The Regulatory Role of MicroRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC)
1.1. HBV-HCC Pathogenesis Continuum
1.2. The Deregulation of MiRNA in HBV-HCC Continuum
2. MiRNA Dysregulation in the HBV-HCC Continuum
2.1. Early/Chronic HBV Infection
MiRNA Regulating HBV Genome Expression
2.2. HBV-Induced Inflammation Pathways
MiRNA Regulating HBV-Induced Inflammation Pathways
2.3. MiRNA Regulating HBV-Induced Fibrosis/Cirrhosis
2.4. HBV Deregulated MiRNA in HBV-HCC
2.4.1. HBV–HBx-Downregulated MiRNA in HBV-HCC
2.4.2. HBx-Upregulated MiRNA in HBV-HCC
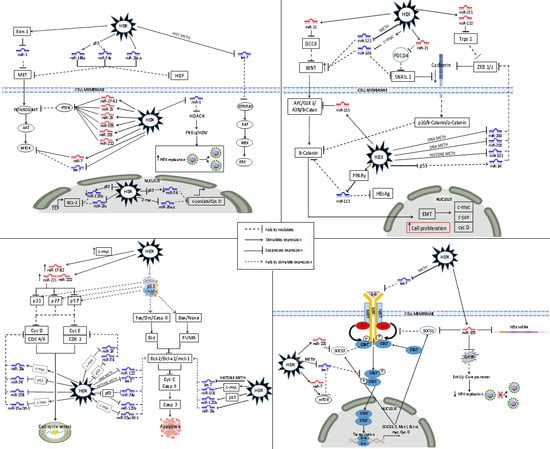
3. HBV–HBx-Dysregulated MiRNA in the Principal HBV-HCC Cancer Pathways
3.1. Dysregulated MiRNA in the p13K/MAPK Pathway in HBV-HCC
3.2. Dysregulated MiRNA in the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in HBV-HCC
3.3. Dysregulated MiRNA in the TP 53 Pathway in HBV-HCC
3.4. Dysregulated MiRNAs in the JAK/STAT Pathway in HBV-HCC
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer, I.A.f.R.O. World Health Organization. Globocan 2012: Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.Aspx (accessed on 1 September 2014).
- Wong, M.C.; Jiang, J.Y.; Goggins, W.B.; Liang, M.; Fang, Y.; Fung, F.D.; Leung, C.; Wang, H.H.; Wong, G.L.; Wong, V.W. International incidence and mortality trends of liver cancer: A global profile. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. Ca: A Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Vos, T.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Assadi, R.; Bhala, N.; Cowie, B. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 388, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, A.I.; Khan, S.A.; Toledano, M.B.; Waked, I.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors and pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2008, 14, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. elife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Jilbert, A.R. Conceptual models for the initiation of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1786–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection—Natural history and clinical consequences. New Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-H.; Yeh, S.-H.; Chen, P.-J. Role of microRNAs in hepatitis B virus replication and pathogenesis. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2011, 1809, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, D.; Babb de Villiers, C.; Chasela, C.; Urban, M.I.; Kramvis, A. Analysis of risk factors associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in black South Africans: 2000–2012. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréchot, C. Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus—Related hepatocellular carcinoma: Old and new paradigms. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Gusev, Y.; Aderca, I.; Mettler, T.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Brackett, D.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringelhan, M.; O’connor, T.; Protzer, U.; Heikenwalder, M. The direct and indirect roles of HBV in liver cancer: Prospective markers for HCC screening and potential therapeutic targets. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, W.A. Molecular Biology of Human Cancers: An Advanced Student’s Textbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garzon, R.; Marcucci, G.; Croce, C.M. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidigal, J.A.; Ventura, A. The biological functions of miRNAs: Lessons from in vivo studies. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, N.; Cohen, S.M. microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Kozaki, K.-i.; Tanaka, S.; Arii, S.; Imoto, I.; Inazawa, J. miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2009, 31, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziapostolou, M.; Polytarchou, C.; Aggelidou, E.; Drakaki, A.; Poultsides, G.A.; Jaeger, S.A.; Ogata, H.; Karin, M.; Struhl, K.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M. An HNF4α-miRNA inflammatory feedback circuit regulates hepatocellular oncogenesis. Cell 2011, 147, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Saigo, K.; Urashima, T.; Toyoda, H.; Okanoue, T.; Shimotohno, K. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Yang, B.; Peng, X.; Ding, H.; You, H.; Tien, P. Circulating microRNAs in hepatitis B virus–infected patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locarnini, S. Molecular virology of hepatitis B virus. Semin.Liver Dis. 2004, 24 (Suppl. 1), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Fan, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. Hepatitis B virus-encoded microRNA controls viral replication. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01919-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.-L.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, H. MicroRNAs associated with HBV infection and HBV-related HCC. Theranostics 2014, 4, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, Q.-J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Markowitz, G.J.; Ning, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Y. TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, J. Ectopic expression of microRNA-155 enhances innate antiviral immunity against HBV infection in human hepatoma cells. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Majumder, S.; Nuovo, G.; Kutay, H.; Volinia, S.; Patel, T.; Schmittgen, T.D.; Croce, C.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T. Role of microRNA-155 at early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by choline-deficient and amino acid–defined diet in C57BL/6 mice. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arataki, K.; Hayes, C.N.; Akamatsu, S.; Akiyama, R.; Abe, H.; Tsuge, M.; Miki, D.; Ochi, H.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M. Circulating microRNA-22 correlates with microRNA-122 and represents viral replication and liver injury in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Med Virol. 2013, 85, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kanda, T.; Jiang, X.; Haga, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Wu, S.; Yasui, S.; Nakamoto, S.; Yokosuka, O. Serum microRNA-122 and Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein are useful tools for liquid biopsy of the patients with hepatitis B virus and advanced liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bandiera, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. miR-122—A key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, L.; Yan, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, E.; Ye, X.; Gao, G.F.; Wang, F. Loss of microRNA 122 expression in patients with hepatitis B enhances hepatitis B virus replication through cyclin G1-modulated P53 activity. Hepatology 2012, 55, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Fan, H.; Jin, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Ju, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Z.; Meng, S. miR-122-induced down-regulation of HO-1 negatively affects miR-122-mediated suppression of HBV. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sui, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.-K.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.-J.; Fan, H.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Tang, H. HBV-Encoded miR-2 Functions as an Oncogene by Downregulating TRIM35 But Upregulating RAN in Liver Cancer Cells. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6838411/ (accessed on 1 October 2019). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, V.S.; Drake, A.; Chen, J. Virus-specific host miRNAs: Antiviral defenses or promoters of persistent infection? Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Mitchelson, K.; Rao, H.; Luo, M.; Xie, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, R. MicroRNAs-372/373 promote the expression of hepatitis B virus through the targeting of nuclear factor I/B. Hepatology 2011, 54, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cai, G.; Li, D.; Yin, W. MicroRNAs and liver disease: Viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Postgrad. Med J. 2014, 90, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkawy, A.M.; Mann, D.A. Nuclear factor-κB and the hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.-B.; Qiao, L. Pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Bozorgzadeh, A.; Pierce, R.H.; Kurtis, J.; Crispe, I.N.; Orloff, M.S. TLR-dependent cross talk between human Kupffer cells and NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunn, C.; Brunetto, M.; Reynolds, G.; Christophides, T.; Kennedy, P.T.; Lampertico, P.; Das, A.; Lopes, A.R.; Borrow, P.; Williams, K. Cytokines induced during chronic hepatitis B virus infection promote a pathway for NK cell–mediated liver damage. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tacke, F.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C. Inflammatory pathways in liver homeostasis and liver injury. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 36, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-κB and STAT3–key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arzumanyan, A.; Friedman, T.; Kotei, E.; Ng, I.O.; Lian, Z.; Feitelson, M.A. Epigenetic repression of E-cadherin expression by hepatitis B virus x antigen in liver cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoop, J.N.; van der Molen, R.G.; Baan, C.C.; van der Laan, L.J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kusters, J.G.; Janssen, H.L. Regulatory T cells contribute to the impaired immune response in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2005, 41, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kanda, T.; Wu, S.; Nakamura, M.; Miyamura, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Banerjee, A.; Yokosuka, O. Regulation of microRNA by hepatitis B virus infection and their possible association with control of innate immunity. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, A.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Koike, K. Mutual antagonism between hepatitis B viral mRNA and host microRNA let-7. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.H.; Xu, F.; Chow, S.; Feng, L.; Yin, D.; Ng, T.B.; Chen, Y. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatocellular carcinoma transformation through interleukin-6 activation of microRNA-21 expression. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandopadhyay, M.; Banerjee, A.; Sarkar, N.; Panigrahi, R.; Datta, S.; Pal, A.; Singh, S.P.; Biswas, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chakravarty, R. Tumor suppressor micro RNA miR-145 and onco micro RNAs miR-21 and miR-222 expressions are differentially modulated by hepatitis B virus X protein in malignant hepatocytes. