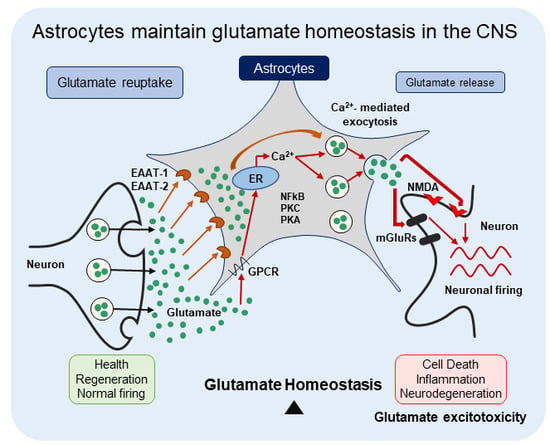
Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Glutamate Uptake in the CNS
2.1. Glutamate Uptake Transporters
2.1.1. Na+-Independent Glutamate Uptake Transporters
2.1.2. Na+-Dependent Glutamate Uptake Transporters
2.2. Expression Profile of EAAT-1 and EAAT-2
2.3. EAAT-2 and EAAT-1 in Astrocytes Play the Major Role in Glutamate Uptake in the CNS
2.4. Mechanism of Glutamate Uptake by EAATs
2.5. Metabolism of Glutamate in Astrocytes
2.6. EAAT-1 and EAAT-2 Regulation of Expression
2.6.1. Transcriptional and Translational Modifications
2.6.2. Post-Translational Modifications and Regulation of the Transporter Activity
3. Glutamate Release by Astrocytes
3.1. Physiological Role of Astroglial Glutamate Release
3.2. Mechanisms of Glutamate Release by Astrocytes
3.2.1. Ca2+-Mediated Exocytosis
3.2.2. Bestrophin-1 and TREK-1 Channel-Mediated Glutamate Release.
3.2.3. Glutamate Release through P2X7 Receptors
3.2.4. Cystine/Glutamate Antiporters
3.2.5. Reversal of Glutamate Uptake Transporters
3.2.6. Gap Junction Hemichannels
3.2.7. Volume-Regulated Anion Channels (VRACs)
3.3. An Issue of Debate Shrouds Astroglial Glutamate Release
4. Dysregulation of Astrocytic Glutamate Uptake and/or Release Leads to CNS Disorders
5. Mechanism of Glutamate Excitotoxicity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, C.; Aloisi, F.; Meinl, E. Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, D.; Johnston, G. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergebnisse der Physiol. Rev. Physiol. 1974, 69, 97–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonnum, F. Glutamate: A Neurotransmitter in Mammalian Brain. J. Neurochem. 1984, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, C.M.; Swanson, R.A. Astrocyte glutamate transport: Review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 2000. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, N.B.; Attwell, D. Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarkey, E.B.; Parpura, V. Mechanisms of glutamate release from astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehre, K.P.; Danbolt, N.C. The number of glutamate transporter subtype molecules at glutamatergic synapses: Chemical and stereological quantification in young adult rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8751–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulenburg, V.; Gomeza, J. Neurotransmitter transporters expressed in glial cells as regulators of synapse function. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.R.; Ziemens, D.; Untiet, V.; Fahlke, C. Molecular and cellular physiology of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 136, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Bannai, S. Uptake of glutamate and cysteine in C-6 glioma cells and in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.J.; Chang, Y.F.; Schwarcz, R.; Brookes, N. Characterization of l-alpha-aminoadipic acid transport in cultured rat astrocytes. Brain Res. 1996, 741, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, T.; Baba, A. l-lactate inhibits l-cystine/l-glutamate exchange transport and decreases glutathione content in rat cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 59, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, D.; Fontana, A. Involvement of the cystine transport system xc- in the macrophage-induced glutamate-dependent cytotoxicity to neurons. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 3578–3585. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, S.; Ishita, S.; Sugawara, K.; Mawatari, K. Cystine/glutamate antiporter expression in retinal Müller glial cells: Implications for DL-alpha-aminoadipate toxicity. Neuroscience 1993, 57, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.C.; Rothstein, J.D.; Sontheimer, H. Compromised glutamate transport in human glioma cells: Reduction-mislocalization of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters and enhanced activity of cystine-glutamate exchange. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10767–10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidharan, P.; Plaitakis, A. Cloning and characterization of a glutamate transporter cDNA from human cerebellum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1216, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidharan, P.; Wittenberg, I.; Plaitakis, A. Molecular cloning of human brain glutamate/aspartate transporter II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1191, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, T.; Schulte, S.; Hofmann, K.; Stoffel, W. Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10955–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Bjørås, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bendahan, A.; Eide, L.; Koepsell, H.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Seeberg, E.; Kanner, B.I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain l-glutamate transporter. Nature 1992, 360, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, Y.; Hediger, M.A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 1992, 360, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman, W.A.; Vandenberg, R.J.; Arriza, J.L.; Kavanaught, M.P.; Amara, S.G. An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature 1995, 375, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriza, J.L.; Eliasof, S.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4155–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Schousboe, A. High affinity glutamate transporters: Regulation of expression and activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, U.; Storck, T.; Conradt, M.; Stoffel, W. Functional properties and substrate specificity of the cloned L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter GLAST-1 from rat brain expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5759–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerangue, N.; Arriza, J.L.; Amara, S.G.