46, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Schwarzschild, M.A. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, V.W.; Nicholas, A.P. Nonmotor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: Expanding the View of Parkinson’s Disease Beyond a Pure Motor, Pure Dopaminergic Problem. Neurol. Clin. 2013, 31, S1–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P.; Chabardes, S.; Chang, J.W.; Matthews, K.; McIntyre, C.C.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Schulder, M.; et al. Deep brain stimulation: Current challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Du, A.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.P. Deep Brain Stimulation: A Potential Treatment for Dementia in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Parkinson’s Disease Dementia (PDD). Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouraki, V.; Seshadri, S. Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Genet. 2014, 87, 245–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hou, N.-N.; Wu, H.-M.; Zuo, X.; Lian, Y.-Z.; Zhang, C.-N.; Wang, Z.-F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.-H. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease in China: An Updated Systematical Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 603854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Brundin, P. Parkinson Disease Epidemiology, Pathology, Genetics, and Pathophysiology. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandybur, G. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s & Essential Tremor|Mayfield Brain & Spine, Cincinnati, (n.d.). Available online: https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-dbs.htm (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Amon, A.; Alesch, F. Systems for deep brain stimulation: Review of technical features. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrent, A.G. History of Surgery for Movement Disorders. In Textbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1467–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchiel, K.J. Thalamotomy for Movement Disorders. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 6, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miocinovic, S.; Somayajula, S.; Chitnis, S.; Vitek, J.L. History, Applications, and Mechanisms of Deep Brain Stimulation. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, E.A. Stereoencephalotomy. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1952, 148, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohye, C.; Kubota, K.; Hongo, T.; Nagao, T.; Narabayashi, H. Ventrolateral and Subventrolateral Thalamic Stimulation. Arch. Neurol. 1964, 11, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarket Approval (PMA), (n.d.). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfPMA/pma.cfm?id=P960009 (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Deuschl, G.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Krack, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schäfer, H.; Bötzel, K.; Daniels, C.; Deutschländer, A.; Dillmann, U.; Eisner, W.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Vigil, J.; MacCracken, E.; Gasparaitis, A.; Young, J.; Kang, W.; Bernard, J.; Warnke, P.; Kang, U.J. Low-frequency stimulation of STN-DBS reduces aspiration and freezing of gait in patients with PD. Neurology 2014, 84, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomstedt, P.; Persson, R.S.; Hariz, G.-M.; Linder, J.; Fredricks, A.; Häggström, B.; Philipsson, J.; Forsgren, L.; Hariz, M. Deep brain stimulation in the caudal zona incerta versus best medical treatment in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomised blinded evaluation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Mavinkurve, G.; Russo, G.S.; Walter, B.; DeLong, M.R.; Bakay, R.A.; Vitek, J.L. Somatotopic organization in the internal segment of the globus pallidus in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 222, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowska, K. Zona incerta as a therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2019, 267, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevathasan, W.; Debu, B.; Aziz, T.; Bloem, B.R.; Blahak, C.; Butson, C.; Czernecki, V.; Foltynie, T.; Fraix, V.; Grabli, D.; et al. Pedunculopontine nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: A clinical review. Mov. Disord. 2017, 33, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baizabal-Carvallo, J.F.; Kagnoff, M.N.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Fekete, R.; Jankovic, J. The safety and efficacy of thalamic deep brain stimulation in essential tremor: 10 years and beyond. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 85, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytagoridis, A.; Sandvik, U.; Åström, M.; Bergenheim, T.; Blomstedt, P. Long term follow-up of deep brain stimulation of the caudal zona incerta for essential tremor. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 83, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidailhet, M.; Jutras, M.-F.; Roze, E.; Grabli, D. Deep brain stimulation for dystonia. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 116, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-G.; Mao, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Cui, Z.-Q.; Pan, L.-S.; Ning, X.-J.; Xu, B.-X.; Ma, L.; Ling, Z.