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Dong, S.; Qiao, F.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Lao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, T.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. HBx-mediated miR-21 upregulation represses tumor-suppressor function of PDCD4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Momeni, M.; Hassanshahi, G.; Arababadi, M.K.; Kennedy, D. Ectopic expression of micro-RNA-1, 21 and 125a in peripheral blood immune cells is associated with chronic HBV infection. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4833–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Rooge, S.B.; Varshney, A.; Vasudevan, M.; Bhardwaj, A.; Venugopal, S.K.; Trehanpati, N.; Kumar, M.; Geffers, R.; Kumar, V. Global microRNA expression profiling in the liver biopsies of hepatitis B virus–infected patients suggests specific microRNA signatures for viral persistence and hepatocellular injury. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayes, C.; Chayama, K. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-M.; Hu, Z.-B.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.-Y.; Zhang, J.-F.; Shen, H.-B.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zen, K. Serum microRNA profiles serve as novel biomarkers for HBV infection and diagnosis of HBV-positive hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zen, K. A pilot study of serum microRNA signatures as a novel biomarker for occult hepatitis B virus infection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 201, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yao, B.; Dou, C.; Xu, M.; Xue, Y.; Ding, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q. Long non-coding RNA TUSC7 acts a molecular sponge for miR-10a and suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11429–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Z.; Hong, H.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Huang, M.; Li, C.; Xia, J. miR-106a is downregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chronic hepatitis B and associated with enhanced levels of interleukin-8. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 629862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akamatsu, S.; Hayes, C.N.; Tsuge, M.; Miki, D.; Akiyama, R.; Abe, H.; Ochi, H.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; Takahashi, S. Differences in serum microRNA profiles in hepatitis B and C virus infection. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, T.; Jiang, D.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z. Expression and clinical significance of miR-122 and miR-29 in hepatitis B virus-related liver. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 7912–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, N.T.; Duong, D.C.; Van Tong, H.; Hien, T.T.T.; Hoan, P.Q.; Bang, M.H.; Binh, M.T.; Ky, T.D.; Tung, N.L.; Thinh, N.T. Optimisation of quantitative miRNA panels to consolidate the diagnostic surveillance of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waidmann, O.; Bihrer, V.; Pleli, T.; Farnik, H.; Berger, A.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; Piiper, A. Serum microRNA-122 levels in different groups of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, e58–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, A.; Rider, P.J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, K.; Mu, Y.; Hao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhu, Y. A liver-specific microRNA binds to a highly conserved RNA sequence of hepatitis B virus and negatively regulates viral gene expression and replication. Faseb J. 2011, 25, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Hao, J.; Fan, H.; Ju, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L.; Chu, X. Hepatitis B virus mRNA-mediated miR-122 inhibition upregulates PTTG1-binding protein, which promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth and cell invasion. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.-L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.-G.; Chen, E.-M.; Chen, W.-Q.; Li, L.-J. Plasma miRNA-122-5p and miRNA-151a-3p identified as potential biomarkers for liver injury among CHB patients with PNALT. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Dong, C. Identification and characterization of interferon signaling-related microRNAs in occult hepatitis B virus infection. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Mao, R.C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Qin, Y.L.; Lu, M.J.; Zhang, J.M. Serum micro RNA-124 is a novel biomarker for liver necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, J. circHIPK3 regulates cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124 and regulating AQP3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, N.; Potenza, N.; Pisaturo, M.; Mosca, N.; Tonziello, G.; Signoriello, G.; Messina, V.; Sagnelli, C.; Russo, A.; Sagnelli, E. Liver microRNA hsa-miR-125a-5p in HBV chronic infection: Correlation with HBV replication and disease progression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, N.; Papa, U.; Mosca, N.; Zerbini, F.; Nobile, V.; Russo, A. Human microRNA hsa-miR-125a-5p interferes with expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5157–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhuang, N.; Zhao, D.; He, J.; Shi, L. Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes TRAIL-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase A20. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giray, B.G.; Emekdas, G.; Tezcan, S.; Ulger, M.; Serin, M.S.; Sezgin, O.; Altintas, E.; Tiftik, E.N. Profiles of serum microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-Y.; Chou, S.-F.; Lee, J.-W.; Chen, H.-L.; Chen, C.-M.; Tao, M.-H.; Shih, C. MicroRNA-130a can inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via targeting PGC1α and PPARγ. Rna 2015, 21, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ji, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.-D. Hepatitis B viral RNA directly mediates down-regulation of the tumor suppressor microRNA miR-15a/miR-16-1 in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18484–18493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Jiao, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Ye, X. Hepatitis B virus regulates apoptosis and tumorigenesis through the microRNA-15a-Smad7-transforming growth factor beta pathway. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-M.; Kim, T.S.; Jo, E.-K. MiR-146 and miR-125 in the regulation of innate immunity and inflammation. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambrecht, J.; Jan Poortmans, P.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; Mannaerts, I.; van Grunsven, L.A. Circulating ECV-associated miRNAs as potential clinical biomarkers in early stage HBV and HCV induced liver fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Min, B.Y.; Jang, E.S.; Kim, N.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Shin, C.M.; Lee, S.H.; Park, Y.S. c-Myc-mediated overexpression of miR-17-92 suppresses replication of hepatitis B virus in human hepatoma cells. J. Med Virol. 2013, 85, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.-Q.; Teng, M.-K.; Niu, L.-W.; Huang, A.-L.; Liang, Z. Hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma at the miRNA level. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2011, 17, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Zhou, G.; Li, G.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Serum miR-181b is correlated with hepatitis B virus replication and disease progression in chronic hepatitis B patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 2346–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Up-regulated MicroRNA-181a induces carcinogenesis in Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting E2F5. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Functional analysis of miR-181a and Fas involved in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 331, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazalhosseini, B.; Mohamed, R.; Apalasamy, Y.D.; Langmia, I.M.; Mohamed, Z. Circulating microRNA as a marker for predicting liver disease progression in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Rev. Da Soc. Bras. De Med. Trop. 2017, 50, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunetto, M.R.; Cavallone, D.; Oliveri, F.; Moriconi, F.; Colombatto, P.; Coco, B.; Ciccorossi, P.; Rastelli, C.; Romagnoli, V.; Cherubini, B. A serum microRNA signature is associated with the immune control of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, K.O.; Jacobsen, K.S.; Mirza, A.H.; Winther, T.N.; Størling, J.; Glebe, D.; Pociot, F.; Hogh, B. Hepatitis B virus upregulates host microRNAs that target apoptosis-regulatory genes in an in vitro cell model. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Tanahashi, T.; Tanaka, J.; Kumada, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Taguchi, Y. Comprehensive miRNA expression analysis in peripheral blood can diagnose liver disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L. MiR-139-5p, miR-940 and miR-193a-5p inhibit the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SPOCK1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ninomiya, M.; Kondo, Y.; Kimura, O.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Kogure, T.; Morosawa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Shimosegawa, T. The expression of miR-125b-5p is increased in the serum of patients with chronic hepatitis B infection and inhibits the detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.-J.; Wang, C.-M.; Li, M.-Y.; Han, P.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Zoulim, F.; Ma, X.; Xu, D.-P. Altered expression profiles of microRNAs in a stable hepatitis B virus-expressing cell line. Chin. Med J. 2009, 122, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; He, Z. miR-200c targets nuclear factor IA to suppress HBV replication and gene expression via repressing HBV Enhancer I activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Cui, M.; Liu, F.; You, X.; Du, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Z.; Ye, L. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits tumor suppressor miR-205 through inducing hypermethylation of miR-205 promoter to enhance carcinogenesis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, IN24–IN26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Gan, J.; Zhang, J. miR-203a is involved in HBx-induced inflammation by targeting Rap1a. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yang, J.; Ouyang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, G.; Lu, Z.