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Differential modulation of human glutamate transporter subtypes by arachidonic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6433–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriza, J.L.; Fairman, W.A.; Wadiche, J.I.; Murdoch, G.H.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5559–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owe, S.G.; Marcaggi, P.; Attwell, D. The ionic stoichiometry of the GLAST glutamate transporter in salamander retinal glia. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibata, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ikenaka, K.; Wada, K.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y. Glutamate transporter GLAST is expressed in the radial glia-astrocyte lineage of developing mouse spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 9212–9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.; Levey, A.I.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Jin, L.; Wu, D.; Nash, N.; Kuncl, R.W. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 1994, 13, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Lehre, K.P.; van Lookeren Campagne, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Danbolt, N.C.; Storm-Mathisen, J. Glutamate transporters in glial plasma membranes: Highly differentiated localizations revealed by quantitative ultrastructural immunocytochemistry. Neuron 1995, 15, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takayasu, Y.; Iino, M.; Takatsuru, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Ozawa, S. Functions of glutamate transporters in cerebellar Purkinje cell synapses. Acta Physiol. 2009, 197, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouiche, A.; Rauen, T. Coincidence of L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter (GLAST) and glutamine synthetase (GS) immunoreactions in retinal glia: Evidence for coupling of GLAST and GS in transmitter clearance. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 42, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehre, K.P.; Davanger, S.; Danbolt, N.C. Localization of the glutamate transporter protein GLAST in rat retina. Brain Res. 1997, 744, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, U.V.; Hediger, M.A. Distribution of the glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 in rat circumventricular organs, meninges, and dorsal root ganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 421, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, D.N.; Lehre, K.P. Immunocytochemical Localization of a High-affinity Glutamate-Aspartate Transporter, GLAST, in the Rat and Guinea-pig Cochlea. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, Y.; Matsubara, A.; Danbolt, N.; Laake, J.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Usami, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Ottersen, O. Discrete cellular and subcellular localization of glutamine synthetase and the glutamate transporter GLAST in the rat vestibular end organ. Neuroscience 1997, 79, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowatzki, E.; Cheng, N.; Hiel, H.; Yi, E.; Tanaka, K.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.R.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E. The Glutamate-Aspartate Transporter GLAST Mediates Glutamate Uptake at Inner Hair Cell Afferent Synapses in the Mammalian Cochlea. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7659–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, A.; Asan, E.; Püschel, B.; Kugler, P. Cellular and regional distribution of the glutamate transporter GLAST in the CNS of rats: Nonradioactive in situ hybridization and comparative immunocytochemistry. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Kitanaka, J.; Sawada, M.; Suzumura, A.; Marunouchi, T.; Baba, A. Expression of glutamate transporters in cultured glial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 188, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domercq, M.; Matute, C. Expression of glutamate transporters in the adult bovine corpus callosum. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1999, 67, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullensvang, K.; Lehre, K.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Danbolt, N.C. Differential Developmental Expression of the Two Rat Brain Glutamate Transporter Proteins GLAST and GLT. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, A.E.; Durry, S.; Aida, T.; Stock, M.C.; Rüther, U.; Tanaka, K.; Rose, C.R.; Kafitz, K.W. Laminar and subcellular heterogeneity of GLAST and GLT-1 immunoreactivity in the developing postnatal mouse hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, A.; Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.J. Glutamate transporter protein subtypes are expressed differentially during rat CNS development. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8363–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachez, C.; Danbolt, N.C.; Récasens, M. Transient expression of the glial glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT in hippocampal neurons in primary culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 59, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Kayal, A.R.; Munir, M.; Jin, H.; Robinson, M.B. The glutamate transporter, GLT-1, is expressed in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurochem. Int. 1998, 33, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennerick, S.; Dhond, R.P.; Benz, A.; Xu, W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Danbolt, N.C.; Isenberg, K.E.; Zorumski, C.F. Neuronal expression of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 in hippocampal microcultures. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Shibata, T.; Nagashima, M.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y. Glutamate transporter GLT-1 is transiently localized on growing axons of the mouse spinal cord before establishing astrocytic expression. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 5706–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Brambrink, A.M.; Lehmann, C.; Portera-Cailliau, C.; Koehler, R.; Rothstein, J.; Traystman, R.J. Hypoxia?ischemia causes abnormalities in glutamate transporters and death of astroglia and neurons in newborn striatum. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, C.; Okada, R.; Mitani, A.; Fukaya, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Fujihara, Y.; Shirakawa, T.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, M. Glutamate Transporters Regulate Lesion-Induced Plasticity in the Developing Somatosensory Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4995–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benediktsson, A.M.; Marrs, G.S.; Tu, J.C.; Worley, P.F.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E.; Dailey, M.E. Neuronal activity regulates glutamate transporter dynamics in developing astrocytes. Glia 2012, 60, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, A.; Barbaresi, P.; Reimer, R.; Edwards, R.; Conti, F. The glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 is localized both in the vicinity of and at distance from axon terminals in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 2001, 108, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitry-Yamate, C.L.; Vutskits, L.; Rauen, T. Neuronal-induced and glutamate-dependent activation of glial glutamate transporter function. J. Neurochem. 2002, 82, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Sutherland, M.L. Glutamate Transporter Cluster Formation in Astrocytic Processes Regulates Glutamate Uptake Activity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6301–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, T.; Otsubo, Y.; Yatani, Y.; Shirakawa, H.; Kaneko, S. Mechanisms of substrate transport-induced clustering of a glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astroglial-neuronal cultures. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.A.; Liu, J.; Miller, J.W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Farrell, K.; Stein, B.A.; Longuemare, M.C. Neuronal regulation of glutamate transporter subtype expression in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlag, B.D.; Vondrasek, J.R.; Munir, M.; Kalandadze, A.; Zelenaia, O.A.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Regulation of the glial Na+-dependent glutamate transporters by cyclic AMP analogs and neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.A.; Aizenman, E. Hundred-fold increase in neuronal vulnerability to glutamate toxicity in astrocyte-poor cultures of rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 103, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennerick, S.; Zorumski, C.F. Glial contributions to excitatory neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal cells. Nature 1994, 368, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Jahr, C.E. Synaptic activation of glutamate transporters in hippocampal astrocytes. Neuron 1997, 19, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Nakamura, T.; Nidaira, T.; Nakamura, K.; Ooashi, N.; Ito, E.; Watase, K.; Tanaka, K.; Wada, K.; Kudo, Y.; et al. Optical detection of synaptically induced glutamate transport in hippocampal slices. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.A.; Barbour, B. Currents evoked in Bergmann glial cells by parallel fibre stimulation in rat cerebellar slices. J. Physiol. 1997, 502, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergles, D.E.; Dzubay, J.A.; Jahr, C.E. Glutamate transporter currents in bergmann glial cells follow the time course of extrasynaptic glutamate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14821–14825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Jahr, C.E. Glial contribution to glutamate uptake at Schaffer collateral-commissural synapses in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7709–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Pardo, C.A.; Bristol, L.A.; Jin, L.; Kuncl, R.W.; Kanai, Y.; Hediger, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Schielke, J.P.; et al. Knockout of Glutamate Transporters Reveals a Major Role for Astroglial Transport in Excitotoxicity and Clearance of Glutamate. Neuron 1996, 16, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, K.; Watase, K.; Manabe, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, K.; Iwama, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Ichihara, N.; Kikuchi, T.; et al. Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 1997, 276, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, G.T.; Sun, Y.; Frederick, N.M.; Zhou, Y.; Dhamne, S.C.; Hameed, M.Q.; Miranda, C.; Bedoya, E.A.; Fischer, K.D.; Armsen, W.; et al. Conditional Deletion of the Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 Reveals That Astrocytic GLT-1 Protects against Fatal Epilepsy While Neuronal GLT-1 Contributes Significantly to Glutamate Uptake into Synaptosomes. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5187–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watase, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Kano, M.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, Y.; Okuyama, S.; Sakagawa, T.; Ogawa, S.; Kawashima, N.; et al. Motor discoordination and increased susceptibility to cerebellar injury in GLAST mutant mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peghini, P.; Janzen, J.; Stoffel, W. Glutamate transporter EAAC-1-deficient mice develop dicarboxylic aminoaciduria and behavioral abnormalities but no neurodegeneration. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3822–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E. Glutamate transporters bring competition to the synapse. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.B.; Dowling, J.E. A glutamate-activated chloride current in cone-driven ON bipolar cells of the white perch retina. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3852–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otis, T.S.