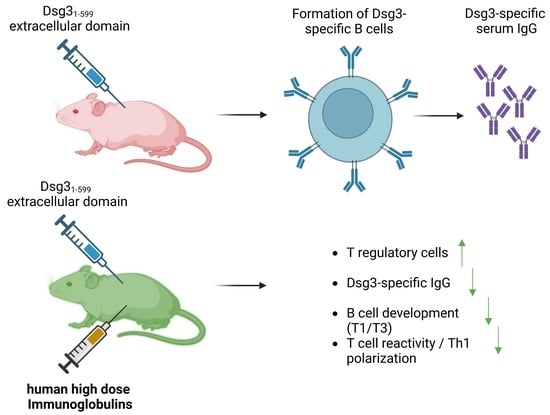
T Regulatory Cell-Associated Tolerance Induction by High-Dose Immunoglobulins in an HLA-Transgenic Mouse Model of Pemphigus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Impact of IVIg Treatment on Dsg3-Specific IgG in Immunized HLA-DRB1*04:02-tg Mice
3.2. Induction of T Regulatory Cells in Lymphatic Tissue
3.3. Effects of IVIg Treatment on B-Cell Maturation in Lymphatic Tissue
3.4. Reduced Type I T-Cell Response against Dsg3 upon IVIg Treatment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmidt, E.; Kasperkiewicz, M.; Joly, P. Pemphigus. Lancet 2019, 394, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollmann, R.; Schmidt, T.; Eming, R.; Hertl, M. Pemphigus: A Comprehensive Review on Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.R. Cell Adhesion Molecules as Targets of Autoantibodies in Pemphigus and Pemphigoid, Bullous Disses Due to Defective Epidermal Cell Adhesion. In Advances in Immunology; Dixon, F.J., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 53, pp. 291–325. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, M.G.; Wang, Z.; Rothenberger, K.; Koch, P.J.; Amagai, M.; Stanley, J.R. Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagai, M.; Stanley, J.R. Desmoglein as a Target in Skin Disease and Beyond. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Bergman, R. Pemphigus Vulgaris and Pemphigus Foliaceus: Differences in Epidemiology and Mortality. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2017, 97, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K.; Schmidt, E. Epidemiology of Pemphigus. JID Innov. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajda, T.; Hazelton, J.; Patel, M.; Seiffert-Sinha, K.; Steinman, L.; Robinson, W.; Haab, B.B.; Sinha, A.A. Multiplexed autoantigen microarrays identify HLA as a key driver of anti-desmoglein and -non-desmoglein reactivities in pemphigus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudemann, C.; Maglie, R.; Llamazares-Prada, M.; Beckert, B.; Didona, D.; Tikkanen, R.; Schmitt, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Waschke, J.; Hertl, M.; et al. Human Desmocollin 3–Specific IgG Antibodies Are Pathogenic in a Humanized HLA Class II Transgenic Mouse Model of Pemphigus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 142, 915–923.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, V.; Heupel, W.-M.; Efthymiadis, A.; Schmidt, E.; Eming, R.; Rankl, C.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Müller, T.; Drenckhahn, D.; Waschke, J. Desmocollin 3-mediated Binding Is Crucial for Keratinocyte Cohesion and Is Impaired in Pemphigus. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30556–30564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didona, D.; Maglie, R.; Eming, R.; Hertl, M. Pemphigus: Current and Future Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, P.; Horwath, B.; Patsatsi, A.; Uzun, S.; Bech, R.; Beissert, S.; Bergman, R.; Bernard, P.; Borradori, L.; Caproni, M.; et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolles, S.; Sewell, W.A.C.; Misbah, S.A. Clinical uses of intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 142, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballow, M. The IgG molecule as a biological immune response modifier: Mechanisms of action of intravenous immune serum globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enk, A.; Hadaschik, E.; Eming, R.; Fierlbeck, G.; French, L.; Girolomoni, G.; Hertl, M.; Jolles, S.; Kárpáti, S.; Steinbrink, K.; et al. European Guidelines (S1) on the use of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in dermatology. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernik, A.; Beutner, E.H.; Bystryn, J.-C. Intravenous immunoglobulin selectively decreases circulating autoantibodies in pemphigus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.H.O.; Enk, A.H. High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Skin Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépanier, P.; Bazin, R. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) inhibits CD8 cytotoxic T-cell activation. Blood 2012, 120, 2769–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, G.N.; Massoud, A.H.; Dembele, M.; Yona, M.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Mazer, B.D. Induction of Regulatory T Cells by Intravenous Immunoglobulin: A Bridge between Adaptive and Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourmishev, L.A.; Guleva, D.V.; Miteva, L.G. Intravenous Immunoglobulins: Mode of Action and Indications in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Dermatoses. Int. J. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimouni, D.; Blank, M.; Ashkenazi, L.; Milner, Y.; Frusic-Zlotkin, M.; Anhalt, G.J.; David, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Protective effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in an experimental model of pemphigus vulgaris. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 142, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Tiburzy, B.; Ishii, N.; Pipi, E.; Wende, S.; Rentz, E.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Zillikens, D.; Manz, R.A.; Ludwig, R.J.; et al. Effects of Intravenous Immunoglobulins on Mice with Experimental Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipi, E.; Kasprick, A.; Iwata, H.; Goletz, S.; Hundt, J.E.; Sadeghi, H.; Schmidt-Jiménez, L.F.; Schmidt, E.; Sjögren, J.; Zillikens, D.; et al. Multiple Modes of Action Mediate the Therapeutic Effect of Intravenous IgG in Experimental Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 142, 1552–1564.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emtenani, S.; Hertl, M.; Schmidt, E.; Hudemann, C. Mouse models of pemphigus: Valuable tools to investigate pathomechanisms and novel therapeutic interventions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, R.; Hennerici, T.; Bäcklund, J.; Feliciani, C.; Visconti, K.C.; Willenborg, S.; Wohde, J.; Holmdahl, R.; Sønderstrup, G.; Hertl, M. Pathogenic IgG Antibodies against Desmoglein 3 in Pemphigus Vulgaris Are Regulated by HLA-DRB1*04:02–Restricted T Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4391–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, C.; Stauber, A.; Wassmuth, R.; Uter, W.; Schuler, G.; Hertl, M. Dichotomy of Autoreactive Th1 and Th2 Cell Responses to Desmoglein 3 in Patients with Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV) and Healthy Carriers of PV-Associated HLA Class II Alleles. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei, D.; Müller, R.; Ishii, N.; Llamazares, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Hertl, M.; Eming, R. IgG Autoantibodies Against Desmocollin 3 in Pemphigus Sera Induce Loss of Keratinocyte Adhesion. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, C.; Höhne, A.; Dieckmann, D.; Schuler, G.; Hertl, M. Type I Regulatory T Cells Specific for Desmoglein 3 Are More Frequently Detected in Healthy Individuals than in Patients with Pemphigus Vulgaris. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6468–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möbs, C.; Schmidt, T. Research Techniques Made Simple: Monitoring of T-Cell Subsets using the ELISPOT Assay. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, e55–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, I.; Nimmerjahn, F. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: How does IgG modulate the immune system? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordé, L.; Spindeldreher, S.; Palmer, E.; Karle, A. Massive immune response against IVIg interferes with response against other antigens in mice: A new mode of action? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, S.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Baek, H.-S.; Lee, H.-B.; Oh, J.-W. Long-term Efficacy of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy for Moderate to Severe Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2011, 3, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroiss, M.; Hohenleutner, U.; Gruss, C.; Glaessl, A.; Landthaler, M.; Stolz, W. Transient and Partial Effect of High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Polyarteritis nodosa. Dermatology 2001, 203, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, O.J.; Powrie, F.M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance in the intestine. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a018341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traxinger, B.R.; Richert-Spuhler, L.E.; Lund, J.M. Mucosal tissue regulatory T cells are integral in balancing immunity and tolerance at portals of antigen entry. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Lan, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Yan, C.-S.; Kuang, J.-L.; et al. Adoptive Transfer of Induced-Treg Cells Effectively Attenuates Murine Airway Allergic Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iriki, H.; Takahashi, H.; Wada, N.; Nomura, H.; Mukai, M.; Kamata, A.; Ito, H.; Yamagami, J.; Matsui, T.; Kurebayashi, Y.; et al. Peripheral tolerance by Treg via constraining OX40 signal in autoreactive T cells against desmoglein 3, a target antigen in pemphigus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2026763118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Willenborg, S.; Hünig, T.; Deeg, C.A.; Sonderstrup, G.; Hertl, M.; Eming, R. Induction of T regulatory cells by the superagonistic anti-CD28 antibody D665 leads to decreased pathogenic IgG autoantibodies against desmoglein 3 in a HLA-transgenic mouse model of pemphigus vulgaris. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunkow, M.E.; Jeffery, E.W.; Hjerrild, K.A.; Paeper, B.; Clark, L.B.; Yasayko, S.-A.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Galas, D.; Ziegler, S.F.; Ramsdell, F. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahl, K.; Loddenkemper, C.; Drouin, C.; Freyer, J.; Arnason, J.; Eberl, G.; Hamann, A.; Wagner, H.; Huehn, J.; Sparwasser, T. Selective depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induces a scurfy-like disease. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriki, H.; Takahashi, H.; Amagai, M. Diverse Role of OX40 on T Cells as a Therapeutic Target for Skin Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Gong, F.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Qi, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesions in relation to Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in patients with Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddur, M.S.; Rabin, M.; Hegde, P.; Bolgert, F.; Guy, M.; Vallat, J.-M.; Magy, L.; Bayry, J.; Kaveri, S.V. Intravenous immunoglobulin exerts reciprocal regulation of Th1/Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in Guillain–Barré syndrome patients. Immunol. Res. 2014, 60, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padet, L.; St-Amour, I.; Aubin, E.; Bazin, R. Neutralization of mitogenic lectins by intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) prevents T cell activation: Does IVIg really have a direct effect on T cells? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundblad, A.; Huetz, F.; Portnoï, D.; Coutinho, A. Stimulation of B and T cells by in vivo high dose immunoglobulin administration in normal mice. J. Autoimmun. 1991, 4, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polakova, A.; Kauter, L.; Ismagambetova, A.; Didona, D.; Solimani, F.; Ghoreschi, K.; Hertl, M.; Möbs, C.; Hudemann, C. Detection of rare autoreactive T cell subsets in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieber, K.; Zimmer, C.L.; Hertl, M. Detection of autoreactive CD4+ T cells by MHC class II multimers in HLA-linked human autoimmune diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagai, M.; Tsunoda, K.; Suzuki, H.; Nishifuji, K.; Koyasu, S.; Nishikawa, T. Use of autoantigen-knockout mice in developing an active autoimmune disease model for pemphigus. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieudonné, Y.; Gies, V.; Guffroy, A.; Keime, C.; Bird, A.K.; Liesveld, J.; Barnas, J.; Poindron, V.; Douiri, N.; Soulas-Sprauel, P.; et al. Transitional B cells in quiescent SLE: An early checkpoint imprinted by IFN. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 102, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Yang, M.; Zhu, J.; Jin, T. Transitional B cells involved in autoimmunity and their impact on neuroimmunological diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenkämper, A.; Lutalo, P.M.K.; Spencer, J. Translational Mini-Review Series on B cell subsets in disease. Transitional B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical implications and effects of B cell-targeted therapies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 167, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Z.; Cong, W.; Fei, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhu, H.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. Pivotal Role of Lesional and Perilesional T/B Lymphocytes in Pemphigus Pathogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, A.-K.E.; Kleinau, S. Marginal zone B cells: From housekeeping function to autoimmunity? J. Autoimmun. 2021, 119, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hudemann, C.; Hoffmann, J.; Schmidt, E.; Hertl, M.; Eming, R. T Regulatory Cell-Associated Tolerance Induction by High-Dose Immunoglobulins in an HLA-Transgenic Mouse Model of Pemphigus. Cells 2023, 12, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091340
Hudemann C, Hoffmann J, Schmidt E, Hertl M, Eming R. T Regulatory Cell-Associated Tolerance Induction by High-Dose Immunoglobulins in an HLA-Transgenic Mouse Model of Pemphigus. Cells. 2023; 12(9):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091340
Chicago/Turabian StyleHudemann, Christoph, Jochen Hoffmann, Enno Schmidt, Michael Hertl, and Rüdiger Eming. 2023. "T Regulatory Cell-Associated Tolerance Induction by High-Dose Immunoglobulins in an HLA-Transgenic Mouse Model of Pemphigus" Cells 12, no. 9: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091340
APA StyleHudemann, C., Hoffmann, J., Schmidt, E., Hertl, M., & Eming, R. (2023). T Regulatory Cell-Associated Tolerance Induction by High-Dose Immunoglobulins in an HLA-Transgenic Mouse Model of Pemphigus. Cells, 12(9), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091340