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Serum microRNA-210 levels in different groups of chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 450, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-L.; Li, Y.-X.; Zheng, S.-Q.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. Suppression of hepatitis B virus replication by microRNA-199a-3p and microRNA-210. Antivir. Res. 2010, 88, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, A.K.; Johnson, J.L.; Palmer, C.; McLachlan, A. Members of the nuclear receptor superfamily regulate transcription from the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid promoter. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, F.; Yang, C.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. microRNA-4717 differentially interacts with its polymorphic target in the PD1 3′ untranslated region: A mechanism for regulating PD-1 expression and function in HBV-associated liver diseases. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Tang, S.; Xia, L.; Du, R.; Xie, H.; Song, J.; Fan, R.; Bi, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, G. MicroRNA-501 promotes HBV replication by targeting HBXIP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Ao, F.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, Y. MicroRNA-548 down-regulates host antiviral response via direct targeting of IFN-λ1. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, G. MicroRNA-602 regulating tumor suppressive gene RASSF1A is over-expressed in hepatitis B virus-infected liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, J.; Tian, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Run, W.; Tian, L.; Jia, X.; Gao, Y. Serum microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential marker for detecting liver pathologies. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Fan, X.; Li, G.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Epigenetically-Regulated MicroRNA-9-5p Suppresses the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via TGFBR1 and TGFBR2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puche, J.E.; Lee, Y.A.; Jiao, J.; Aloman, C.; Fiel, M.I.; Muñoz, U.; Kraus, T.; Lee, T.; Yee, H.F., Jr.; Friedman, S.L. A novel murine model to deplete hepatic stellate cells uncovers their role in amplifying liver damage in mice. Hepatology 2013, 57, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kan, F.; Ye, L.; Yan, T.; Cao, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, W. Proteomic and transcriptomic studies of HBV-associated liver fibrosis of an AAV-HBV-infected mouse model. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenner, D.A. Molecular pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Transactions of the American Clinical and Climatological Association 2009, 120, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, R.K. Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Suhail, M.; Abdel-Hafiz, H.; Ali, A.; Fatima, K.; Damanhouri, G.A.; Azhar, E.; Chaudhary, A.G.; Qadri, I. Potential mechanisms of hepatitis B virus induced liver injury. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Han, M.; Ma, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, J. miR-185 Inhibits Fibrogenic Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Prevents Liver Fibrosis. Mol. Ther. -Nucleic Acids 2018, 10, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhogal, R.K.; Stoica, C.M.; McGaha, T.L.; Bona, C.A. Molecular aspects of regulation of collagen gene expression in fibrosis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 25, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, Y.; Takizawa, T.; Yoshida, H.; Uchida, E. Dysregulated miRNA in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Hepatol. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Park, S.H.; Yi, Y.; Choi, S.-G.; Lee, C.; Parks, W.T.; Cho, H.; De Caestecker, M.P.; Shaul, Y.; Roberts, A.B. The hepatitis B virus encoded oncoprotein pX amplifies TGF-β family signaling through direct interaction with Smad4: Potential mechanism of hepatitis B virus-induced liver fibrosis. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Tanaka, M.; Kuroda, M.; Harada, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Tajima, A.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Shimotohno, K. The progression of liver fibrosis is related with overexpression of the miR-199 and 200 families. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-F.; Sun, C.-C.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Li, D.-J. miR-33a levels in hepatic and serum after chronic HBV-induced fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, X.-L.; Guo, X.-X.; Shi, M.-J.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Chen, Q.-L.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Xu, L.-M.; Huang, S. MiR-27a as a predictor for the activation of hepatic stellate cells and hepatitis B virus-induced liver cirrhosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Zang, Y. MicroRNA-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by targeting the TGF β signalling pathway. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yao, Q.; Butt, A.M.; Guo, J.; Tian, Z.; Bao, X.; Li, H.; Meng, Q.; Lu, J. Expression profiling of serum microRNA-101 in HBV-associated chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appourchaux, K.; Dokmak, S.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Treton, X.; Lapalus, M.; Gattolliat, C.-H.; Porchet, E.; Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Boyer, N.; Vidaud, M. MicroRNA-based diagnostic tools for advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.J.; Lai, R.T.; Lu, J.; Xiang, X.G.; Zhao, G.D.; Tang, W.L.; Cai, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.J.; Xie, Q. Correlation between circulating miR-122 and prognosis of chronic HBV-related liver failure. J. Dig. Dis. 2016, 17, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Lin, B.; Ye, Y.; Wen, D.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X. Differential expression of serum microRNAs in cirrhosis that evolve into hepatocellular carcinoma related to hepatitis B virus. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Qi, H.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J.; Yu, F. MicroRNA-125a-5p contributes to hepatic stellate cell activation through targeting FIH1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Dong, P.; Chen, Z.; Lin, D.; Chen, B.; Yu, F. Serum microRNA-125a-5p, a useful biomarker in liver diseases, correlates with disease progression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, N.; Chakravarty, R. Hepatitis B virus infection, microRNAs and liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17746–17762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, N.; Huang, C.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Q.; Yu, K.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Shi, G. Serum MicroRNA Levels as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker for the Early Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Fibrosis. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xin, H.; Cao, Y.; Geng, M. MicroRNA in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2014, 19, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Shi, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Su, S.; Chen, Q. MiRNA-target network analysis identifies potential biomarkers for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) syndrome development evaluation in hepatitis B caused liver cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, S.K.; Jiang, J.; Kim, T.-H.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.-S.; Torok, N.J.; Wu, J.; Zern, M.A. Liver fibrosis causes downregulation of miRNA-150 and miRNA-194 in hepatic stellate cells, and their overexpression causes decreased stellate cell activation. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 298, G101–G106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakner, A.M.; Steuerwald, N.M.; Walling, T.L.; Ghosh, S.; Li, T.; McKillop, I.H.; Russo, M.W.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Schrum, L.W. Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, P.; Hu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tang, F. Micro RNA-194 protects against chronic hepatitis B-related liver damage by promoting hepatocyte growth via ACVR 2B. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4534–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Mu, Y.; Liu, P. Serum miR-21 and miR-26a Levels Negatively Correlate with Severity of Cirrhosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Microrna (Shariqahunited Arab Emir.) 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, J.C.; Liu, T.; Qu, Y.; Lu, L.G.; Xu, M.Y. Micro RNA profile analysis in the liver fibrotic tissues of chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, M.; Qu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.; Lu, L. Analysis of the differential expression of circulating microRNAs during the progression of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5647–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, G.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes the development of liver fibrosis and hepatoma through downregulation of miR-30e targeting P4HA2 mRNA. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Wei, B. MicroRNAome of splenic macrophages in hypersplenism due to portal hypertension in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Xue, D.; Shen, D.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Pan, K.; Yang, Y. MicroRNA-942 mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating BAMBI expression in human liver fibrosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Reviews. Genet. 2009, 10, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, R.J.; Bagga, S.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus molecular biology and pathogenesis. Hepatoma Res. 2016, 2, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatitis B virus x protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Yu, E.; Suh, D.J.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Surzycki, S.J.; Lee, Y.I. Aberrant epigenetic modifications in hepatocarcinogenesis induced by hepatitis B virus X protein. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, H.-O.; Liu, Y.-D.; Liu, W.-S.; Pan, D.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yang, L.; Fu, Q.; Xu, J.-J.; Gu, J.-X. Decreased expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (Hnf4α)/microRNA-122 (miR-122) axis in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma enhances potential oncogenic GALNT10 protein activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1170–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neuveut, C.; Wei, Y.; Buendia, M.A. Mechanisms of HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Huang, P.; Ju, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Lin28B over-expression mediates the repression of let-7 by hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 15108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Toh, S.T.; Sung, W.