Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
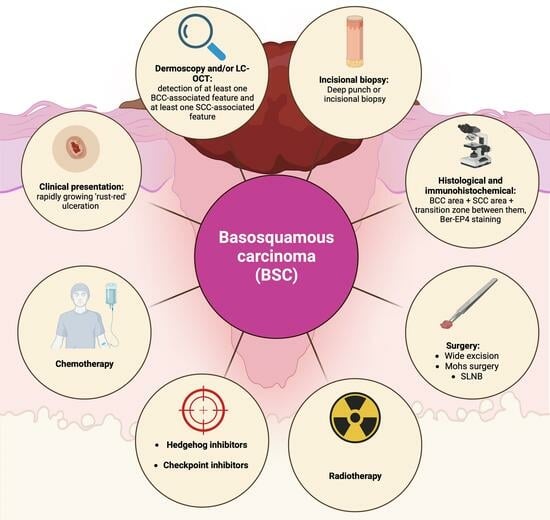
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Definition
3.2. Epidemiology
3.3. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics
3.4. Diagnosis of Basosquamous Carcinoma
3.4.1. Dermoscopy of BSC
3.4.2. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography (LC-OCT) of BSC
3.4.3. Histopathologic Features of BSC
3.4.4. Immunohistologic Features of BSC
3.5. Genetics and Pathogenesis
3.6. Biologic Behavior and Prognosis
3.7. Treatment of BSC
3.7.1. Wide Surgical Excision
3.7.2. Mohs’ Micrographic Surgery (MMS)
3.7.3. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB)
3.7.4. Radiotherapy
3.7.5. Antitumoral Drugs: Chemotherapy
3.7.6. Sonic Hedgehog Inhibitors (HHIs)
| Study | N° of CR | Skin Neoplasm | Treatment | Duration of Treatment (Months/Cycles) | Time to Complete Response (Months) | Durability of Response | Progression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| McGrane et al. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017 [68] | 1 | mBSC | Vismodegib 150 mg day | 28 months | 3 | Complete response on primary BSC, partial response on metastasis | No |
| Sahuquillo-Torralba et al. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2019 [69] | 1 | laBSC | Vismodegib 150 mg day | 7 months | 7 | 9 months after discontinuation of therapy | No |
| Apalla et al. Eur Dermatol. 2019 [70] | 2 | laBSC | Vismodegib 150 mg day | 6 months | 6 | 12 and 18 months after discontinuation of therapy | No |
| Pirruccello et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2023 [71] | 1 | laBSC | Vismodegib 150 mg day + Cemiplimab 350 mg every 3 weeks | 31 cycles of Cemiplimab | 21 | / | No |
| Toffoli et al. Dermatol. Ther. 2022. Jun, 35(6), e15436. [76] | 2 | laBSC | Sonidegib 200 mg day | On course | 6 | Therapy will be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity | No |
| Dika et al. Exp Dermatol. 2023. Jul 11. [77] | 1 | laBSC | Sonidegib 200 mg day + surgery | 8 months of Sonidegib | 8 | Complete remission after 6 months | No |
3.7.7. Checkpoint Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Stefano, A.; Dispenza, F.; Petrucci, A.G.; Citraro, L.; Croce, A. Features of biopsy in diagnosis of metatypical basal cell carcinoma (basosquamous carcinoma) of head and neck. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2012, 66, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.Z.; Rieger, K.E.; Sarin, K.Y. Basosquamous carcinoma: Controversy, advances, and future directions. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacCormac, H. The relation of rodent ulcer to squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Arch. Middlesex. Hosp. 1910, 19, 172–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, M. Basal squamous cell epithelioma. Arch. Dermatol. Syph. 1928, 18, 50–73. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, C.; Poletti, E.; Crowson, A.N. Basosquamous carcinoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, P.H.; Ratz, J.L.; Knoepp, T.G.; Barnes, C.J.; Finlay, R.E. Basosquamous carcinoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2003, 29, 830–832. [Google Scholar]
- Ciążyńska, M.; Sławińska, M.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Lange, D.; Lewandowski, B.; Reich, A.; Pabianek, M.; Szczepaniak, K.; Hankiewicz, A.; Ułańska, M.; et al. Clinical and epidemiological analysis of basosquamous carcinoma: Results of the multicenter study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burston, J.; Clay, R.D. the problems of histological diagnosis in baso-squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. J. Clin. Pathol. 1959, 12, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, J. Basal cell carcinoma of the skin with areas of squamous cell carcinoma: A basosquamous cell carcinoma? J. Clin. Pathol. 1985, 38, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarallo, M.; Cigna, E.; Frati, R.; Delfino, S.; Innocenzi, D.; Fama, U.; Corbianco, A.; Scuderi, N. Metatypical basal cell carcinoma: A clinical review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 27, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Khachemoune, A. Reappraising basosquamous carcinoma: A summary of histologic features, diagnosis, and treatment. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldbury, J.W.; Wain, R.; Abas, S.; Dobson, C.M.; Iyer, S.S. Basosquamous Carcinoma: A Single Centre Clinicopathological Evaluation and Proposal of an Evidence-Based Protocol. J. Skin Cancer 2018, 2018, 6061395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBoit, P.E.; International Agency for Research on Cancer; World Health Organization; International Academy of Pathology; European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer; Universitätsspital Zürich. Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2006.