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Jahr, C.E. Postsynaptic glutamate transport at the climbing fiber-Purkinje cell synapse. Science 1997, 277, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Ransom, B.R. Intracellular sodium homeostasis in rat hippocampal astrocytes. J. Physiol. 1996, 491, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, I.A.; Deas, J.; Erecińska, M. Ion homeostasis in brain cells: Differences in intracellular ion responses to energy limitation between cultured neurons and glial cells. Neuroscience 1997, 78, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Waxman, S.G.; Ransom, B.R. Effects of glucose deprivation, chemical hypoxia, and simulated ischemia on Na+ homeostasis in rat spinal cord astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3554–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuemare, M.C.; Rose, C.R.; Farrell, K.; Ransom, B.R.; Waxman, S.G.; Swanson, R.A. K(+)-induced reversal of astrocyte glutamate uptake is limited by compensatory changes in intracellular Na+. Neuroscience 1999, 93, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.C.; Schousboe, A.; Hertz, L. Metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 1982, 39, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinelli, S.E.; Nicklas, W.J. Glutamate metabolism in rat cortical astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 1992, 58, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Sonnewald, U.; Huang, X.; Stevenson, J.; Zielke, H.R. Exogenous glutamate concentration regulates the metabolic fate of glutamate in astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnewald, U.; Westergaard, N.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate transport and metabolism in astrocytes. Glia 1997, 21, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, L.; Dringen, R.; Schousboe, A.; Robinson, S.R. Astrocytes: Glutamate producers for neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 57, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Diamond, J.S.; Jahr, C.E. Clearance of glutamate inside the synapse and beyond. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1999, 9, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, L.K.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Sarup, A.; Bak, L.K.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Larsson, O.M. Role of astrocytic transport processes in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, H.; Drejer, J.; Schousboe, A.; Diemer, N.H. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 1984, 43, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erecińska, M.; Silver, I.A. Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1990, 35, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerangue, N.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 1996, 383, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, L.M.; Warr, O.; Attwell, D. Stoichiometry of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 expressed inducibly in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line selected for low endogenous Na+-dependent glutamate uptake. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9620–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, C.L.; Kimelberg, H.K. Excitatory amino acids directly depolarize rat brain astrocytes in primary culture. Nature 1984, 311, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadiche, J.I.; Amara, S.G.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Ion fluxes associated with excitatory amino acid transport. Neuron 1995, 15, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairman, W.A.; Sonders, M.S.; Murdoch, G.H.; Amara, S.G. Arachidonic acid elicits a substrate-gated proton current associated with the glutamate transporter EAAT4. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untiet, V.; Kovermann, P.; Gerkau, N.J.; Gensch, T.; Rose, C.R.; Fahlke, C. Glutamate transporter-associated anion channels adjust intracellular chloride concentrations during glial maturation. Glia 2017, 65, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, N.R.; Dhankhar, A.; Mason, G.F.; Rothman, D.L.; Behar, K.L.; Shulman, R.G. Stoichiometric coupling of brain glucose metabolism and glutamatergic neuronal activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellerin, L.; Magistretti, P.J. Glutamate uptake stimulates Na+,K+-ATPase activity in astrocytes via activation of a distinct subunit highly sensitive to ouabain. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, J.-Y.; Marquet, P.; Magistretti, P.J. A quantitative analysis of l -glutamate-regulated Na + dynamics in mouse cortical astrocytes: Implications for cellular bioenergetics. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, L.; Magistretti, P.J. Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: A mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10625–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardinelli, Y.; Magistretti, P.J.; Chatton, J.-Y. Astrocytes generate Na+-mediated metabolic waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14937–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Chatton, J.-Y. Relationship between l-glutamate-regulated intracellular Na+ dynamics and ATP hydrolysis in astrocytes. J. Neural Transm. 2005, 112, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaman, I.; Bélanger, M.; Magistretti, P.J. Astrocyte–neuron metabolic relationships: For better and for worse. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, J.-Y.; Magistretti, P.J.; Barros, L.F. Sodium signaling and astrocyte energy metabolism. Glia 2016, 64, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waniewski, R.A.; Martin, D.L. Exogenous glutamate is metabolized to glutamine and exported by rat primary astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 1986, 47, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hernandez, A.; Bell, K.P.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine synthetase: Glial localization in brain. Science 1977, 195, 1356–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammer, W. Glutamine synthetase in the central nervous system is not confined to astrocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 26, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Reimer, R.J.; Krizaj, D.; Barber, D.