-K.; Tan, P.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.Y.; Jooi, L.L.; Lee, C.G. Lethal-7 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x protein and targets signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Liao, C.-Y.; Yang, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-M.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Overexpression of endothelin 1 triggers hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish and promotes cell proliferation and migration through the AKT pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Pei, R.; Jiang, M.; Schlaak, J.F.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. Modulation of hepatitis B virus replication and hepatocyte differentiation by MicroRNA-1. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J.; Kutay, H.; Nasser, M.W.; Nuovo, G.J.; Wang, B.; Majumder, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Volinia, S.; Croce, C.M.; Schmittgen, T.D. Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5049–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xiang, T.; Ren, G.; Tan, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z. miR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA methyltransferase 3A. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.L.K.; Wong, C.C.L.; Lee, J.M.F.; Fan, D.N.Y.; Tsang, F.H.; Ng, I.O.L.; Wong, C.M. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver cancer metastasis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Tie, Y.; Xing, R.; Zhu, J.; Sun, Z.; Wei, L.; Zheng, X. MicroRNA-101 regulates expression of the v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (FOS) oncogene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wei, X.; Tang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Shen, A.; Wu, Z. Circulating microRNA-101 as a potential biomarker for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Ding, S.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Functional analysis of miR-101-3p and Rap1b involved in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Qin, L.; Shen, B. Biomarker MicroRNAs for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A functional survey and comparison. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.-W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Fu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhu, H.; Diao, W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X. Hepatitis B virus-human chimeric transcript HBx-LINE1 promotes hepatic injury via sequestering cellular microRNA-122. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Dash, S.; Feitelson, M.; Lim, K.; Wu, T. Epigenetic regulation of MicroRNA-122 by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma and hepatitis b virus X protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, W.; Hou, K.; Liang, M. MiR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in hepatoma cells. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, K.; Tian, Y.; Peng, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Gong, G. HBx down-regulated Gld2 plays a critical role in HBV-related dysregulation of miR-122. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-G.; Wang, C.-M.; Tian, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, W.-S.; Li, R.-F.; Liu, Y.-G. miR-122 inhibits viral replication and cell proliferation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and targets NDRG3. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Giovannini, C.; Veronese, A.; Ferracin, M.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Croce, C.M.; Tavolari, S. MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L. Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Andersen, J.B.; Durkin, M.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K. MicroRNA-124 suppresses growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting STAT3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Liao, B.; Dai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J. Serum exosomal miR-125b is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Tan, C.; Tang, C.; Ren, G.; Xiang, T.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, Z. Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by the hepatitis B virus x protein in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Cui, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. HBx elevates oncoprotein AEG-1 expression to promote cell migration by downregulating miR-375 and miR-136 in malignant hepatocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, L.J.; Tan, Y.-X.; Ren, H.; Qi, Z.-T. Identification of deregulated miRNAs and their targets in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 5442. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.C.L.; Wong, C.M.; Tung, E.K.K.; Au, S.L.K.; Lee, J.M.F.; Poon, R.T.P.; Man, K.; Ng, I.O.L. The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D. miR-139-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Yan, C. Downregulation of microRNA-145 caused by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes expression of CUL5 and contributes to pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Zhang, L.J.; Huang, X.H.; Chen, L.Z.; Su, Q.; Zeng, W.T.; Li, W.; Wang, Q. mi R-145 suppresses cell invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Mi R-145 targets ADAM 17. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fan, Z.; Kang, L.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, H.; Lin, J.; Jiang, K. Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.; Xu, L.; Gong, J.; Fang, J.; Zhuang, S. MicroRNA-148a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatoma cells by targeting Met/Snail signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Shen, H.; Gagea, M.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Beretta, L. Differentiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Multifaceted effects of miR-148a on tumor growth and phenotype and liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, S. Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in hepatitis B virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Hepatology 2010, 52, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Hu, M.; Li, P.; Lu, C.; Li, M. Mir-152 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells by targeting KIT. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, M.; Wei, S. MicroRNAs Play Significant Roles in Pathogenesis of HBV-Related Diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Shen, X.; Lao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, X.; Hu, J.; Gong, P.; Cui, H.; Lu, S. HBx represses RIZ1 expression by DNA methyltransferase 1 involvement in decreased miR-152 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, K.; Xu, J.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Song, E. Hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates expression of the miR-16 family in malignant hepatocytes in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, T.; Li, Z.; Peng, J.; Cui, Z.; Ye, X. Hepatitis B virus inhibits apoptosis of hepatoma cells by sponging the MicroRNA 15a/16 cluster. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13370–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.S.; Yen, C.J.; Chou, R.H.; Chen, J.N.; Huang, W.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Yu, Y.L. Downregulation of microRNA-15b by hepatitis B virus X enhances hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via fucosyltransferase 2-induced Globo H expression. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, S.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Kou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Du, L.; Jiang, S. Modulation of HBV replication by microRNA-15b through targeting hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 6578–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.H.; Yeh, S.H.; Lu, C.C.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. MicroRNA-18a prevents estrogen receptor-α expression, promoting proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L. HBX protein-induced downregulation of microRNA-18a is responsible for upregulation of connective tissue growth factor in HBV infection-associated hepatocarcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georges, S.A.; Biery, M.C.; Kim, S.-y.; Schelter, J.M.; Guo, J.; Chang, A.N.; Jackson, A.L.; Carleton, M.O.; Linsley, P.S.; Cleary, M.A. Coordinated regulation of cell cycle transcripts by p53-Inducible microRNAs, miR-192 and miR-215. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10105–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lian, J.; Jing, Y.; Dong, Q.; Huan, L.; Chen, D.; Bao, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Yao, M. miR-192, a prognostic indicator, targets the SLC39A6/SNAIL pathway to reduce tumor metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, W.K. MicroRNA Profiling of Human Hepatocytes Induced by HBx in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Fu, H.; Li, S.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, X. MicroRNA-193b regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2828–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.; Browne, G.; Tulchinsky, E. ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: At the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Xiao, Z.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. MiR-205 modulates abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma cells via targeting acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (ACSL1) mRNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Yu, D.-C.; Li, Q.-G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Ding, Y.-T. Expression of serum miR-16, let-7f, and miR-21 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significances. Clin. Lab. 2014, 60, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, E.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X. MiR-216b is involved in pathogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through HBx-miR-216b-IGF2BP2 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 6, e1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Seike, M.; Soeno, C.; Mizutani, H.; Kitamura, K.; Minegishi, Y.; Noro, R.; Yoshimura, A.; Cai, L.; Gemma, A. MiR-23a regulates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhou, P.; Gao, P.; Jiang, S.; Lobie, P.E.; Zhu, T. c-MYC-regulated miR-23a/24-2/27a cluster promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by targeting Sprouty2. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18121–18133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; He, X.; Ding, J.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, X.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, J. Upregulation of miR-23a approximately 27a approximately 24 decreases transforming growth factor-beta-induced tumor-suppressive activities in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Ni, J.; Cui, D.; Yu, C.; Cai, Z. Tumor-specific expression of microRNA-26a suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma growth via cyclin-dependent and-independent pathways. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liang, L.; Zhang, X.F.; Jia, H.L.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, X.C.; Gao, X.M.; Qiao, P.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, Y.Y. MicroRNA-26a suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting interleukin-6-Stat3 pathway. Hepatology 2013, 58, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Shi, J.; Budhu, A.; Yu, Z.; Forgues, M.; Roessler, S.; Ambs, S.; Chen, Y.; Meltzer, P.S.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression, survival, and response to interferon in liver cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.; Fang, J.H.; Yun, J.P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.H.; Zhuang, S.M. Effects of MicroRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C.-G.; Xu, F.-F.; Sun, W.-S.; Liu, Y.-G.; Jia, J.-H. miR-29c targets TNFAIP3, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Tan, D.; Hou, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liu, G. miR-338-3p is down-regulated by hepatitis B virus X and inhibits cell proliferation by targeting the 3′-UTR region of cyclinD1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8514–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.S.; Fu, X.H.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, L.Z.; Li, W.; Bi, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Fu, Q. Bead-based microarray analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: miR-338 is downregulated. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, B.; Li, W.-F. Decreased miR-34a promotes growth by regulating MAP4K4 in hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Hermeking, H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corney, D.C.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Godwin, A.K.; Wang, W.; Nikitin, A.Y. MicroRNA-34b and MicroRNA-34c are targets of p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and adhesion-independent growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8433–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, F.; Fu, H.; Liu, Q.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, X. Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, J.; Yu, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. MicroRNA-363-3p is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and inhibits tumorigenesis by directly targeting specificity protein 1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Liu, C. miR-429 represses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in HBV-related HCC. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates oncogene Rab18 to result in the dysregulation of lipogenesis and proliferation of hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Kong, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Cai, N.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Ye, L. Hepatitis B virus X protein accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis with partner survivin through modulating miR-520b and HBXIP. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.M.; Yan, X.H.; Hu, Y.W.; Huang, J.L.; Cao, S.W.; Ren, T.Y.; Tang, Y.T.; Lin, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. miRNA-548p suppresses hepatitis B virus X protein associated hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating oncoprotein hepatitis B x-interacting protein. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui-Nguyen, T.M.; Pakala, S.B.; Sirigiri, D.R.; Martin, E.; Murad, F.; Kumar, R. Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-S.; Yen, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chiu, S.-J.; Shih, W.-L.; Ho, C.-Y.; Wei, T.-T.; Pan, H.-L. miRNA-7/21/107 contribute to HBx-induced hepatocellular carcinoma progression through suppression of maspin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hua, L.; Yao, K.-H.; Chen, J.-T.; Hu, J.-H. miR-107 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting Axin2. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mosca, N.; Castiello, F.; Coppola, N.; Trotta, M.C.; Sagnelli, C.; Pisaturo, M.; Sagnelli, E.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. Functional interplay between hepatitis B virus X protein and human miR-125a in HBV infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, T.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Sun, S. Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin expression. Hepatology 2009, 50, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-F.; Dai, X.-P.; Zhang, W.; Sun, S.-H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Kou, Z.-H.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Du, L.-Y. Upregulation of microRNA-146a by hepatitis B virus X protein contributes to hepatitis development by downregulating complement factor H. MBio 2015, 6, e02459-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Z.H.; Han, Q.J.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.G.; Zhang, J. miR146a impairs the IFN-induced anti-HBV immune response by downregulating STAT1 in hepatocytes. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, X.; Lu, F.; Zhang, T.; Hao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; McCrae, M.A.; Zhuang, H. Aberrant expression of microRNA 155 may accelerate cell proliferation by targeting sex-determining region Y box 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2012, 118, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Tan, S.; Wu, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, C.; Gong, Y.; Liang, X. HBV suppresses ZHX2 expression to promote proliferation of HCC through miR-155 activation. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wen, H.; Jing, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, X.; Nan, K.; Yao, Y.; Tian, T. Micro RNA-155-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing PTEN through the PI 3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguda, B.D.; Kim, Y.; Piper-Hunter, M.G.; Friedman, A.; Marsh, C.B. MicroRNA regulation of a cancer network: Consequences of the feedback loops involving miR-17-92, E2F, and Myc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19678–19683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connolly, E.; Melegari, M.; Landgraf, P.; Tchaikovskaya, T.; Tennant, B.C.; Slagle, B.L.; Rogler, L.E.; Zavolan, M.; Tuschl, T.; Rogler, C.E. Elevated expression of the miR-17–92 polycistron and miR-21 in hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to the malignant phenotype. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damania, P.; Sen, B.; Dar, S.B.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, A.; Gupta, E.; Sarin, S.K.; Venugopal, S.K. Hepatitis B virus induces cell proliferation via HBx-induced microRNA-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting programmed cell death protein4 (PDCD4) and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, S.; Lavker, R.M.; Cai, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; You, X.; Chi, X.; Wang, T.; Ye, L.; Niu, J.; Zhang, X. Hepatitis B virus X protein mutant HBxΔ127 promotes proliferation of hepatoma cells through up-regulating miR-215 targeting PTPRT. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-J.; Tang, Y.-S.; Huang, S.-F.; Ai, J.-G.; Wang, H.-X.; Zhang, L.-P. HBx protein-induced upregulation of microRNA-221 promotes aberrant proliferation in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting estrogen receptor-α. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rong, M.; Chen, G.; Dang, Y. Increased miR-221 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its role in enhancing cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.-F.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.-J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Bei, Y.-H.; Yang, C.-Q. MiR-222 overexpression promotes proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by downregulating p27. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 893. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, Q.W.; Ching, A.K.; Chan, A.W.; Choy, K.-W.; To, K.-F.; Lai, P.B.; Wong, N. MiR-222 overexpression confers cell migratory advantages in hepatocellular carcinoma through enhancing AKT signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Fornari, F.; Callegari, E.; Sabbioni, S.; Lanza, G.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Negrini, M. MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, A.T.; Ma, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Yang, Y.; Tantoso, E.; Li, K.-B.; Ooi, L.L.J.; Tan, P. Profiling microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals microRNA-224 up-regulation and apoptosis inhibitor-5 as a microRNA-224-specific target. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13205–13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, S.H.; Wu, S.Y.; Zuchini, R.; Lin, X.Z.; Su, I.J.; Tsai, T.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Wu, C.T.; Liu, H.S. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through degradation of microRNA-224. Hepatology 2014, 59, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scisciani, C.; Vossio, S.; Guerrieri, F.; Schinzari, V.; De Iaco, R.; de Meo, P.D.O.; Cervello, M.; Montalto, G.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G. Transcriptional regulation of miR-224 upregulated in human HCCs by NFκB inflammatory pathways. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-J.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.-D.; Bai, B.; Xue, M.-H. miR-27a as an oncogenic microRNA of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shan, C.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Upregulated microRNA-29a by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances hepatoma cell migration by targeting PTEN in cell culture model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L.; Xu, Z.; Jin, L.; Wang, T.; Song, C.; Yang, K. miR-30c-1* promotes natural killer cell cytotoxicity against human hepatoma cells by targeting the transcription factor HMBOX 1. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; Tan, X.; Xiong, D.