-P.; et al. Partial improvement in performance of patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease at an early stage of fornix deep brain stimulation. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Fosdick, L.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Leoutsakos, J.-M.; Munro, C.; Oh, E.; Drake, K.E.; Lyman, C.H.; Rosenberg, P.B.; Anderson, W.S.; et al. A Phase II Study of Fornix Deep Brain Stimulation in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 54, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharre, D.W.; Weichart, E.; Nielson, D.; Zhang, J.; Agrawal, P.; Sederberg, P.B.; Knopp, M.V.; Rezai, A.R.; Initiative, F.T.A.D.N. Deep Brain Stimulation of Frontal Lobe Networks to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, M.M.; Hamani, C.; Martinez-Canabal, A.; Ellegood, J.; Laliberté, C.; Nobrega, J.N.; Sankar, T.; Lozano, A.M.; Frankland, P.W.; Lerch, J.P. Deep brain stimulation of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex causes reorganization of neuronal processes and vasculature. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxton, A.W.; Tang-Wai, D.F.; McAndrews, M.P.; Zumsteg, D.; Wennberg, R.; Keren, R.; Wherrett, J.; Naglie, G.; Hamani, C.; Smith, G.S.; et al. A phase I trial of deep brain stimulation of memory circuits in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.; Hardenacke, K.; Lenartz, D.; Gruendler, T.; Ullsperger, M.; Bartsch, C.; Mai, J.K.; Zilles, K.; Bauer, A.; Matusch, A.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer’s dementia. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 20, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Lago, F.M.; Thompson, A.; Oyama, G.; Hardwick, A.; Sporrer, J.M.; Zeilman, P.; Foote, K.D.; Bowers, D.; Ward, H.E.; Sanchez-Ramos, J.; et al. Differential and Better Response to Deep Brain Stimulation of Chorea Compared to Dystonia in Huntington’s Disease. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2013, 91, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.; Evans, A.; Bear, R.E.; Velakoulis, D.; Bittar, R.G. The anteromedial GPi as a new target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive compulsive disorder. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, W.; Lenartz, D.; Schormann, M.; Lee, S.-H.; Kuhn, J.; Koulousakis, A.; Mai, J.; Daumann, J.; Maarouf, M.; Klosterkötter, J.; et al. Unilateral deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in patients with treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: Outcomes after one year. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, D.; Mantione, M.; Figee, M.; Munckhof, P.V.D.; Koerselman, F.; Westenberg, H.; Bosch, A.; Schuurman, R. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Nucleus Accumbens for Treatment-Refractory Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, D.; Graat, I.; Mocking, R.; de Koning, P.; Vulink, N.; Figee, M.; Ooms, P.; Mantione, M.; Munckhof, P.V.D.; Schuurman, R. Efficacy of Deep Brain Stimulation of the Ventral Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule for Refractory Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Clinical Cohort of 70 Patients. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammen, A.; Cavaleri, J.; Lam, J.; Frank, A.C.; Mason, X.; Choi, W.; Penn, M.; Brasfield, K.; Van Noppen, B.; Murray, S.B.; et al. Neuromodulation of OCD: A review of invasive and non-invasive methods. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 909264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-S.; Sammartino, F.; Young, N.A.; Corrigan, J.; Krishna, V.; Rezai, A.R. Anatomic Review of the Ventral Capsule/Ventral Striatum and the Nucleus Accumbens to Guide Target Selection for Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, B.D.; A Gabriels, L.; A Malone, D.; Rezai, A.R.; Friehs, G.M.; Okun, M.; A Shapira, N.; Foote, K.; Cosyns, P.R.; Kubu, C.S.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral internal capsule/ventral striatum for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Worldwide experience. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 15, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Baldermann, J.C.; Kibleur, A.; Treu, S.; Akram, H.; Elias, G.J.B.; Boutet, A.; Lozano, A.M.; Al-Fatly, B.; Strange, B.; et al. A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabardès, S.; Polosan, M.; Krack, P.; Bastin, J.; Krainik, A.; David, O.; Bougerol, T.; Benabid, A.L. Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Subthalamic Nucleus Target. World Neurosurg. 2012, 80, S31.e1–S31.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, J.; Boutet, A.; Elias, G.J.; Gouveia, F.V.; Loh, A.; Giacobbe, P.; Bhat, V.; Kucharczyk, W.; Lozano, A.M. Brain Structures and Networks Underlying Treatment Response to Deep Brain Stimulation Targeting the Inferior Thalamic Peduncle in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2022, 100, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Dallapiazza, R.F.; De Vloo, P.; Elias, G.J.; Fomenko, A.; Boutet, A.; Giacobbe, P.; Lozano, A.M. Inferior thalamic peduncle deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: A phase 1 pilot trial. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyten, L.; Hendrickx, S.; Raymaekers, S.; Gabriels, L.; Nuttin, B. Electrical stimulation in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis alleviates severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 21, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, P.E.; Windels, F.; Morris, J.; Coyne, T.; Marsh, R.; Giorni, A.; Mohan, A.; Sachdev, P.; O’leary, E.; Boschen, M.; et al. A randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled trial of deep brain stimulation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymaekers, S.; Vansteelandt, K.; Luyten, L.; Bervoets, C.; Demyttenaere, K.; Gabriels, L.; Nuttin, B. Long-term electrical stimulation of bed nucleus of stria terminalis for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 22, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanova, V. Deep brain stimulation for epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 88, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, D.A., Jr.; Dougherty, D.D.; Rezai, A.R.; Carpenter, L.L.; Friehs, G.M.; Eskandar, E.N.; Rauch, S.L.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Machado, A.G.; Kubu, C.S.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Ventral Capsule/Ventral Striatum for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewernick, B.H.; Hurlemann, R.; Matusch, A.; Kayser, S.; Grubert, C.; Hadrysiewicz, B.; Axmacher, N.; Lemke, M.; Cooper-Mahkorn, D.; Cohen, M.X.; et al. Nucleus Accumbens Deep Brain Stimulation Decreases Ratings of Depression and Anxiety in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baizabal-Carvallo, J.F.; Alonso-Juarez, M. Low-frequency deep brain stimulation for movement disorders. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 31, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Biase, L.; Fasano, A. Low-frequency deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: Great expectation or false hope? Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, T.; Raedt, R.; Vonck, K.; Wadman, W.; Boon, P. Comparison of hippocampal Deep Brain Stimulation with high (130Hz) and low frequency (5Hz) on afterdischarges in kindled rats. Epilepsy Res. 2010, 88, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdhani, R.A.; Patel, A.; Swope, D.; Kopell, B.H. Early Use of 60 Hz Frequency Subthalamic Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Case Series and Review. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2015, 18, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okun, M.S.; Foote, K.D. Parkinson’s disease DBS: What, when, who and why? The time has come to tailor DBS targets. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.L.; Fernandez, H.H.; Haq, I.; Okun, M. Pearls in Patient Selection for Deep Brain Stimulation. Neurologist 2007, 13, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghika, J.; Villemure, J.-G.; Fankhauser, H.; Favre, J.; Assal, G.; Ghika-Schmid, F. Efficiency and safety of bilateral contemporaneous pallidal stimulation (deep brain stimulation) in levodopa-responsive patients with Parkinson’s disease with severe motor fluctuations: A 2-year follow-up review. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Hamasaki, T.; Kuratsu, J.-I. Thalamic stimulation alleviates levodopa-resistant rigidity in a patient with non-Parkinson’s disease parkinsonian syndrome. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.J.; Cajigas, I.; Guest, J.D.; Noga, B.R.; Widerström-Noga, E.; Haq, I.; Fisher, L.; Luca, C.C.; Jagid, J.R. MR Tractography-Based Targeting and Physiological Identification of the Cuneiform Nucleus for Directional DBS in a Parkinson’s Disease Patient With Levodopa-Resistant Freezing of Gait. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 676755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Q.; Sun, B.; Huang, P.; Li, D. Revisiting the L-Dopa Response as a Predictor of Motor Outcomes After Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 604433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wächter, T.; Mínguez-Castellanos, A.; Valldeoriola, F.; Herzog, J.; Stoevelaar, H. A tool to improve pre-selection for deep brain stimulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2010, 258, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamikhah, M.; Akhoundi, F.H.; Rohani, M. Mechanism of Deep Brain Stimulation. Handb. Neuromodulation 2022, 1, 245–264. [Google Scholar]
- Okun, M.S. Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, C.; Beck, J.C.; Bower, J.H.; Roberts, E.; Ritz, B.; Ross, G.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Savica, R.; Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Willis, A.W.; et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease across North America. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis. 2018, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, S.; Duyckaerts, C. Is Lewy pathology in the human nervous system chiefly an indicator of neuronal protection or of toxicity? Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.A.; Alcalay, R.N. Neuropathology of genetic synucleinopathies with parkinsonism: Review of the literature. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1504–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Südhof, T.C. Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of α-Synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 8, a024091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Steur, E.N.J.