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Copenhagen, D.R.; Edwards, R.H. Molecular Analysis of System N Suggests Novel Physiological Roles in Nitrogen Metabolism and Synaptic Transmission. Cell 1999, 99, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bröer, S.; Brookes, N. Transfer of glutamine between astrocytes and neurons. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bröer, A.; Albers, A.; Setiawan, I.; Edwards, R.H.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Lang, F.; Wagner, C.A.; Bröer, S. Regulation of the glutamine transporter SN1 by extracellular pH and intracellular sodium ions. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, A.J.; McDonald, J.M.; Gelbard, A.S.; Gledhill, R.F.; Duffy, T.E. The metabolic fate of 13N-labeled ammonia in rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 4982–4992. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.J.L.; Lai, J.C.K. Cerebral ammonia metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rats. Neurochem. Pathol. 1987, 6, 67–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaggi, P.; Coles, J.A. Ammonium in nervous tissue: Transport across cell membranes, fluxes from neurons to glial cells, and role in signalling. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 64, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Zielińska, M.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine as a mediator of ammonia neurotoxicity: A critical appraisal. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rama Rao, K.V.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine in the pathogenesis of acute hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Stridh, M.H.; McNair, L.F.; Sonnewald, U.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate oxidation in astrocytes: Roles of glutamate dehydrogenase and aminotransferases. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C. Glutamate Pays Its Own Way in Astrocytes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2013, 4, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi-Castañeda, D.; Suárez-Pozos, E.; Ortega, A. Regulation of Glutamate Transporter Expression in Glial Cells. In Advances in Neurobiology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 16, pp. 199–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, R.; Rothstein, J.D. Regulation and dysregulation of glutamate transporters. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 277–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Civenni, G.; Racagni, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Schousboe, I.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate receptor agonists up-regulate glutamate transporter GLAST in astrocytes. Neuroreport 1996, 8, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Anderson, C.M.; Stein, B.A.; Swanson, R.A. Glutamate induces rapid upregulation of astrocyte glutamate transport and cell-surface expression of GLAST. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10193–10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Dehnes, Y.; Danbolt, N.C.; Schousboe, A. The high-affinity glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST, and EAAT4 are regulated via different signalling mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, E.; Gorter, J.A.; Ijlst-Keizers, H.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Yankaya, B.; Leenstra, S.; Troost, D. Expression and functional role of mGluR3 and mGluR5 in human astrocytes and glioma cells: Opposite regulation of glutamate transporter proteins. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; You, J.-R.; Wei, K.-C.; Gean, P.-W. Stimulating ERK/PI3K/NFκB signaling pathways upon activation of mGluR2/3 restores OGD-induced impairment in glutamate clearance in astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bayghen, E.; Espinoza-Rojo, M.; Ortega, A. Glutamate down-regulates GLAST expression through AMPA receptors in Bergmann glial cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bayghen, E.; Ortega, A. Glutamate-dependent transcriptional regulation of GLAST: Role of PKC. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apricò, K.; Beart, P.M.; Crawford, D.; O’Shea, R.D. Binding and transport of [3H](2S,4R)- 4-methylglutamate, a new ligand for glutamate transporters, demonstrate labeling of EAAT1 in cultured murine astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 75, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Lane, M.; Krizman, E.; Sattler, R.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. The transcription factor Pax6 contributes to the induction of GLT-1 expression in astrocytes through an interaction with a distal enhancer element. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenaia, O.; Schlag, B.D.; Gochenauer, G.E.; Ganel, R.; Song, W.; Beesley, J.S.; Grinspan, J.B.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Epidermal growth factor receptor agonists increase expression of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astrocytes through pathways dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and transcription factor NF-kappaB. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, M.; Maucher, T.; Rozyczka, J.; Bayatti, N.; Engele, J. Regulation of glial glutamate transporter expression by growth factors. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 183, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, M.; Engele, J. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP), a neuron-derived peptide regulating glial glutamate transport and metabolism. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3596–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ikegaya, Y.; Matsuura, S.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H.; Matsuki, N. Transient upregulation of the glial glutamate transporter GLAST in response to fibroblast growth factor, insulin-like growth factor and epidermal growth factor in cultured astrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3717–3725. [Google Scholar]