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, T.; Qi, J.; Liu, J.; Qin, C. The miR-545/374a cluster encoded in the Ftx lncRNA is overexpressed in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis and tumor progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Han, S.; Feng, B.; Chu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, R. Hepatitis B virus X protein-mediated non-coding RNA aberrations in the development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chien, P.-H.; Chen, W.-S.; Chien, Y.-F.; Hsu, Y.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Lin, C.-W.; Huang, T.-C.; Yu, Y.-L. Hepatitis B virus-encoded X protein downregulates EGFR expression via inducing microRNA-7 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Zhao, J.; Yang, A.; Zhang, R. MicroRNA-7 arrests cell cycle in G1 phase by directly targeting CCNE1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, J.; Saba, G.T. Wnt-/-β-catenin pathway signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edamoto, Y.; Hara, A.; Biernat, W.; Terracciano, L.; Cathomas, G.; Riehle, H.M.; Matsuda, M.; Fujii, H.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Ohgaki, H. Alterations of RB1, p53 and Wnt pathways in hepatocellular carcinomas associated with hepatitis C, hepatitis B and alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, S.; Marais, R.; Zhu, A. The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El–Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Kawada, N. MicroRNAs in hepatic pathophysiology. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Song, J. Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the proliferation inhibition activity of microRNA-7 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3566–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, V.; Turcios, L.; Marti, F.; Gedaly, R. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, E.; Gramantieri, L.; Domenicali, M.; D’abundo, L.; Sabbioni, S.; Negrini, M. MicroRNAs in liver cancer: A model for investigating pathogenesis and novel therapeutic approaches. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Franklin, D.A.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y. MDM2–p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7161–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Hung, S.-P.; Chen, M.-F.; Yeh, C.-T.; Tsai, S.-L.; Chu, C.-M.; Liaw, Y.-F. Genetic alterations of INK4alpha/ARF locus and p53 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, S.; Takehara, T.; Hikita, H.; Kodama, T.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Ishida, H.; Noda, T.; Nagano, H. The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.J.-F.; Gong, H.-Y.; Tseng, H.-C.; Wang, W.-L.; Wu, J.-L. miR-122 targets an anti-apoptotic gene, Bcl-w, in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, Q.-J.; Gong, Z.-B.; Zhou, L.; You, N.; Wang, S.; Li, X.-L.; Li, J.-J.; An, J.-Z.; Wang, D.-S. MicroRNA-34a targets Bcl-2 and sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib treatment. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 13, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Zeng, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, J.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Pei, X. MicroRNA-125b induces cancer cell apoptosis through suppression of Bcl-2 expression. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Tian, W.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y. MicroRNA-101 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via targeting Mcl-1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Matsubara, K.; Geng-Sun, Q.; Jackson, P.; Groopman, J.D.; Manning, J.E.; Harris, C.C.; Herman, J.G. SOCS-1, a negative regulator of the JAK/STAT pathway, is silenced by methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and shows growth-suppression activity. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Li, J. The Pivotal Role of microRNA-155 in the Control of Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Yeganeh, M.; Donates, Y.; Tobelaim, W.; Chababi, W.; Mayhue, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Ramanathan, S.; Saucier, C.; Ilangumaran, S. Regulation of MET receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.X.; Ming, Z.Y.; Li, K.Z.; Wu, G.B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.N. In vivo and in vitro effects of microRNA-221 on hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression through the JAK–STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting SOCS3. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3500–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-X.; Ling, Y.; Wang, H.-Y. Role of nonresolving inflammation in hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Kroh, E.; Wood, B.; Arroyo, J.D.; Dougherty, K.J.; Miyaji, M.M.; Tait, J.F.; Tewari, M. Blood cell origin of circulating microRNAs: A cautionary note for cancer biomarker studies. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagy, Z.B.; Barták, B.K.; Kalmár, A.; Galamb, O.; Wichmann, B.; Dank, M.; Igaz, P.; Tulassay, Z.; Molnár, B. Comparison of circulating miRNAs expression alterations in matched tissue and plasma samples during colorectal cancer progression. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Jiang, T.; Kang, X. Circulating microRNAs in cancer: Origin, function and application. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Peng, F.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y. Interaction of lncRNA-MALAT1 and miR-124 regulates HBx-induced cancer stem cell properties in HepG2 through PI3K/Akt signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Q.; Ling, C. MiR-124 suppresses cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PIK3CA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Ma, H.S.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, L.; Liu, T. LAMC1 mRNA promotes malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by competing for MicroRNA-124 binding with CD151. Iubmb Life 2017, 69, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maltseva, D.V.; Rodin, S.A. Laminins in metastatic cancer. Mol. Biol. 2018, 52, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| miRNA | HBV | Comment | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| Let-7 fam | Down | Let 7a/b/c/d/e/f/g/I all downregulated by HBx protein which inhibits IL-6, IL-10, TLR4 expression | [40,51] |
| Let-7a-3p | Up | Upregulated in early stage HBV/targets DDX3X/expression can be downregulated in sera but upregulated in tissue | [57,58] |
| Let-7c | Up | Impairs immune response and HBV evasion/targets HDAC4/MET to enhance HBV replication via FXRA | [58,59,60] |
| miR-1 | Up | Targets HDAC4, MET to enhance (HBV replication)HBV RE by augmenting FXRA expression | [56] |
| miR-10a | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV infection/upregulated in sera, Targets EphA4 which is an epithelial-mesynchymal-transition (EMT) suppressor | [58,59,61] |
| miR-106a | Down | Downregulated by HBx, targets IL-8 in CHB | [40,62] |
| miR-122 | Up | Upregulated in sera for HBeAg positive patients/correlates with HBV DNA/in sera and tissue | [32,60,63,64] |
| Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. Healthy Controls (HC)/upregulated in CHB vs. HC sera | [25,33,59,65] | |
| Up | Upregulated in HBV also HBeAg+ vs. HBeAg–/correlates with HBV DNA/HBsAg | [63,66] | |
| mir-122 | Down | Suppress HBV by targeting HBV mRNAs/targets Cyclin G1/HO-1 to promote HBV infection by inhibiting HO-1 | [28,35,36,67,68] |
| miR-122-5p | Up | Upregulated in CHB/biomarker for liver injury | [69] |
| Down | Decreased level in occult HBV infection (OBI) vs. HC | [70] | |
| miR-124 | Up | Serum miRNA correlates with necrosis/inflammation and upregulated in CHB vs. HC/targets AQP3 | [71,72] |
| miR-125 | Up | Impairs immune response and HBV evasion | [56] |
| miR-125a-5p | Up | Correlates with HBsAg/HBeAg and HBV-DNA/suppresses HBV expression by blocking HBsAg mRNA/targets KLF13 | [40,58,73,74] |
| miR-125a | Up | HBx upregulated in HBV infection | [40,75] |
| miR-125b | Up | Upregulated in CHB sera/correlated with HBV DNA, HBsAg, HBeAg | [59,63] |
| miR-125b-5p | Up | Upregulated 2.85 fold in CHB/targets STAT3 | [57,58,76] |
| miR-1275 | Up | Upregulated in HBV patients/correlated with serum ϒ-glutamyl transpeptidase | [63] |
| miR-130a | Up Down | Upregulated by NFκB/ Marker for OBI/upregulated vs. HC, ASC, CHB Targets PGC1α and PPARγ to regulate HBV replication/possible dual role in HBV | [70] [77] |
| miR-15a | Down | Downregulated by HBx/Suppresses HBV infection by binding to HBx mRNA/targets TGF-β/Smad7 | [28,78,79] |
| miR-146 | Up | Targets/stimulates HBx/NFκB in HBV infection | [80] |
| miR-150 | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV sera/downregulated in HBV asymptomatic vs. CHB | [59,60,81] |
| miR-151-3p | Up | Upregulated in CHB/biomarker for liver injury | [69] |
| miR-155 | Up | Blocks SOCS1 to upregulate JAK/STAT/targets C/EBP Suppresses HBV by augmenting INF signaling | [30,31] |
| miR-16-1 | Down | Downregulated by HBx RNA | [78] |
| miR-17 | Down | Downregulated in HBV-infected persons | [40] |
| miR-17-92 | Up | HBV transactivates c-Myc to upregulate miR-17-92 which suppresses HBV mRNA | [82] |
| miR-181a-d | Up | Correlated with HBV DNA and HBV disease progression/downregulates HLA-A, HBsAg by targeting HLA-A, E2F5 | [40,83,84,85,86] |
| miR-182 | Down | Downregulated in CHB leading to HBV-related cirrhosis | [87] |
| miR-191 | Up | Upregulated by HBx protein | [40] |
| miR-192 | Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. HC serum | [65,88] |
| miR-192-5p | Up | HBV activated/correlated with HBV Replication | [88,89] |
| miR-193a-5p | Down | Downregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation/targets SPOCK3 | [90,91] |
| miR-193b | Up | Upregulated by HBx protein/directly targets Mcl-1 | [40,92] |
| miR-196a | Down | Downregulated by HBx | [40,83,93] |
| miR-196c | Up | Upregulated in HBV-infected persons | [40] |
| miR-1974 | Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. normal liver (NL)/upregulated A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-199a-5p | Up | Upregulated in early HBV-immune tolerant/HBx upregulated/Target STAT2/low in blood sera but up in tissue | [40,57] |
| miR-20a | Down | Downregulated by HBx | [40] |
| miR-200b | Down | Downregulated in sera (ECVs) in CHB | [81] |
| miR-200c | Down | HBx reduced in HBV infection/targets nuclear factor IA to suppress HBV replication | [28,94] |
| miR-205 | Down | Targets HBx mRNA | [28,95] |
| miR-203a | Up | Upregulated in HBV infection/promotes inflammation targets IL-6, IL-8 | [96] |
| miR-21 | Up | Upregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation/impairs immune response and HBV evasion/up in CHB vs. HC serum | [56,65,90] |