- Wermker, K.; Roknic, N.; Goessling, K.; Klein, M.; Schulze, H.-J.; Hallermann, C. Basosquamous Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Clinical and Histologic Characteristics and Their Impact on Disease Progression. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualdi, G.; Soglia, S.; Fusano, M.; Monari, P.; Giuliani, F.; Porreca, A.; Di Nicola, M.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.; Amerio, P. Characterization of Basosquamous Carcinoma. A distinct type of keratinizing tumour. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2021, 101, adv00353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller, D.E.; Berg, J.W.; Sherman, G.; Krause, C.J. Cutaneous Basosquamous Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Comparative Analysis. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1979, 87, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.C.; Edwards, M.J.; Cawte, T.G.; Sewell, C.L.; McMasters, K.M. Basosquamous carcinoma: Analysis of prognostic factors influencing recurrence. Cancer 2000, 88, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkenstein, S.; Wohlschlaeger, J.; Liebau, J.; Arens, A.; Lehnerdt, G.; Jahnke, K.; Neumann, A. Basosquamous carcinoma-A rare but aggressive skin malignancy. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, e304–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, D.M. Cutaneous basosquamous carcinoma. Review of the literature and report of 35 cases. Arch. Pathol. 1973, 95, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Mougel, F.; Kanitakis, J.; Faure, M.; Euvrard, S. Basosquamous cell carcinoma in organ transplant patients: A clinicopathologic study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, e151–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betti, R.; Crosti, C.; Ghiozzi, S.; Cerri, A.; Moneghini, L.; Menni, S. Basosquamous cell carcinoma: A survey of 76 patients and a comparative analysis of basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2013, 23, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomel, J.; Lallas, A.; Argenziano, G.; Reggiani, C.; Piana, S.; Apalla, Z.; Ferrara, G.; Moscarella, E.; Longo, C.; Zalaudek, I. Dermoscopy of basosquamous carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akay, B.N.; Saral, S.; Heper, A.O.; Erdem, C.; Rosendahl, C. Basosquamous carcinoma: Dermoscopic clues to diagnosis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camela, E.; Ilut Anca, P.; Lallas, K.; Papageorgiou, C.; Manoli, S.M.; Gkentsidi, T.; Eftychidou, P.; Liopyris, K.; Sgouros, D.; Apalla, Z.; et al. Dermoscopic Clues of Histopathologically Aggressive Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes. Medicina 2023, 59, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgouros, D.; Apalla, Z.; Theofili, M.; Damaskou, V.; Kokkalis, G.; Kitsiou, E.; Lallas, A.; Kanelleas, A.; Stratigos, A.; Nikolaidou, C.; et al. How to spot a basosquamous carcinoma: A study on demographics, clinical-dermatoscopic features and histopathological correlations. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.; Zalaudek, I. Reflectance confocal microscopic presentation of basosquamous carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e547–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappilli, S.; Cinotti, E.; Lenoir, C.; Tognetti, L.; Perez-Anker, J.; Rubegni, P.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J.; Perrot, J.L.; Del Marmol, V.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography of basosquamous carcinoma: A case series with histopathological correlation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppa, M.; Fontaine, M.; Dejonckheere, G.; Cinotti, E.; Yélamos, O.; Diet, G.; Tognetti, L.; Miyamoto, M.; Orte Cano, C.; Perez-Anker, J.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography of basal cell carcinoma: A descriptive study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovitch, I.; Huilgol, S.C.; Selva, D.; Richards, S.; Paver, R. Basosquamous carcinoma: Treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery. Cancer 2005, 104, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, D.; Lowe, L.; Brown, D.L. Basosquamous carcinoma—An under-recognized, high-risk cutaneous neoplasm: Case study and review of the literature. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2006, 59, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.L.; Collins, D.; Chapman, A. Basosquamous carcinoma: Appearance and reality. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 2017, omw095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, I.; Kovacevic, P.; Visnjic, M.; Jankovic, D.; Binic, I.; Jankovic, A.; Ilic, I. Application of sentinel lymph node biopsy in cutaneous basosquamous carcinoma. Ann. Dermatol. 2011, 23 (Suppl. S1), S123–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malloney, M.L. What is basosquamous carcinoma? Dermatol. Surg. 2000, 26, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.S.; Helm, K.F.; Maloney, M.E. The Immunohistochemical Characteristics of the Basosquamous Cell Carcinoma. Dermatol. Surg. 1997, 23, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.V.; Mentrikoski, M.J.; Verduin, L.; Brill, L.B., 2nd; Wick, M.R. Basal cell carcinoma vs basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: An immunohistochemical reappraisal. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haensel, D.; Gaddam, S.; Li, N.Y.; Gonzalez, F.; Patel, T.; Cloutier, J.M.; Sarin, K.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Rieger, K.E.; Aasi, S.Z.; et al. LY6D marks pre-existing resistant basosquamous tumor subpopulations. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, A.; Bîrjovanu, C.; Ciurea, A.M.; Niculescu, D.; Orzan, O.A.; Ion, A.; Alexandru, D.O.; Pirici, I.; Vîlcea, E.J.; Marinescu, E.A.; et al. Immunohistochemical expression of p53, Ki67, α-SMA, CD44 and CD31 in different histological subtypes of basal cell carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022, 63, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.; Tan, C.Z.; Kuonen, F.; Hodgkinson, L.M.; Chiang, F.; Cho, R.J.; South, A.P.; Tang, J.Y.; Chang, A.L.S.; Rieger, K.E. Genetic mutations underlying phenotypic plasticity in basosquamous carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2263–2271.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalla, Z.; Papageorgiou, C.; Lallas, A.; Sotiriou, E.; Lazaridou, E.; Vakirlis, E.; Kyrgidis, A.; Ioannides, D. Spotlight on vismodegib in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma: An evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuka, A.G.; Book, S.E. Basal Cell Carcinoma: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Histopathology, and Management. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, X.; Parmentier, L.; King, B.; Bezrukov, F.; Kaya, G.; Zoete, V.; Seplyarskiy, V.B.; Sharpe, H.J.; McKee, T.; Letourneau, A.; et al. Genomic analysis identifies new drivers and progression pathways in skin basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S.S.; Rayhan, D.J.; Hazany, S.; Kolodney, M.S. Mutational landscape of basal cell carcinomas by whole-exome sequencing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammareri, P.; Rose, A.M.; Vincent, D.F.; Wang, J.; Nagano, A.; Libertini, S.; Ridgway, R.A.; Athineos, D.; Coates, P.J.; McHugh, A.; et al. Inactivation of TGFbeta receptors in stem cells drives cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- South, A.P.; Purdie, K.J.; Watt, S.A.; Haldenby, S.; Breems, N.Y.D.; Dimon, M.; Arron, S.; Kluk, M.J.; Aster, J.C.; McHugh, A.; et al. NOTCH1 Mutations Occur Early during Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, C.R.; Zhou, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Drummond, J.A.; Peng, S.A.; Saade, R.E.; Tsai, K.Y.; Curry, J.L.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Lai, S.Y.; et al. Mutational Landscape of Aggressive Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6582–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaederle, M.; Elkin, S.K.; Tomson, B.N.; Carter, J.L.; Kurzrock, R. Squamousness: Next-generation sequencing reveals shared molecular features across squamous tumor types. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapore, E.; Atwood, S.X. Defining the genetics of Basosquamous Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2258–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokami, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Kiyohara, E.; Tanemura, A.; Fujimoto, M. c-FOS Expression in Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma with Spontaneous Basosquamous Transition. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2023, 103, adv5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, D.; Carucci, J.A. Mohs Surgery for Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dermatol. Clin. 2011, 29, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.A.; Danial, C.; Liu, A.; Li, S.; Chang, A.L.S. Overall and progression-free survival in metastatic basosquamous cancer: A case series. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Desai, S.; Nodzenski, M.; Dubina, M.; Kim, N.; Martini, M.; Fife, D.; Reid, D.; Pirigyi, M.; Poon, E.; et al. Active ascertainment of recurrence rate after treatment of primary basal cell carcinoma (BCC). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciążyńska, M.; Pabianek, M.; Sławińska, M.; Reich, A.; Lewandowski, B.; Szczepaniak, K.; Ułańska, M.; Nejc, D.; Brodowski, R.; Sobjanek, M.; et al. Risk Factors and Clinicopathological Features for Developing a Subsequent Primary Cutaneous Squamous and Basal Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kececi, Y.; Argon, A.; Kebat, T.; Sir, E.; Gungor, M.; Vardar, E. Basosquamous carcinoma: Is it an aggressive tumor? J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2015, 49, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaria, A. Recurrence of Basosquamous Carcinoma after Mohs Micrographic Surgery. Dermatology 2010, 221, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.J.; Cappel, M.A.; Killian, J.M.; Brewer, J.D. Basosquamous carcinoma and metatypical basal cell carcinoma: A review of treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagakia, D.; Zapandioti, P.; Tryspiannis, G.; Grekou, A.; Tsoutsos, D. Sentinel lymph node metastasis in primary cutaneous basosquamous carcinoma. A cross-sectional study. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Shiomi, T.; Tahira, M.; Yamamoto, O. Metastatic basosquamous carcinoma detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deganello, A.; Gitti, G.; Struijs, B.; Paiar, F.; Gallo, O. Palliative combined treatment for unresectable cutaneous basosquamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2013, 33, 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, E.R.; Helwig, E.B. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: A clinicopathologic study of seventeen cases. Cancer 1980, 46, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhacheva, A.; Awan, M.; Barker, C.A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Bradfield, L.; Brady, M.S.; Buzurovic, I.; Geiger, J.L.; Parvathaneni, U.; Zaky, S.; et al. Definitive and Postoperative Radiation Therapy for Basal and Squamous Cell Cancers of the Skin: Executive Summary of an American Society for Radiation Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 10, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, A.; Ansai, S.I.; Ueno, T.; Kawana, S.; Shimizu, A.; Naito, Z.; Saeki, H. A Case of Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Cisplatin and Adriamycin. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2017, 84, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, C.; Apalla, Z.; Timotheadou, E.; Loga, K.; Lazaridou, E.; Dionysopoulos, D. A Case of Metastatic Basosquamous Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2023, 13, e2023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, Y.T.; Sheen, M.C.; Sheu, H.M.; Sheen, Y.S. Intra-arterial infusion chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced basosquamous carcinoma of the nose. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 14, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Chang, J.; Li, S.; Henry, S.; Wood, D.J.; Chang, A.L.S. Increased risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma after vismodegib therapy for basal cell carcinoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig, S.; Sampogna, F.; Tejera-Vaquerizo, A. Study on the risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma after vismodegib therapy for basal cell carcinoma: Not a case-control study. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 1172–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, T.; Abrouk, M.; Sima, C.S.; Sadetsky, N.; Hou, J.; Caro, I.; Chren, M.-M.; Arron, S. Risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma after treatment of basal cell carcinoma with vismodegib. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, A.A.; Aldahan, A.S.; Hughes, O.B.; Shah, V.V.; Strasswimmer, J. Hedgehog pathway inhibitor therapy for locally advanced and metastatic basal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and pooled analysis of interventional studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrane, J.; Carswell, S.; Talbot, T. Metastatic spinal cord compression from basal cell carcinoma of the skin treated with surgical decompression and vismodegib: Case report and review of Hedgehog signalling pathway inhibition in advanced basal cell carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahuquillo-Torralba, A.; Llavador-Ros, M.; Caballero-Daroqui, J.; Botella-Estrada, R. Complete response of a locally advanced Basosquamous carcinoma with Vismodegib treatment. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2019, 85, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalla, Z.; Giakouvis, V.; Gavros, Z.; Lazaridou, E.; Sotiriou, E.; Bobos, M.; Vakirlis, E.; Lallas, A. Complete response of locally advanced Basosquamous carcinoma to Vismodegib in two patients. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirruccello, J.; Afzal, M.Z.; Voudouri, M.; Shirai, K. Complete response of a large basosquamous carcinoma following treatment with cemiplimab and vismodegib. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e251273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borradori, L.; Sutton, B.; Shayesteh, P.; Daniels, G.A. Rescue therapy with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors of advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and basosquamous carcinoma: Preliminary experience in five cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 1382–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzmer, R.; Loquai, C.; Robert, C.; Dréno, B.; Guminski, A.; Lewis, K.; Arntz, R.; Martelli, S.; Squittieri, N.; Kheterpal, M. Key Clinical Adverse Events in Patients with Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Sonidegib or Vismodegib: A Post Hoc Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, R.; Guminksi, A.; Gutzmer, R.; Lear, J.T.; Lewis, K.D.; Chang, A.L.S.; Combemale, P.; Dirix, L.; Kaatz, M.; Kudchadkar, R.