- Bonde, C.; Sarup, A.; Schousboe, A.; Gegelashvili, G.; Noraberg, J.; Zimmer, J. GDNF pre-treatment aggravates neuronal cell loss in oxygen-glucose deprived hippocampal slice cultures: A possible effect of glutamate transporter up-regulation. Neurochem. Int. 2003, 43, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, P.; Webb, A.; Zerguine, A.; Choi, J.; Son, D.-S.; Lee, E. Mechanism of raloxifene-induced upregulation of glutamate transporters in rat primary astrocytes. Glia 2014, 62, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.-S.Y.; Sidoryk, M.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Z.; Aschner, M. Estrogen and tamoxifen reverse manganese-induced glutamate transporter impairment in astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karki, P.; Webb, A.; Smith, K.; Lee, K.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. cAMP Response Element-binding Protein (CREB) and Nuclear Factor κB Mediate the Tamoxifen-induced Up-regulation of Glutamate Transporter 1 (GLT-1) in Rat Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28975–28986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.; Sidoryk-Wêgrzynowicz, M.; Wang, N.; Webb, A.; Son, D.-S.; Lee, K.; Aschner, M. GPR30 Regulates Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 Expression in Rat Primary Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26817–26828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zschocke, J.; Bayatti, N.; Clement, A.M.; Witan, H.; Figiel, M.; Engele, J.; Behl, C. Differential Promotion of Glutamate Transporter Expression and Function by Glucocorticoids in Astrocytes from Various Brain Regions. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34924–34932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poblete-Naredo, I.; Angulo, C.; Hernández-Kelly, L.; López-Bayghen, E.; Aguilera, J.; Ortega, A. Insulin-dependent regulation of GLAST/EAAT1 in Bergmann glial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 451, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzo, M.E.; Frizzo, J.K.; Amadio, S.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Perry, M.L.; Bernardi, G.; Volonté, C. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate induces glutamate transporter-1 expression in hippocampus. Hippocampus 2007, 17, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, T.; Johng, S.; Rohrback, S.; Kang, N.; Choi, D.-S. Regulation of ethanol-sensitive EAAT2 expression through adenosine A1 receptor in astrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.-W.; Nguyen, K.T.D.; Pow, D.V.; Knight, T.; Buljan, V.; Bennett, M.R.; Balcar, V.J. Distribution of Glutamate Transporter GLAST in Membranes of Cultured Astrocytes in the Presence of Glutamate Transport Substrates and ATP. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozyczka, J.; Figiel, M.; Engele, J. Endothelins negatively regulate glial glutamate transporter expression. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Grammas, P. Endothelin-1 is Elevated in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain Microvessels and is Neuroprotective. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 21, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, V.I.; Rozanski, V.E.; Beyer, C.; Küppers, E. Dopamine Regulates the Expression of the Glutamate Transporter GLT1 but Not GLAST in Developing Striatal Astrocytes. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 39, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.-J.; Her, L.-S.; Liaw, H.-J.; Chen, M.-C.; Tzeng, S.-F. Retinoic acid mediates the expression of glutamate transporter-1 in rat astrocytes through genomic RXR action and non-genomic protein kinase C signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korn, T.; Magnus, T.; Jung, S. Autoantigen specific T cells inhibit glutamate uptake in astrocytes by decreasing expression of astrocytic glutamate transporter GLAST: A mechanism mediated by tumor necrosis factor-α. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1878–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitcheran, R.; Gupta, P.; Fisher, P.B.; Baldwin, A.S. Positive and negative regulation of EAAT2 by NF-κB: A role for N-myc in TNFα-controlled repression. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, P.; Webb, A.; Smith, K.; Johnson, J.; Lee, K.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Yin Yang 1 Is a Repressor of Glutamate Transporter EAAT2, and It Mediates Manganese-Induced Decrease of EAAT2 Expression in Astrocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torp, R.; Lekieffre, D.; Levy, L.M.; Haug, F.M.; Danbolt, N.C.; Meldrum, B.S.; Ottersen, O.P. Reduced postischemic expression of a glial glutamate transporter, GLT1, in the rat hippocampus. Exp. Brain Res. 1995, 103, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, M.; Li, P.; Mangin, J.-M.; Huntsman, M.; Gallo, V. Chronic Perinatal Hypoxia Reduces Glutamate-Aspartate Transporter Function in Astrocytes through the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 17864–17871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, D.; Guo, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, G.; Qin, H.; Wu, S. FGF2 alleviates PTSD symptoms in rats by restoring GLAST function in astrocytes via the JAK/STAT pathway. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradt, M.; Storck, T.; Stoffel, W. Localization of N-glycosylation sites and functional role of the carbohydrate units of GLAST-1, a cloned rat brain L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 229, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raunser, S.; Haase, W.; Bostina, M.; Parcej, D.N.; Kühlbrandt, W. High-yield Expression, Reconstitution and Structure of the Recombinant, Fully Functional Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 from Rattus norvegicus. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchbach, M.E.R.; Tian, G.; Guo, H.; Lin, C.G. Association of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters, Especially EAAT2, with Cholesterol-rich Lipid Raft Microdomains. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 34388–34396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casado, M.; Bendahan, A.; Zafra, F.; Danbolt, N.C.; Aragón, C.; Giménez, C.; Kanner, B.I. Phosphorylation and modulation of brain glutamate transporters by protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 27313–27317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Zelenaia, O.; Correale, D.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Expression of the GLT-1 subtype of Na+-dependent glutamate transporter: Pharmacological characterization and lack of regulation by protein kinase C. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalandadze, A.; Wu, Y.; Robinson, M.B. Protein Kinase C Activation Decreases Cell Surface Expression of the GLT-1 Subtype of Glutamate Transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45741–45750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.I.; Susarla, B.T.S.; Robinson, M.B. Evidence that protein kinase Cα interacts with and regulates the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- GUILLET, B.; VELLY, L.; CANOLLE, B.; MASMEJEAN, F.; NIEOULLON, A.; PISANO, P. Differential regulation by protein kinases of activity and cell surface expression of glutamate transporters in neuron-enriched cultures. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 46, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conradt, M.; Stoffel, W. Inhibition of the high-affinity brain glutamate transporter GLAST-1 via direct phosphorylation. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.I.; López-Colom, A.M.; Ortega, A. Sodium-dependent glutamate transport in Müller glial cells: Regulation by phorbol esters. Brain Res. 1999, 831, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.I.; Ortega, A. Regulation of the Na+-dependent high affinity glutamate/aspartate transporter in cultured Bergmann glia by phorbol esters. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 50, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susarla, B.T.S.; Seal, R.P.; Zelenaia, O.; Watson, D.J.; Wolfe, J.H.; Amara, S.G.; Robinson, M.B. Differential regulation of GLAST immunoreactivity and activity by protein kinase C: Evidence for modification of amino and carboxyl termini. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundy, D.F.; McBean, G.J. Pre-incubation of synaptosomes with arachidonic acid potentiates inhibition of [3H]D-aspartate transport. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 291, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, C.; Mennini, T. Arachidonic Acid Inhibits3h-Glutamate Uptake with Different Potencies in Rodent Central Nervous System Regions Expressing Different Transporter Subtypes. Pharmacol. Res. 1997, 35, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volterra, A.; Trotti, D.; Cassutti, P.; Tromba, C.; Salvaggio, A.; Melcangi, R.C.; Racagni, G. High sensitivity of glutamate uptake to extracellular free arachidonic acid levels in rat cortical synaptosomes and astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masliah, E.; Hansen, L.; Alford, M.; Deteresa, R.; Mallory, M. Deficient glutamate tranport is associated with neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegaya, Y.; Matsuura, S.; Ueno, S.; Baba, A.; Yamada, M.K.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsuki, N. β-Amyloid Enhances Glial Glutamate Uptake Activity and Attenuates Synaptic Efficacy. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32180–32186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volterra, A.; Trotti, D.; Floridi, S.; Racagni, G. Reactive oxygen species inhibit high-affinity glutamate uptake: Molecular mechanism and neuropathological implications. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 738, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, O.; Horn, T.F.; Yu, N.; Gruol, D.L.; Bloom, F.E. Inhibition of astrocyte glutamate uptake by reactive oxygen species: Role of antioxidant enzymes. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotti, D.; Rizzini, B.L.; Rossi, D.; Haugeto, O.; Racagni, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Volterra, A. Neuronal and glial glutamate transporters possess an SH-based redox regulatory mechanism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, D.J.; Dixit, S.; Warner, T.A.; Kennard, J.A.; Scharf, D.A.; Kessler, E.S.; Moore, L.M.; Consoli, D.C.; Bown, C.W.; Eugene, A.J.; et al. Altered glutamate clearance in ascorbate deficient mice increases seizure susceptibility and contributes to cognitive impairment in APP/PSEN1 mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 71, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell-Bell, A.H.; Finkbeiner, S.M.; Cooper, M.S.; Smith, S.J. Glutamate induces calcium waves in cultured astrocytes: Long-range glial signaling. Science 1990, 247, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Basarsky, T.A.; Liu, F.; Jeftinija, K.; Jeftinija, S.; Haydon, P.G. Glutamate-mediated astrocyte–neuron signalling. Nature 1994, 369, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, M. Direct signaling from astrocytes to neurons in cultures of mammalian brain cells. Science 1994, 263, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasti, L.; Volterra, A.; Pozzan, T.; Carmignoto, G. Intracellular calcium oscillations in astrocytes: A highly plastic, bidirectional form of communication between neurons and astrocytes in situ. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 7817–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Carmignoto, G.; Pasti, L.; Vesce, S.; Rossi, D.; Rizzini, B.L.; Pozzan, T.; Volterra, A. Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature 1998, 391, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangršič, T.; Potokar, M.; Stenovec, M.; Kreft, M.; Fabbretti, E.; Nistri, A.; Pryazhnikov, E.; Khiroug, L.; Giniatullin, R.; Zorec, R. Exocytotic Release of ATP from Cultured Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28749–28758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Ye, C.; Ge, W.