| miR-210 | Up | Correlates with HBV DNA and HBsAg/marker for necroinflammation/suppresses HBV infection by targeting HBsAg pre-S1 region | [58,59,97,98] |
| miR-215-5p | Up | HBV activated miRNA/correlates with HBV replication | [89] |
| miR-221-3p | Up | Upregulated in early HBV/targets TBK1/upregulated in blood sera/tissue | [57] |
| miR-22 | Up | Upregulated in HBV-infected persons/correlates with HBeAg, HBeAg positive persons/correlated with miR-122 | [32,63] |
| Up | Upregulated in A0 vs. A3 inflammation/targets HDAC4, ERα to inhibit HBsAg/HBeAg | [90] | |
| miR-223-3p | Up | 5.55-fold upregulated in CHB in blood sera | [59,76] |
| miR-23a/b | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV infection/upregulated in sera | [40,58,59,83] |
| miR-236 | Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. HC sera | [59] |
| miR-30c | Up | Upregulated by HBx protein | [40] |
| miR-3200 | Up | Upregulated in CHB leading to LC | [87] |
| HBV-mir-3 | Up | Mediates HBV RE by blocking HBc mRNA to downregulate HBV virions | [27] |
| miR-338-3p | Down | Downregulated in HBV | [40] |
| miR-339 | Up | Upregulated in CHB leading to LC | [87] |
| miR-34a | Up | Upregulated A3 vs. A0 inflammation/promotes Tregs that block effector T-cells | [28,29,90] |
| miR-342-3p | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV infection in sera/HBx-induced deregulation | [40,58,59,87] |
| miR-3613-3p | Up | Upregulated in CHB/Target STAT3/down in sera | [57] |
| miR-3615 | Up | Upregulated in CHB leading to LC | [87] |
| miR-371 | Up | Upregulated by HBx protein | [40] |
| miR-372 | Up | Correlates with HBV DNA in CHB/deregulated by HBx/targets NFIB/HNF4, RXR, and PPAR to regulate HBV transcription | [39,40,99] |
| miR-373 | Up | Correlates with HBV DNA in CHB/deregulated by HBx | [39,40] |
| miR-375 | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV in sera | [58,59] |
| miR-378 | Down | Down-regulated in HBV | [40] |
| miR-423 | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV infection/upregulated in sera | [58,59] |
| miR-4485 | Down | Downregulated in CHB re progression to HBV-LC | [87] |
| miR-451 | Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. NL/Upregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-4508 | Up | Upregulated in CHB leading to LC | [87] |
| miR-4717 | Down | Significant upregulation of PD-1 (programmed cell death) | [100] |
| miR-486-5p | Down | Downregulated in CHB vs. NL | [90] |
| MiR-501 | Up | Targets HBX1P to induce HBV RE | [101] |
| miR-548 | Down | Inhibits IFN-ϓ1, downregulates immune response/promotes HBV | [102] |
| miR-548d-5p | Up | Upregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-602 | Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. HC/targets RASSFIA/ascending upregulation on HBV-HCC continuum | [103] |
| miR-659 | Down | Downregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-711 | Down | Downregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-720 | Up | Upregulated in HBV patients also correlates with HBeAg+ HBeAg– | [63] |
| miR-760 | Up | Upregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-762 | Down | Downregulated in CHB vs. NL | [90] |
| miR-767-3p | Up | Upregulated in A3 vs. A0 inflammation | [90] |
| miR-885-5p | Up | Upregulated in CHB vs. HC | [104] |
| miR-92a | Up | Upregulated > three-fold in HBV in sera/ | [58,59,81] |
| miR-935 | Up | Upregulated in CHB leading to LC | [87] |
| miR-940 | Down | Downregulated in CHB/downregulated in sera and tissue | [57] |
| miR-9-5p | Down | Downregulated in CHB/even lower with higher fibrosis scores | [105] |
| miR-99a | Up | Upregulated in HBV+ patients also HBeAg+/upregulated in sera | [58,59,63] |
| mIr-99b | Up | Upregulated by HBx protein | [40] |
| MiRNA | Deregulation | Comment | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | Up | Upregulated in late-stage fibrosis (f3–4)/targets ATF2/E2F3/CREB3L2/up in tissue and sera | [57] |
| miR-10b-5p | Up | Upregulated advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis/targets ATF2/E2F3/CREB3L2/up in tissue and sera | [57] |
| miR-101 | Down | Downregulated in HBV fibrosis/HBx downregulated via EZH2-induced methylation/suppresses TGF-B signaling to block collagen | [58,119] |
| Up | Suppresses TGF-β signaling to block collagen/upregulated in cirrhosis versus CHB | [120] | |
| miR-103 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-122 | Up | Upregulated in early fibrosis/significant decrease as f0–2 progresses to f3–4 | [33,58,81,121] |
| Down | Downregulated in advanced f4 vs. f0–1/suppresses TGF-β pathway to block collagen | [33] | |
| miR-122-5p | Up | Correlates with degree of fibrogenic damage | [69,122,123] |
| miR-1224-3p | Up | Upregulated in early fibrosis (f1–2)/target ELK1/AKT2/upregulated in sera/tissue | [57] |
| miR-1227-3p | Up | Upregulated early fibrosis (f1–2)/target HSPG2/PTEN/downregulated in sera | [57] |
| miR-125b-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis | [76] |
| miR-125a-5p | Up | Targets F1H1 in HBV-related fibrosis vs. H. Controls | [124,125] |
| miR-126 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB stage | [118] |
| miR-1275 | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB stage | [118] |
| miR-128 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-130a | Up | Upregulated in fibrosis/f3 > f0/upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB/IFNs trigger JAK/STAT | [118] |
| miR-133a | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis | [126] |
| miR-133b | Up | Upregulated in advanced vs. early fibrosis/targets ATF2/E2F3/CREB3L2/upregulated in sera and tissue | [57] |
| miR-140-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-141-3p | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. HCC | [123] |
| miR-142-3p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-143 | Down | Downregulated in advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis | [127] |
| miR-146a | Up | Upregulated in CHB fibrosis/upregulated in cirrhosis vs. HC/HBx upregulated > CFH fiber proteins | [104,118,121,128] |
| miR-148a/b | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-149-5p | Down | Downregulated in HBV-induced cirrhosis | [129] |
| miR-150 | Down | Inhibits collagen-1 expression and HSC activation/targets c-myb | [130] |
| miR-151a-3p | Down | Downregulated as injury increases | [69] |
| miR-151-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB/predictor of activated HSCs | [118] |
| miR-17 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-17-3p | Down | Downregulated as injury increases/downregulated in cirrhosis vs. fibrosis | [129] |
| miR-17-92 | Down | MiR-17-92 family (miR-19a/b/92) downregulated in activated HSCs | [131] |
| miR-181b | Up | Promote fibrosis via TGF-β or NF-κB pathways/correlates with HBV DNA/downregulated in f4 vs. f1/upregulated in cirrhosis | [58,126] |
| miR-185 | Down | TGF-1 > miR-185 > RICTOR/RHEB > HSCs > ECM > fibrosis/downregulated in HBV-induced fibrosis | [111] |
| miR-1915 | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-19b | Down | Downregulated in activated HSCs/CHB led fibrosis/f3 > f0 | [131] |
| miR-192 | Down | Downregulated in sera of CHB patients re ECVs | [81] |
| miR-193-5p | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. HBV-HCC | [123] |
| miR-194 | Down | Inhibits collagen-1 expression and HSC/targets rac1 | [130] |
| Up | Upregulated as injury increases/targets ACVR28 | [132] | |
| miR-199 | Down | Downregulated as injury/cirrhosis develops | [126] |
| miR-199-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-199a-3p | Down | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-199a | Up | Upregulated in HBV-led fibrosis | [40] |
| miR-200a/b | Up | Upregulated in early HBV-fibrosis | [40,81] |
| miR-20a | Up | Upregulated in CHB fibrosis/f3–4 < f0–2 | [121] |
| miR-20b-5p | Down | Downregulated in advanced fibrosis versus early fibrosis/Targets p21/upregulated in sera | [57] |
| miR-206 | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. HBV-HCC | [123] |
| miR-21 | Down | Downregulated in advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis/acts via TGF-B/NF-kB pathways/downregulated f0–2 > f3–4 in CHB fibrosis | [58,118,127] |
| Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis progression | [118,133] | |
| miR-214-3p | Down | AUC 0.87 predictor of fibrosis/suppresses TGF-B pathway blocks collagen | [58,134] |
| miR-214-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis | [126] |
| miR-215 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. HC | [104,128] |
| miR-221-3p | Up | Promotes fibrosis via TGF-B/NF-kB paths/f4 down vs. F1 | [57,118] |
| miR-221 | Down | Downregulated in CHB fibrosis but/f3–4 < f0–2 | [58,121] |
| Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis | [118,126] | |
| miR-222 | Up | CHB fibrosis via TGF-β/NF-κB pathways/increasing significant upregulation from f0–4Upregulation in cirrhosis | [58,121,126] |
| miR-222-3p | Up | Upregulated 13.88-fold in cirrhosis | [76,118] |
| miR-223 | Down | Downregulated in advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis/see article for path | [127] |
| miR-224 | Down | Downregulated in CHB led fibrosis/f3–4 significantly less downregulated than f0–2 | [121] |
| Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. HC | [104,128] | |
| miR-23a/b | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-26a | Down | Increasingly downregulated in cirrhosis continuum | [133] |
| miR-26a-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. HBV-HCC | [123] |
| miR-27-3p | Up/Down | Biomarker for cirrhosis | [129] |
| miR-27a | Up | TGF-1 > miR-27a > PPARγ, FOXO1, APC, P53 and RXRα α-SMA and COL1A2 (activated HSCs) | [118] |
| miR-27b | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-2861 | Up | Upregulated stage f4 vs. f0 fibrosis | [135] |
| miR-29a | Up | Upregulated in CHB fibrosis/f3–4 < f0–2 | [121] |
| Down | Increasingly downregulated as cirrhosis develops via TGF-B, NFκB | [40] | |
| miR-29b | Down | Blocks collagen/TGF-B/targets COL1A1, COL4A5, COL5A3 | [58,117] |
| miR-30b/c | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-30e | Down | HBx-led downregulation of miR-30e >> P4HA2 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [118,123,136] |
| Down | Targets IL-6R in fibrogenic pathway | [134] | |
| miR-301a | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-324-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-33a | Up | Stimulates TGF-B, HSCs and promotes fibrosis/targets SMAD7 to stimulate TGF-B HSCs/upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [116,118] |
| miR-331-3p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-338-3p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-34a/b/c | Up | Upregulated in HBV-led fibrosis | [40] |