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of sonidegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma: 42-month analysis of the phase II randomized, double-blind BOLT study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; Costa, C.; Scalvenzi, M. Response to “Efficacy of sonidegib in histologic subtypes of advanced basal cell carcinoma: Results from the final analysis of the randomized phase 2 Basal Cell Carcinoma Outcomes with LDE225 Treatment (BOLT) trial at 42 months”. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, e299–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffoli, L.; Agozzino, M.; di Meo, N.; Zalaudek, I.; Conforti, C. Locally advanced basosquamous carcinoma: Our experience with sonidegib. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dika, E.; Melotti, B.; Comito, F.; Tassone, D.; Baraldi, C.; Campione, E.; Mussi, M.; Venturi, F. Neoadjuvant treatment of basosquamous carcinomas with Sonidegib: An innovative approach. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 2038–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelin, E.; Mazzoletti, V.; Cavallo, F.; Nardello, C.; Corio, A.; Toffoli, L.; Tagliaferri, L.; Conforti, C.; Di Meo, N.; Zalaudek, I. Treatment of locally advanced and metastatic basosquamous carcinoma, navigating among sonic hedgehog pathway inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy: A case series and literature review. Australas. J. Dermatol 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalhout, S.Z.; Emerick, K.S.; Kaufman, H.L.; Miller, D.M. Immunotherapy for Non-melanoma Skin Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Stricker, I.; Neid, M.; Tannapfel, A.; Susok, L. Impressive response to four cemiplimab cycles of a sonidegib-resistant giant basosquamous carcinoma of the midface. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e490–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratigos, A.J.; Sekulic, A.; Peris, K.; Bechter, O.; Prey, S.; Kaatz, M.; Lewis, K.D.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Chang, A.L.S.; Dalle, S.; et al. Cemiplimab in locally advanced basal cell carcinoma after hedgehog inhibitor therapy: An open-label, multi-centre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanovszki, D.; Kiss, N.; Tóth, B.; Tóth, V.; Szakonyi, J.; Lőrincz, K.; Hársing, J.; Kuroli, E.; Imrédi, E.; Kerner, T.; et al. Real-World Experience with Cemiplimab Treatment for Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma-A Retrospective Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In, G.K.; Nallagangula, A.; Choi, J.S.; Tachiki, L.; Blackburn, M.J.; Capone, S.; Bollin, K.B.; Reuben, D.Y.; Shirai, K.; Zhang-Nunes, S.; et al. Clinical activity of PD-1 inhibition in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Chang, A.L.S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Treating Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 20, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.; Gurizzan, C.; Ottini, A.; Caspani, F.; Bergamini, C.; Locati, L.D.; Marchiselli, C.; Alberti, A.; Lorini, L.; Licitra, L.F.; et al. The association of cemiplimab plus sonidegib for synchronous cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Two case reports. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1111146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | N° of CR | Skin Neoplasm | Treatment | Duration of Treatment (Cycles) | Time to Complete Response (Cycles) | Durability of Response | Progression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pirruccello et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2023 [71] | 1 | laBSC | Vismodegib 150 mg day + Cemiplimab 350 mg every 3 weeks | 31 cycles | 21 cycles | / | No |
| Borradori et al. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016 [72] | 1 | laBSC resistant to Vismodegib | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg, every 2 weeks | 4 cycles | 4 cycles | / | No |
| Gambichler et al. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022 [80] | 1 | laBSC resistant to Sonidegib | Cemiplimab 350 mg every 3 weeks | / | 4 cycles | / | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murgia, G.; Denaro, N.; Boggio, F.; Nazzaro, G.; Benzecry, V.; Bortoluzzi, P.; Passoni, E.; Garrone, O.; Marzano, A. Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2023, 12, 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232737
Murgia G, Denaro N, Boggio F, Nazzaro G, Benzecry V, Bortoluzzi P, Passoni E, Garrone O, Marzano A. Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches. Cells. 2023; 12(23):2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232737
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurgia, Giulia, Nerina Denaro, Francesca Boggio, Gianluca Nazzaro, Valentina Benzecry, Paolo Bortoluzzi, Emanuela Passoni, Ornella Garrone, and Angelo Marzano. 2023. "Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches" Cells 12, no. 23: 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232737
APA StyleMurgia, G., Denaro, N., Boggio, F., Nazzaro, G., Benzecry, V., Bortoluzzi, P., Passoni, E., Garrone, O., & Marzano, A. (2023). Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches. Cells, 12(23), 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232737