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D. Advances in markers of prodromal Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundin, P.; Melki, R. Prying into the Prion Hypothesis for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9808–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.E.; Stecher, B.; Labrie, V.; Brundin, L.; Brundin, P. Triggers, Facilitators, and Aggravators: Redefining Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 42, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Yankee, E.L. A review on Parkinson’s disease treatment. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2022, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarkov, A.; Barreto, G.E.; Grizzell, J.A.; Echeverria, V. Strategies for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: Beyond Dopamine. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocks, D.R. Anticholinergic drugs used in Parkinson’s disease: An overlooked class of drugs from a pharmacokinetic perspective. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 2, 39–46. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.wcmq.idm.oclc.org/10952768/ (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Bronstein, J.M.; Tagliati, M.; Alterman, R.L.; Lozano, A.M.; Volkmann, J.; Stefani, A.; Horak, F.B.; Okun, M.S.; Foote, K.D.; Krack, P.; et al. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: An expert consensus and review of key issues. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Gill, S.; Varma, T.; Jenkinson, C.; Quinn, N.; Mitchell, R.; Scott, R.; Ives, N.; Rick, C.; Daniels, J.; et al. Deep brain stimulation plus best medical therapy versus best medical therapy alone for advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD SURG trial): A randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Ma, W.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, Z. Deep brain stimulation of pallidal versus subthalamic for patients with Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory-Magne, F.; Brefel-Courbon, C.; Simonetta-Moreau, M.; Fabre, N.; Lotterie, J.A.; Chaynes, P.; Berry, I.; Lazorthes, Y.; Rascol, O. Does ageing influence deep brain stimulation outcomes in Parkinson’s disease? Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, B.L.; Vitek, J.L. Surgical Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, V.C.; Burchiel, K.J.; Hogarth, P.; Favre, J.; Hammerstad, J.P. Pallidal vs Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loher, T.J.; Burgunder, J.-M.; Weber, S.; Sommerhalder, R.; Krauss, J.K. Effect of chronic pallidal deep brain stimulation on off period dystonia and sensory symptoms in advanced Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzone, M.; Ferrarin, M.; Pedotti, A.; Bergamasco, B.; Bosticco, E.; Lanotte, M.; Perozzo, P.; Tavella, A.; Torre, E.; Recalcati, M.; et al. High-frequency electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: Kinetic and kinematic gait analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 23, s103–s104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, J.M.; Janszen, M.A.; Favre, J. Thalamic deep brain stimulation for the treatment of head, voice, and bilateral limb tremor. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 91, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, M.; Rizzone, M.; Bergamasco, B.; Lanotte, M.; Recalcati, M.; Pedotti, A.; Lopiano, L. Effects of bilateral subthalamic stimulation on gait kinematics and kinetics in Parkinson?s disease. Exp. Brain Res. 2004, 160, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringelbach, M.L.; Green, A.L.; Owen, S.L.F.; Schweder, P.M.; Aziz, T.Z. Sing the mind electric—principles of deep brain stimulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N. Probing and Regulating Dysfunctional Circuits Using Deep Brain Stimulation. Neuron 2013, 77, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, D.; Llinás, R. Voltage-Sensitive Dye Imaging of Neocortical Spatiotemporal Dynamics to Afferent Activation Frequency. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9403–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Levy, R.; Ashby, P.; Tasker, R.; Dostrovsky, J. Does stimulation of the GPi control dyskinesia by activating inhibitory axons? Mov. Disord. 2001, 16, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostrovsky, J.O.; Levy, R.; Wu, J.P.; Hutchison, W.; Tasker, R.R.; Lozano, A. Microstimulation-Induced Inhibition of Neuronal Firing in Human Globus Pallidus. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 84, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouz, A.; Gross, C.; Dupont, J.; Bioulac, B. MPTP induced hemiparkinsonism in monkeys: Behavioral, mechanographic, electromyographic and immunohistochemical studies. Exp. Brain Res. 1992, 90, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, A.; Fedele, E.; Galati, S.; Pepicelli, O.; Frasca, S.; Pierantozzi, M.; Peppe, A.; Brusa, L.; Orlacchio, A.; Hainsworth, A.H.; et al. Subthalamic stimulation activates internal pallidus: Evidence from cGMP microdialysis in PD patients. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, C.C.; Hahn, P.J. Network perspectives on the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 38, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okun, M.S.; Tagliati, M.; Fernandez, H.H.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Alterman, R.L.; Foote, K. Management of Referred Deep Brain Stimulation Failures: A Retrospective Analysis From Two Movement Disorder Centers. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante, L.; Morgante, F.; Moro, E.; Epifanio, A.; Girlanda, P.; Ragonese, P.; Antonini, A.; Barone, P.; Bonuccelli, U.; Contarino, M.F.; et al. How many parkinsonian patients are suitable candidates for deep brain stimulation of subthalamic nucleus? Results of a questionnaire. Park. Relat. Disord. 2007, 13, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner-Fisman, G.; Herzog, J.; Fisman, D.N.; Tamma, F.; Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R.; Lang, A.; Deuschl, G. Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation: Summary and meta-analysis of outcomes. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, S290–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Cyr, J.A.; Trépanier, L.L.; Kumar, R.; Lozano, A.M.; Lang, A.E. Neuropsychological consequences of chronic bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2000, 123, 2091–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, L.; Tarsy, D. Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of atypical parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, C.; Defebvre, L.; Destee, A.; Bleuse, S.; Clement, F.; Blatt, J.L.; Krystkowiak, P.; Devos, D. STN-DBS frequency effects on freezing of gait in advanced Parkinson disease. Neurology 2008, 71, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabid, A.L.; Chabardes, S.; Mitrofanis, J.; Pollak, P. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Shukla, A.W.; Hu, W.; Almeida, L.; Holanda, V.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Okun, M.S.; Li, L. Deep Brain Stimulation at Variable Frequency to Improve Motor Outcomes in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pr. 2018, 5, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roediger, J.; A Dembek, T.; Achtzehn, J.; Busch, J.L.; Krämer, A.-P.; Faust, K.; Schneider, G.-H.; Krause, P.; Horn, A.; A Kühn, A. Automated deep brain stimulation programming based on electrode location: A randomised, crossover trial using a data-driven algorithm. Lancet Digit. Heal. 2022, 5, e59–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathkour, M.; Garces, J.; Scullen, T.; Hanna, J.; Valle-Giler, E.; Kahn, L.; Arrington, T.; Houghton, D.; Lea, G.; Biro, E.; et al. Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients 70 Years and Older with Parkinson Disease. World Neurosurg. 2016, 97, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.A.; Scullen, T.; Kahn, L.; Mathkour, M.; Gouveia, E.E.; Garces, J.; Evans, L.M.; Lea, G.; Houghton, D.J.; Biro, E.; et al. Comparison of elderly and young patient populations treated with deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: Long-term outcomes with up to 7 years of follow-up. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 131, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videnovic, A.; Metman, L.V. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: Prevalence of adverse events and need for standardized reporting. Mov. Disord. 2007, 23, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, K.A.; Weaver, F.M.; Stern, M.; Hur, K.; Harris, C.L.; Luo, P.; Marks, W.J.; Rothlind, J.; Sagher, O.; Moy, C.; et al. Pallidal versus Subthalamic Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, J.; Albanese, A.; Kulisevsky, J.; Tornqvist, A.-L.; Houeto, J.-L.; Pidoux, B.; Bonnet, A.-M.; Mendes, A.; Benabid, A.-L.; Fraix, V.; et al. Long-term effects of pallidal or subthalamic deep brain stimulation on quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousin, P.; Speelman, J.D.; Gielen, F.; Janssens, M. Multicentre European study collaborators Multicentre European study of thalamic stimulation in parkinsonian and essential tremor. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais-Bernard, H.; Xie-Brustolin, J.; Mertens, P.; Polo, G.; Klinger, H.; Adamec, D.; Broussolle, E.; Thobois, S. Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease: Five year follow-up. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ture, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, E.; Ringman, J.M. Cognitive symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical management and prevention. BMJ 2019, 367, l6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, L.; Masliah, E. Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, R12–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, W.; Zhao, M.; Ma, L.; Jiang, X.; Pei, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, H. Interaction between Aβ and Tau in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ye, R.D. Microglial Aβ Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, P.V.; Steadman, D.; Bayle, E.D.; Whiting, P. New approaches for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, M.; Silvestre, S. Alzheimer’s disease: Recent treatment strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, R.T.; Dean, R.L., III; Beer, B.; Lippa, A.S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 1982, 217, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J. Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; The Cochrane Collaboration: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, R.; Dengiz, A. Cognitive performance in patients with Alzheimer’s disease receiving cholinesterase inhibitors for up to 5 years. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2005, 59, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliavini, F.; Tiraboschi, P.; Federico, A. Alzheimer’s disease: The controversial approval of Aducanumab. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 3069–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, R.; Borg, J.J. Aducanumab for Alzheimer’s disease: A regulatory perspective. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcia, J.A.; Viloria, M.A.; Yubero, R.; Sanchez-Sanchez-Rojas, L.; López, A.; Strange, B.A.; Cabrera, M.; Canuet, L.; Gil, P.; Nombela, C. Directional DBS of the Fornix in Alzheimer’s Disease Achieves Long-Term Benefits: A Case Report. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deep Brain Stimulation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Biomarkers and Dose Optimization—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT04856072?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=2 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01559220?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=3 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- The Safety and Efficacy of Long-term Treatment of PINS Stimulator System for Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02253043?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=4 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03959124?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=6 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) of the Nucleus Basalis Meynert (NBM) to Treat Cognitive Deficits in Light to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01094145?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=7 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Study of the Brain Stimulation Effect on Memory Impairment in Alzheimer Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00947934?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=9 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00658125?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=10 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- ADvance II Study: DBS-f in Patients With Mild Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03622905?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=11 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Fornix and NbM as Targets of Stimulation In Alzheimer’s Disease—Tabular View—ClinicalTrials.gov, (n.d.). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03352739?term=Deep+Brain+Stimulation&cond=Alzheimer+Disease&draw=2&rank=14 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Leplus, A.; Lauritzen, I.; Melon, C.; Goff, L.K.-L.; Fontaine, D.; Checler, F. Chronic fornix deep brain stimulation in a transgenic Alzheimer’s rat model reduces amyloid burden, inflammation, and neuronal loss. Brain Struct Funct. 2019, 224, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Rao, Y.; Yuan, T.-F. Deep brain stimulation of fornix for memory improvement in Alzheimer’s disease: A critical review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulousakis, P.; Hove, D.V.D.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Sesia, T. Cognitive Improvements After Intermittent Deep Brain Stimulation of the Nucleus Basalis of Meynert in a Transgenic Rat Model for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preliminary Approach. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 73, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, C.; Huang, X.; Fang, L.; Ao, Q.; Huang, D. The neuroprotective effect of deep brain stimulation at nucleus basalis of Meynert in transgenic mice with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Stimul. 2018, 12, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobs, M.; Lee, D.J.; Lozano, A.M. Modifying the progression of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease with deep brain stimulation. Neuropharmacology 2019, 171, 107860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Laxton, A.W.; Tang-Wai, D.F.; McAndrews, M.P.; Diaconescu, A.O.; Workman, C.; Lozano, A. Increased Cerebral Metabolism After 1 Year of Deep Brain Stimulation in Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldehri, M.; Temel, Y.; Jahanshahi, A.; Hescham, S. Fornix deep brain stimulation induces reduction of hippocampal synaptophysin levels. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2018, 96, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltête, D.; Wallon, D.; Bourilhon, J.; Lefaucheur, R.; Danaila, T.; Thobois, S.; Defebvre, L.; Dujardin, K.; Houeto, J.-L.; Godefroy, O.; et al. Nucleus Basalis of Meynert Stimulation for Lewy Body Dementia. Neurology 2020, 96, e684–e697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.; Lee, J.; Liu, C.Y.; Lozano, A.M.; Lee, D.J. Deep Brain Stimulation for Alzheimer’s Disease: Tackling Circuit Dysfunction. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2020, 24, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohs, R.C.; Knopman, D.; Petersen, R.C.; Ferris, S.H.; Ernesto, C.; Grundman, M.; Sano, M.; Beiliauskas, L.; Geldmacher, D.; Clark, C.; et al. Development of cognitive instruments for use in clinical trials of antidementia drugs: Additions to the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale that broaden its scope. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1997, 11, 13–21. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/alzheimerjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=1997&issue=00112&article=00003&type=Abstract&casa_token=T3Ve16P7d0QAAAAA:l-UlJenZW3fORcJ6SK6RyU0Pc1RsMlD4XfRQ-7QkgtX4Rn4XDeW9bM0ggRFLQzF83VUjBBkcmm4kh7qqiVjmNJkGQQ (accessed on 19 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Peña-Casanova, J. Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale–Cognitive in Clinical Practice. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1997, 9, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombaugh, T.N.; McIntyre, N.J. The Mini-Mental State Examination: A Comprehensive Review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1992, 40, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doraiswamy, P.M.; Bieber, F.; Kaiser, L.; Krishnan, K.R.; Reuning-Scherer, J.; Gulanski, B. The Alzheimer’s disease assessment scale. Neurology 1997, 48, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C. Clinical Dementia Rating: A Reliable and Valid Diagnostic and Staging Measure for Dementia of the Alzheimer Type. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1997, 9, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero-Pardo, C. Should the Mini-Mental State Examination be retired? Neurología 2014, 29, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hescham, S.; Aldehri, M.; Temel, Y.; Alnaami, I.; Jahanshahi, A. Deep brain stimulation for Alzheimer’s Disease: An update. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2018, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.S.; Kennedy, R.E.; Wang, G.; Cutter, G.R. Differences in Alzheimer disease clinical trial outcomes based on age of the participants. Neurology 2015, 84, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hely, M.A.; Reid, W.G.J.; Adena, M.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Morris, J.G.L. The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: The inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, T.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Bescos, A.; Lara, M.; Obuchi, T.; Laxton, A.W.; McAndrews, M.P.; Tang-Wai, D.F.; Workman, C.I.; Smith, G.S.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation Influences Brain Structure in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Stimul. 2014, 8, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwa, Y.; Gondard, E.; Mann, A.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; Alberdi, E.; Matute, C.; Marty, S.; Vaccari, T.; Lozano, A.M.; E Baulieu, E.; et al. Synaptic activity protects against AD and FTD-like pathology via autophagic-lysosomal degradation. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 23, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hofman, K.; Koprich, J.; Brotchie, J.; Volkmann, J.; Ip, C. P 15 Long-term subthalamic deep brain stimulation modulates pathological beta oscillations in the AAV-A53T-Synuclein Parkinson’s disease rat model. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 137, e23–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondard, E.; Chau, H.N.; Mann, A.; Tierney, T.S.; Hamani, C.; Kalia, S.K.; Lozano, A.M. Rapid Modulation of Protein Expression in the Rat Hippocampus Following Deep Brain Stimulation of the Fornix. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okun, M.; Fernandez, H.H.; Wu, S.S.; Kirsch-Darrow, L.; Bowers, D.; Bova, F.J.; Bs, M.S.; Jacobson, C.E.; Wang, X.; Gordon, C.W.; et al. Cognition and mood in Parkinson’s disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: The COMPARE Trial. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxton, A.W.; Lozano, A.M. Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Alzheimer Disease and Dementias. World Neurosurg. 2013, 80, S28.e1–S28.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yan, H.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Han, Y. A circuit view of deep brain stimulation in Alzheimer’s disease and the possible mechanisms. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, A.; Gwun, D.; Chow, C.T.; Boutet, A.; Tasserie, J.; Germann, J.; Santyr, B.; Elias, G.; Yamamoto, K.; Sarica, C.; et al. Probing responses to deep brain stimulation with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.J.; Phibbs, F.; Davis, T.; Fabbri, D. Predicting Motor Responsiveness to Deep Brain Stimulation with Machine Learning. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2021, 2021, 651. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, M.; Jannin, P.; Baxter, J.S. Machine learning in deep brain stimulation: A systematic review. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 122, 102198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, A.; Madhavan, R.; Elias, G.J.B.; Joel, S.E.; Gramer, R.; Ranjan, M.; Paramanandam, V.; Xu, D.; Germann, J.; Loh, A.; et al. Predicting optimal deep brain stimulation parameters for Parkinson’s disease using functional MRI and machine learning. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsman, N.; Glannon, W. Brain, mind and machine: What are the implications of deep brain stimulation for perceptions of personal identity, agency and free will? Bioethics 2012, 27, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.; Maxwell, B.; McAndrews, M.P.; Sadikot, A.; Racine, E. Deep Brain Stimulation and Ethics: Perspectives from a Multisite Qualitative Study of Canadian Neurosurgical Centers. World Neurosurg. 2011, 76, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, D.; Lipsman, N.; Bernstein, M. Neurosurgeons’ perspectives on psychosurgery and neuroenhancement: A qualitative study at one center. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Condition | Area of Stimulation | First Author | Year of Publication | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson’s Disease | Subthalamic nucleus (STN) | Deuschl, Xie | 2006, 2015 | [24,25] |
