The Matrix Receptor CD44 Is Present in Astrocytes throughout the Human Central Nervous System and Accumulates in Hypoxia and Seizures
Abstract
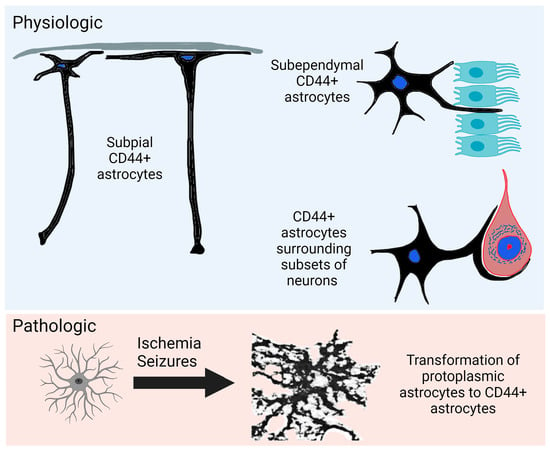
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Autopsy and Biopsy Material
2.2. Epilepsy Surgical Specimens
2.3. Hypoxia Specimens
2.4. Rodent Hypoxia/Ischemia and Seizure Models
2.5. Stroke/Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (tMCAO)
2.6. Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus
2.7. Immunostaining and Antibodies
2.8. Quantification of CD44 in Hypoxia Sections
2.9. Quantification of CD44 in Pilocarpine Sections
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Cell Specificity of CD44 Immunostaining for Astrocytes
3.2. Isocortex
3.3. Subcortical White Matter
3.4. Striatum
3.5. Thalamus
3.6. Hypothalamus, Third Ventricle
3.7. Hippocampus
3.8. Cerebellum
3.9. Brainstem
3.10. Spinal Cord
3.11. CD44+ Astrocytes in the Hypoxic Cortex
3.12. CD44+ Astrocytes in Epilepsy
4. Discussion
4.1. CD44+ Astrocytes Populate the Entire Human CNS
4.2. Interlaminar Astrocytes
4.3. Neurons Surrounded by CD44+ Processes
4.4. Subependymal Astrocytes
4.5. Thalamic Astrocytes
4.6. Cerebellar Astrocytes
4.7. Astrocytes with Vascular Contacts
4.8. Hypoxia
4.9. Seizures
4.10. Regulation of CD44 That Might Be Relevant to Studies in the Human CNS
4.11. There Is a Negative Correlation between CD44 and Protoplasmic Astrocyte Genes/Proteins
4.12. Is There Any Value in Downregulating CD44 in Pathological Situations?
4.13. Limitations
5. Conclusions
- CD44+ astrocytes are present at all levels of the human CNS.
- Some neurons are surrounded by CD44+ processes, including motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, while isocortical, hippocampal, and most diencephalic neurons are not.
- CD44+ processes intercalate between ependymal cells at ventricular surfaces.
- CD44 immunostaining revealed astrocytes in the upper part of the cerebellar molecular layer. These send processes parallel to the pia and radially toward the Purkinje cell layer.
- Velate astrocytes of the cerebellar granule cell layer are CD44+.
- Hypoxia and seizures induce CD44-negative protoplasmic astrocytes to become CD44+.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andriezen, W.L. The Neuroglia Elements in the Human Brain. Br. Med. J. 1893, 2, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, J.A.; Gayol, S.; Yanez, A.; Marco, P. Immunocytochemical and Electron Microscope Observations on Astroglial Interlaminar Processes in the Primate Neocortex. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 48, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberheim, N.A.; Takano, T.; Han, X.; He, W.; Lin, J.H.; Wang, F.; Xu, Q.; Wyatt, J.D.; Pilcher, W.; Ojemann, J.G.; et al. Uniquely Hominid Features of Adult Human Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3276–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, C.; Wolf-Ochoa, M.; Amina, S.; Hong, T.; Vakilzadeh, G.; Hopkins, W.D.; Hof, P.R.; Sherwood, C.C.; Manger, P.R.; Noctor, S.C.; et al. Cortical Interlaminar Astrocytes across the Therian Mammal Radiation. J. Comp. Neurol. 2019, 527, 1654–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Tooyama, I.; Kawamata, T.; Ikeda, K.; McGeer, P.L. Morphological diversities of CD44 positive astrocytes in the cerebral cortex of normal subjects and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1993, 632, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.A.; Wu, X.; Tsankova, N.M.; Guilfoyle, E.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd; Goldman, J.E. Phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity of isocortical and hippocampal astrocytes in the human brain. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodison, S.; Urquidi, V.; Tarin, D. CD44 cell adhesion molecules. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 52, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.A.; McGovern, R.A.; Mikell, C.B.; Wu, X.; Coughlin, D.G.; Crino, P.B.; Weiner, H.L.; Ghatan, S.; Goldman, J.E.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd. Epileptogenic but MRI-normal perituberal tissue in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex contains tuber-specific abnormalities. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgrah, N.; Letarte, M.; Becker, L.E.; Cruz, T.F.; Theriault, E.; Moscarello, M.A. Localization of the CD44 glycoprotein to fibrous astrocytes in normal white matter and to reactive astrocytes in active lesions in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 50, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinner, E.; Gruper, Y.; Ben Zimra, M.; Kristt, D.; Laudon, M.; Naor, D.; Zisapel, N. CD44 Splice Variants as Potential Players in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Butcher, E.C.; Picker, L.J. H-CAM expression in the human nervous system: Evidence for a role in diverse glial interactions. J. Neurocytol. 