| miR-34b-3p | Up | Upregulated in early fibrosis/targets GRB10/PIK3CA/up in sera/tissue | [57] |
| miR-340 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-345-3p | Up | Upregulated in stage f4 vs. f0 fibrosis | [135] |
| miR-346-3p | up | Upregulated in early CHB induced fibrosis stages f1–2 | [57] |
| miR-3620-3p | Up | Upregulated in stage f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-3656 | Up | upregulated stage f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-371a-5p | Up | Upregulated in stage f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-374 | Down | Downregulated in advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis | [127] |
| miR-374b | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-377-3p | Up | Biomarker for cirrhosis | [129] |
| miR-410-3p | Up | Biomarker for cirrhosis | [129] |
| miR-424 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-455-3p | Down | Downregulated in advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis/Targets p21/upregulated in sera | [57] |
| miR-4646-5p | Up | Upregulated f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-4651 | Up | Upregulated f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-4695-5p | Up | Upregulated f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-4800-5p | Up | Upregulation f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-483-5p | Down | Downregulated in f3 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [90] |
| miR-486-3p | Down | Downregulation f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-486-5p | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. HBV-HCC | [123] |
| miR-497-5p | Down | Downregulation f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-499a-5p | Down | Downregulated in early HBV-induced fibrosis/target CDKNIA/IKBKB/upregulated in sera | [57] |
| miR-513-3p | Up | Upregulated in early cirrhosis | [58,118] |
| miR-571 | Up | Upregulated in early cirrhosis | [58,118] |
| miR-574-3p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. HC | [104,128] |
| Upregulated early cirrhosis/differentiates between cirrhosis and HBV-HCC | [118] | ||
| miR-602 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. HC/increasing in HBV-HCC | [103,128] |
| miR-615-3p | Up | Promotes hypersplenism/cirrhosis | [137] |
| miR-638 | Up | Upregulated f4 vs. f0 fibrosis/cirrhosis | [135] |
| miR-652 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-671-5p | Down | Downregulated in advanced versus early fibrosis/targets ATF2/E2F3/CREB3L2/up in sera and tissue | [57] |
| miR-744 | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-885-5p | Up | Upregulated in cirrhosis versus HC | [104,128] |
| miR-92 | Down | Downregulated in CHB fibrosis/f3–f4 > f0–f2 | [121] |
| miR-939 | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [118] |
| miR-940 | Down | Downregulated in cirrhosis vs. CHB | [129] |
| miR-942 | Up | Upregulated in activated HSCs/TGF and LPS induced miR-942 | [138] |
| miR-9-5p | Down | Fibrosis/activates HSCs via TGFBR1/TGFBR2 | [105] |
| miR-96-5p | Up | Upregulated in advanced fibrosis vs. early fibrosis/targets ATF2/E2F3/CREB3L2/up in sera and tissue | [57] |
| miRNA | Expression | Target | Gene Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| let-7 fam | Down | STAT3/RAS/HMGA2C-MYC/IL-6/IL-10/TLR-4/COL1A2/NGF, BCL-XL | Angiogenesis/growth/migration/inflammation/HBx repression | [51,52,145,146] |
| miR-1 | Down | EDN1/PI3K/AKT/HDAC4/MET | Angiogenesis, migration, invasion/modulates HBV replication | [147,148,149] |
| miR-101 | Down | DNMT3A/RASSF1/PRDM2/GSTP1/FOS/MCL-1/EZH2 | Proliferation/migration/invasion, increases HBV replication/induce DNA methylation | [120,150,151,152,153] |
| miR-101-3p | Down | ND, RAP1B/MCL-1,SOX9 | Inhibits HBV, proliferation/migration/promotes apoptosis | [154,155] |
| miR-122 | Down | β-CATENIN | EMT, cell migration, invasion and metastasis. Downregulated by HBx DNA methylation | [28,156] |
| Down | CCNG1 modulated p53/GLD2 | Promotes cell cycle progression/increases HBV replication | [35,157,158,159] | |
| Down | NDRG3/GALNT10 Cyclin G1/PTTG1 | Promotes apoptosis/blocks cell proliferation/invasion | [68,143,160,161] | |
| Down | PBF/ADAM10/Cyclin G1/Igf1R/ADAM 17/BCL-W/NDRG3 | Modulates proliferation, invasion, apoptosis | [28,35,68,162,163] | |
| miR -124 | Down | STAT3 and PIK3CA | Suppresses cell proliferation | [164] |
| miR-125b | Down | SMAD2/4/SIRTUIN7/SUV39H1/LIN28B/PIGF | Modulates EMT, growth, migration, and invasion | [28,165] |
| miR-132 | Down | AKT | Enhances cell proliferation/HBx DNA methylation downregulates miR-132 | [166] |
| miR-136 | Down | AEG-1 | Cell migration, invasion, and metastasis | [167] |
| miR-138 | Down | CCND3 | Promotes cell cycle progression/reduces HBV replication | [168] |
| miR-139-5p | Down | ZEB1/2 | Modulates EMT/metastasis | [28,169,170] |
| miR-145 | Down | MAP3K/CUL5/HDAC2/ADAM17 | Enhances proliferation, cell cycle progression, anti-apoptosis | [54,171,172] |
| miR-148a | Down | HPIP/AKT/ERK/FOXO4/ATF5/mTOR/MET/ACVR1 | Down in HCC tissue/Cell proliferation, EMT, and cell migration | [28,173,174,175] |
| miR-152 | Down | DNMT1/GSTP/CDH1/KIT | Modulates DNA methylation/cell proliferation/migration/invasion, blocks HBV | [176,177,178,179] |
| miR-15a/16-1 | Down | CCND1/BCL-2 | Promotes cell cycle progression/proliferation | [28,78,180,181] |
| miR-15b | Down | FUT2/GloboH/HNFα | Enhances cell proliferation | [182,183] |
| mIR-16 | Down | Cyclin D1, NCOR2 | Promotes apoptosis, decreases proliferation | [28,180] |
| miR-18a | Down | ERα/CTGF | Enhances proliferation, regulates connective tissue growth | [184,185] |
| miR-192 | Down | G1-G2 arrest/SLC39A6/SNAIL | Cell cycle control/regulates metastasis | [28,186,187] |
| miR-193b | Down | ING5/CCND1/ETS1 | Regulate CDK2, proliferation, invasion | [188,189] |
| miR-200 fam | Down | ZEB1/2 | Modulates ZEB1/2 regulated E-cadherin | [28,190] |
| miR-205 | Down | ACSL4/E2F1/ZEB1/2 | Lipogenesis and cell proliferation/promotes EMT | [28,95,191] |
| miR-21 | Down | PTEN/PIP3/AKT | Down in serum/inhibits cell proliferation | [54,192] |
| miR-216b | Down | IGF2BP2/IGF2/AKT/mTOR/MAPK/ERK | Cell proliferation and cell migration | [54,193] |
| miR-222 | Down | p27 | Inhibits cell cycle progression | [54] |
| miR-23a | Down | Myc/E-CADHERIN/SPROUTY2 | Regulates EMT/metastasis | [28,194,195,196] |
| miR-26a/c | Down | IL-6/IFNα/ERα/IL-6/Cyclin D2/Cyclin E2 | Inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis | [197,198,199] |
| miR-29c | Down | BCL-2/MCL-1/TNFA1P3 | Inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis | [200,201] |
| miR-338-3p | Down | CCND1 | Promotes cell cycle progression | [202,203] |
| miR-34a | Down | CCL22/MAP4K4/SIRT1/CCND1/CDK4/6/MET | Modulates metastasis/growth/apoptosis | [29,204,205,206,207] |
| miR-363-3p | Down | SP1 | Modulates tumor growth | [28,208] |
| miR-373 | Down | E-CADHERIN | EMT, cell migration, invasion, and metastasis | [49] |
| miR-375 | Down | AEG-1 | Cell migration, invasion, and metastasis | [167] |
| miR-429 | Down | RAB18, NOTCH1 | Lipogenesis/proliferation, apoptosis | [209,210] |
| miR-520b | Down | HBXIP | Enhancing cell proliferation | [211] |
| miR-548p | Down | HBXIP, IFN-λ1 | Increases growth, blocks apoptosis/immune response | [102,212] |
| miR-661 | Down | MTA1/NK-κB/iNOS/NO | Angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and migration | [213] |
| miRNA | Expression | Target | Gene Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | Up | MASPIN | HBx-induced HBV-HCC progression | [214] |
| miR-107 | Up | AXIN2/MASPIN | Cell proliferation/HBV-HCC progression | [214,215] |
| miR-125a | Up | ERBB2, HBsAg | Suppresses HBsAg | [74,178,216] |
| miR-143 | Up | FNDC3B | Cell migration, invasion and metastasis | [28,217] |
| miR-146a | Up | CFH/STAT1 | Regulates inflammation/IFNα mediated anti- HBV efficiency | [104,218,219] |
| miR-155 | Up | PTEN/SOX6/ZHX2/SOCS1 | Promotes cell growth | [220,221,222] |
| miR-17-92 | Up | E2F1 (C-MYC-repressor), Cyclin G1 | Promotes HCC, blocks HBV replication, enhances proliferation and anchorage-independent growth | [82,223,224] |
| miR-181a | Up | FAS, E2F5 | Inhibits apoptosis, promotes cell growth | [85,86] |
| miR-199a-5p | Up | CHC | Promoting cell proliferation | [168] |
| miR-203a | Up | RAP1A | Increases inflammation/alters MAPK signaling | [96] |
| miR-21 | Up | PDCD4, PTEN | Up in HCC tissue/Targets tumor suppressors/Stops apoptosis/immune response/HBV evasion/promotes cell growth/up in HBV-HCC vs. CHB-L Cirrhosis serum | [54,55,56,65,214,225,226] |
| miR-215 | Up | PTPRP | Proliferation of hepatoma cells | [104,186,227] |
| miR-221 | Up | ERα, DDIT4/BMF/p27/p57 | Cell cycle progression (G1/S) and cell proliferation | [228,229,230] |
| miR-222 | Up | P27(kip1)/PTEN/PPP2R2A/p27/p57 | Promotes cell growth, migration | [54,230,231,232] |
| miR-224 | Up | PAK4/MMP9 inhibitor-5/SMAD4 | Enhance HBV replication, cell growth and invasion | [233,234,235] |
| miR-27a | Up | PPARγ, FOXO1, APC, P53 and RXRα | Enhances proliferation, migration, invasion | [118,236] |
| miR-29a | Up | PTEN/PI3K/AKT/MMP-2 | Enhancing cell migration | [54,237] |
| miR-30c | Up | HMBOX1 | Induces NK activity | [146,238] |
| miR-331-3p | Up | ING5 | Cell proliferation and apoptosis | [239] |
| miR-545/374a | Up | ESRRG | Cell proliferation and cell migration | [240,241] |
| miR-602 | Up | RASSF1a/STAT3/MYC | Cell apoptosis and proliferation, increases HBV | [13,103] |
| miR-7 | Up | EGFR/RAF/EKERK/PI3K-AKT/MASPIN | Inhibits cell growth | [214,241,242,243] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sartorius, K.; Makarova, J.; Sartorius, B.; An, P.; Winkler, C.; Chuturgoon, A.; Kramvis, A. The Regulatory Role of MicroRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) Pathogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121504
Sartorius K, Makarova J, Sartorius B, An P, Winkler C, Chuturgoon A, Kramvis A. The Regulatory Role of MicroRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) Pathogenesis. Cells. 2019; 8(12):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121504
Chicago/Turabian StyleSartorius, Kurt, Julia Makarova, Benn Sartorius, Ping An, Cheryl Winkler, Anil Chuturgoon, and Anna Kramvis. 2019. "The Regulatory Role of MicroRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) Pathogenesis" Cells 8, no. 12: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121504
APA StyleSartorius, K., Makarova, J., Sartorius, B., An, P., Winkler, C., Chuturgoon, A., & Kramvis, A. (2019). The Regulatory Role of MicroRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) Pathogenesis. Cells, 8(12), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121504