| Globus Pallidus internus (GPi) | Bloomstedt, Baker | 2018, 2010 | [26,27] | |
| Zona Incerta | Bloonstedt, Ossowska | 2018, 2020 | [26,28] | |
| Pedunculopontine nucleus | Thevathasan | 2018 | [29] | |
| Essential Tremor | Ventral intermediate thalamus | Baizabal-Carvallo | 2014 | [30] |
| Zona incerta | Fytagoridis | 2012 | [31] | |
| Dystonia | GPi | Vidailhet | 2013 | [32] |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Fornix | [33,34] | ||
| Ventromedial prefrontal cortex | Mao, Lozano | 2018, 2016 | [35,36] | |
| Hippocampus | Scharre, Chakravarty | 2018, 2016 | [37] | |
| Nucleus Basalis Meynert | Kuhn | 2014 | [38] | |
| Huntington’s Disease | GPi | Velez-Lago | 2013 | [39] |
| Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) | Anteromedial GPi | Nair | 2014 | [40] |
| Nucleus Accumbens | Huff, Denys | 2010, 2010 | [41,42] | |
| Anterior limb of the internal capsule (ALIC) | Denys, Kammen | 2020, 2022 | [43,44] | |
| Ventral Capsule/Ventral Striatum (VC/VS) | Park, Kammen, Greenburg | 2019, 2022, 2008 | [44,45,46] | |
| STN | Kammen, Li, Chabardes | 2022,2020, 2013 | [44,47,48] | |
| Inferior thalamic peduncle | Germann, Lee, Kammen | 2022,2019, 2022 | [44,49,50] | |
| Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis | Luyten, Mosley, Raymaekers, Kammen | 2015, 2021, 2016, 2022 | [44,51,52,53] | |
| Epilepsy | Anterior nucleus of thalamus | Salanova | 2018 | [54] |
| Depression | VC/VS | Malone | 2009 | [55] |
| Nucleus Accumbens | Bewernick | 2010 | [56] |
| Brain Region | Laterality | Stimulus Settings | Duration (Months) | Patients | Trial Status | YoP | Author/PI | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -Fornix | Bilateral | 3.9–7.5 mA, 90 µs, 130 Hz | 24 | 1 | Completed | 2022 | Barcia | [128] |
| -Fornix | ND | 3.0–3.5 V, 90 µs, 130 Hz | 12 | 6 | Completed (phase I) | 2010 | Laxton | [37] |
| -Fornix | Bilateral | 3.0–3.5 V, 90 µs, 130 Hz | 12 | 42 | Completed (phase II) | 2016 | Lozano | [34] |
| -Fornix | ND | ND | 12 | 12 | Active, not Recruiting | NP | Lozano | [129] |
| -ND | Bilateral | ND | 23 | 3 | Completed | NP | Rezai | [130] |
| -ND | ND | ND | 12 | 10 | Recruiting | NP | Luming | [131] |
| -Fornix | Bilateral | 1–5 V, 90 ms, 130 Hz | 12 | 6 | Completed (phase I) | 2018 | Mao | [33] |
| -NBM | Bilateral | 2.0–4.5 V, 90 µs, 20 Hz | 12 | 6 | Completed | 2014 | Kuhn | [38] |
| -NBM | ND | 2.0–4.5 V, 60 µs, 20 Hz | 12 | 30 | Recruiting | NP | Chen | [132] |
| -NBM | Bilateral | ND | ND | 6 | Completed | NP | Sturm | [133] |
| -Hypothalamus-Fornix | Bilateral | 2–3 V, 120 ms, 180 Hz | 24 | 5 | Recruiting | NP | Fontaine | [134] |
| -Fornix | Bilateral | ND | 12 | 6 | Completed | NP | Laxton | [135] |
| -Fornix | ND | ND | 12 | 210 | Recruiting | NP | ND | [136] |
| -Fornix-NBM | ND | ND | 12 | 30 | Recruiting | NP | ND | [137] |
| Disease | Action of DBS | Physiological Effects | Year | Author | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD | Neuronal activation through Fornix DBS. | Increased hippocampal volume. | 2020, 2012, 2019, 2015 | Jakobs, Smith, Aldehri, Sankar | [142,143,144,156] |
| Increased acetylcholine levels using NBM DBS. | Increased glucose uptake in amygdalo-hippocampal, temporal, and superior lingual gyrus. | 2021, 2014 | Maltête, Kuhn | [38,145] | |
| Increased prefrontal glucose uptake. | Decreased clinical decline. | 2021 | Lam | [146] | |
| PD | Neuronal inhibition. | Depletion of glutamate and release of GABA and adenosine. | 2012, 2001, 2001 | Lozano, Contreras, Wu | [92,93,94] |
| Neuronal activation. | Increased glutamate and dopamine levels. | 2013, 2005, 1992 | Lozano, Stefani, Benazzouz | [92,96,97] | |
| Neuronal activation and inhibition. | Decoupling of the soma and axons. | 2013 | Lozano | [92] | |
| Disrupt pathologic oscillatory patterns. | Neurotrophin release and generation of new neurons. | 2013, 2010 | Lozano, McIntyre | [92,98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senevirathne, D.K.L.; Mahboob, A.; Zhai, K.; Paul, P.; Kammen, A.; Lee, D.J.; Yousef, M.S.; Chaari, A. Deep Brain Stimulation beyond the Clinic: Navigating the Future of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Cells 2023, 12, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12111478
Senevirathne DKL, Mahboob A, Zhai K, Paul P, Kammen A, Lee DJ, Yousef MS, Chaari A. Deep Brain Stimulation beyond the Clinic: Navigating the Future of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Cells. 2023; 12(11):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12111478
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenevirathne, Degiri Kalana Lasanga, Anns Mahboob, Kevin Zhai, Pradipta Paul, Alexandra Kammen, Darrin Jason Lee, Mohammad S. Yousef, and Ali Chaari. 2023. "Deep Brain Stimulation beyond the Clinic: Navigating the Future of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy" Cells 12, no. 11: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12111478
APA StyleSenevirathne, D. K. L., Mahboob, A., Zhai, K., Paul, P., Kammen, A., Lee, D. J., Yousef, M. S., & Chaari, A. (2023). Deep Brain Stimulation beyond the Clinic: Navigating the Future of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Cells, 12(11), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12111478