1992, 21, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.A.; Wu, X.; McGovern, R.A.; Coughlin, D.G.; Mikell, C.B.; Goodman, R.R.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd. The mTOR pathway is activated in glial cells in mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia 2012, 53 (Suppl. S1), 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M., 2nd; Wenzel, H.J.; Robbins, C.A.; Sosunov, A.A.; Schwartzkroin, P.A. Mouse strain differences in kainic acid sensitivity, seizure behavior, mortality, and hippocampal pathology. Neuroscience 2003, 122, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, Y.; Takashima, S.; Becker, L.E. CD44 expression in tuberous sclerosis. Pathobiology 2000, 68, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, K.; McDermott, D.L.; Dingledine, R. Reciprocal changes of CD44 and GAP-43 expression in the dentate gyrus inner molecular layer after status epilepticus in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, B.; Tome-Garcia, J.; Cheng, W.S.; Nudelman, G.; Beaumont, K.G.; Ghatan, S.; Panov, F.; Caballero, E.; Sarpong, K.; Marcuse, L.; et al. High-resolution transcriptomics informs glial pathology in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, K.; Crino, P.B.; Gorter, J.A.; Nellist, M.; Jansen, F.E.; Spliet, W.G.; van Rijen, P.C.; Wittink, F.R.; Breit, T.M.; Troost, D.; et al. Gene expression analysis of tuberous sclerosis complex cortical tubers reveals increased expression of adhesion and inflammatory factors. Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 704–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaijk, P.; Pals, S.T.; Morsink, F.; Bosch, D.A.; Troost, D. Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in the normal human central nervous system. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 73, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmashri, R.; Ren, B.; Oldham, B.; Jung, Y.; Gough, R.; Dunaevsky, A. Modeling human-specific interlaminar astrocytes in the mouse cerebral cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2021, 529, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, T.J.; Pollen, A.A.; Sandoval-Espinosa, C.; Kriegstein, A.R. Transformation of the Radial Glia Scaffold Demarcates Two Stages of Human Cerebral Cortex Development. Neuron 2016, 91, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletti-González, K.E.; Murphy, K.; Kumaran, M.N.; Ravindranath, A.K.; Wernyj, R.P.; Kaur, S.; Miles, G.D.; Lim, E.; Chan, R.; Chekmareva, M.; et al. Identification of function for CD44 intracytoplasmic domain (CD44-ICD): Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) transcription via novel promoter response element. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18995–19007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, Z.; Merkle, F.T.; Soriano-Navarro, M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Neural stem cells confer unique pinwheel architecture to the ventricular surface in neurogenic regions of the adult brain. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanai, N.; Tramontin, A.D.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Barbaro, N.M.; Gupta, N.; Kunwar, S.; Lawton, M.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; Manuel-García Verdugo, J.; et al. Unique astrocyte ribbon in adult human brain contains neural stem cells but lacks chain migration. Nature 2004, 427, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Sanai, N.; Soriano-Navarro, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, O.; Mirzadeh, Z.; Gil-Perotin, S.; Romero-Rodriguez, R.; Berger, M.S.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Cellular composition and cytoarchitecture of the adult human subventricular zone: A niche of neural stem cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Palay, V.; Palay, S.L. The form of velate astrocytes in the cerebellar cortex of monkey and rat: High voltage electron microscopy of rapid Golgi preparations. Z. Anat. Entwicklungsgesch. 1972, 138, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon y Cajal, S. Histology of the Nervous System; Swanson, N.; Swanson, L.W., Translators; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamachary, B.; Penet, M.F.; Nimmagadda, S.; Mironchik, Y.; Raman, V.; Solaiyappan, M.; Semenza, G.L.; Pomper, M.G.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Hypoxia regulates CD44 and its variant isoforms through HIF-1α in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Li, S.; Du, W.; Ke, Q.; Cai, J.; Yang, J. Hypoxia regulates CD44 expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietras, A.; Katz, A.M.; Ekström, E.J.; Wee, B.; Halliday, J.J.; Pitter, K.L.; Werbeck, J.L.; Amankulor, N.M.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Osteopontin-CD44 signaling in the glioma perivascular niche enhances cancer stem cell phenotypes and promotes aggressive tumor growth. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, E.; Grassi, E.S.; Pantazopoulou, V.; Tong, B.; Lindgren, D.; Berg, T.J.; Pietras, E.J.; Axelson, H.; Pietras, A. CD44 Interacts with HIF-2α to Modulate the Hypoxic Phenotype of Perinecrotic and Perivascular Glioma Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, L.; Feuerstein, G.Z.; Wang, X. Use of suppression subtractive hybridization for differential gene expression in stroke: Discovery of CD44 gene expression and localization in permanent focal stroke in rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Hao, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Xue, X.; et al. FOXP3 suppresses breast cancer metastasis through downregulation of CD44. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegel, H.; Tölg, C.; Hofmann, M.; Ceredig, R. Activated mouse astrocytes and T cells express similar CD44 variants. Role of CD44 in astrocyte/T cell binding. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.; Krill, D.; Dhir, R.; Becich, M.J.; Dong, J.T.; Frierson, H.F., Jr.; Isaacs, W.B.; Isaacs, J.T.; Gao, A.C. Methylation of the CD44 metastasis suppressor gene in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2329–2331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hyman, R. Lack of a consistent relationship between demethylation of the CD44 promoter and CD44 expression. Immunogenetics 2002, 53, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.A.; Guilfoyle, E.; Wu, X.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd; Goldman, J.E. Phenotypic conversions of “protoplasmic” to “reactive” astrocytes in Alexander disease. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7439–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalahmah, O.; Sosunov, A.A.; Shaik, A.; Ofori, K.; Liu, Y.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Adorjan, I.; Menon, V.; Goldman, J.E. Single-nucleus RNA-seq identifies Huntington disease astrocyte states. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.Y.; Smolarek, A.K.; Salerno, D.M.; Maehr, H.; Uskokovic, M.; Liu, F.; Suh, N. Targeting CD44-STAT3 signaling by Gemini vitamin D analog leads to inhibition of invasion in basal-like breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Xue, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, J.; Lei, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Role of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 in up-regulation of GFAP after epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2208–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, J.P.; Kelly, K.A.; VanGilder, R.L.; Sofroniew, M.V.; Miller, D.B. Early activation of STAT3 regulates reactive astrogliosis induced by diverse forms of neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Not Surrounded by CD44+ | Surrounded by CD44+ |
|---|---|
| Isocortex, including Betz cells | Oculomotor nucleus |
| Thalamus | Facial nucleus |
| Basal ganglia | Hypoglossal nucleus |
| Subthalamic nucleus | Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus |
| Hippocampal dentate gyrus | Lateral vestibular nucleus |
| Hippocampal and para-hippocampal pyramidal neurons | Inferior olivary nucleus |
| Locus ceruleus | Spinal anterior motor neurons |
| Red nucleus | Onufrowitz nucleus |
| Substantia nigra | Clarke’s column |
| Colliculi | Intermediolateralis nucleus |
| Pontine base | |
| Cerebellar granule cells | |
| Dentate nucleus +/− | |
| Purkinje cells +/− | |
| Solitary nucleus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Dalahmah, O.; Sosunov, A.A.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Madden, N.; Connolly, E.S.; Troy, C.M.; McKhann, G.M., II; Goldman, J.E. The Matrix Receptor CD44 Is Present in Astrocytes throughout the Human Central Nervous System and Accumulates in Hypoxia and Seizures. Cells 2024, 13, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020129
Al-Dalahmah O, Sosunov AA, Sun Y, Liu Y, Madden N, Connolly ES, Troy CM, McKhann GM II, Goldman JE. The Matrix Receptor CD44 Is Present in Astrocytes throughout the Human Central Nervous System and Accumulates in Hypoxia and Seizures. Cells. 2024; 13(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020129
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Dalahmah, Osama, Alexander A. Sosunov, Yu Sun, Yang Liu, Nacoya Madden, E. Sander Connolly, Carol M. Troy, Guy M. McKhann, II, and James E. Goldman. 2024. "The Matrix Receptor CD44 Is Present in Astrocytes throughout the Human Central Nervous System and Accumulates in Hypoxia and Seizures" Cells 13, no. 2: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020129
APA StyleAl-Dalahmah, O., Sosunov, A. A., Sun, Y., Liu, Y., Madden, N., Connolly, E. S., Troy, C. M., McKhann, G. M., II, & Goldman, J. E. (2024). The Matrix Receptor CD44 Is Present in Astrocytes throughout the Human Central Nervous System and Accumulates in Hypoxia and Seizures. Cells, 13(2), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020129