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, C.; Poo, M.; Duan, S. ATP released by astrocytes mediates glutamatergic activity-dependent heterosynaptic suppression. Neuron 2003, 40, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Meur, K.; Mendizabal-Zubiaga, J.; Grandes, P.; Audinat, E. GABA release by hippocampal astrocytes. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; McGeer, E.G.; McGeer, P.L. Mechanisms of GABA release from human astrocytes. Glia 2011, 59, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.-E.; Jo, S.; Woo, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.J. The amount of astrocytic GABA positively correlates with the degree of tonic inhibition in hippocampal CA1 and cerebellum. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mothet, J.-P.; Pollegioni, L.; Ouanounou, G.; Martineau, M.; Fossier, P.; Baux, G. Glutamate receptor activation triggers a calcium-dependent and SNARE protein-dependent release of the gliotransmitter D-serine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5606–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, K.; Kamiya, T.; Tsuboi, T. Gliotransmitter Release from Astrocytes: Functional, Developmental, and Pathological Implications in the Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, H.R.; Gould, T.M.; Crunelli, V. Spontaneous astrocytic Ca2+ oscillations in situ drive NMDAR-mediated neuronal excitation. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellin, T.; Pascual, O.; Gobbo, S.; Pozzan, T.; Haydon, P.G.; Carmignoto, G. Neuronal Synchrony Mediated by Astrocytic Glutamate through Activation of Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptors. Neuron 2004, 43, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angulo, M.C.; Kozlov, A.S.; Charpak, S.; Audinat, E. Glutamate Released from Glial Cells Synchronizes Neuronal Activity in the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6920–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Ascenzo, M.; Fellin, T.; Terunuma, M.; Revilla-Sanchez, R.; Meaney, D.F.; Auberson, Y.P.; Moss, S.J.; Haydon, P.G. mGluR5 stimulates gliotransmission in the nucleus accumbens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Jiang, L.; Goldman, S.A.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocyte-mediated potentiation of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Blomstrand, F.; Hanse, E. Astrocytes play a critical role in transient heterosynaptic depression in the rat hippocampal CA1 region. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perea, G.; Araque, A. Properties of Synaptically Evoked Astrocyte Calcium Signal Reveal Synaptic Information Processing by Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2192–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araque, A.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Parpura, V.; Haydon, P.G. Calcium elevation in astrocytes causes an NMDA receptor-dependent increase in the frequency of miniature synaptic currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 6822–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiacco, T.A.; McCarthy, K.D. Intracellular Astrocyte Calcium Waves In Situ Increase the Frequency of Spontaneous AMPA Receptor Currents in CA1 Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jourdain, P.; Bergersen, L.H.; Bhaukaurally, K.; Bezzi, P.; Santello, M.; Domercq, M.; Matute, C.; Tonello, F.; Gundersen, V.; Volterra, A. Glutamate exocytosis from astrocytes controls synaptic strength. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, G.; Araque, A. Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses. Science 2007, 317, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Gundersen, V.; Galbete, J.L.; Seifert, G.; Steinhäuser, C.; Pilati, E.; Volterra, A. Astrocytes contain a vesicular compartment that is competent for regulated exocytosis of glutamate. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, L.-H.; Zhou, Z. “Kiss-and-Run” Glutamate Secretion in Cultured and Freshly Isolated Rat Hippocampal Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9236–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, V.; Ni, Y.; Sunjara, V.; Hua, X.; Parpura, V. Vesicular Glutamate Transporter-Dependent Glutamate Release from Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2633–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasti, L.; Zonta, M.; Pozzan, T.; Vicini, S.; Carmignoto, G. Cytosolic calcium oscillations in astrocytes may regulate exocytotic release of glutamate. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Li, N.; Doyle, R.T.; Haydon, P.G. SNARE protein-dependent glutamate release from astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Zorec, R. Gliotransmission: Exocytotic release from astrocytes. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahn, R.; Scheller, R.H. SNAREs—Engines for membrane fusion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Liu, F.; Brethorst, S.; Jeftinija, K.; Jeftinija, S.; Haydon, P.G. Alpha-latrotoxin stimulates glutamate release from cortical astrocytes in cell culture. FEBS Lett. 1995, 360, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maienschein, V.; Marxen, M.; Volknandt, W.; Zimmermann, H. A plethora of presynaptic proteins associated with ATP-storing organelles in cultured astrocytes. Glia 1999, 26, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, R.; Perraut, M.; Chasserot-Golaz, S.; Galli, T.; Aunis, D.; Langley, K.; Grant, N.J. Cultured glial cells express the SNAP-25 analogue SNAP-23. Glia 1999, 27, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fukuda, M.; Van Bockstaele, E.; Pascual, O.; Haydon, P.G. Synaptotagmin IV regulates glial glutamate release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9441–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, I.M.; Ranjan, R.; Schwarz, T.L. Synaptotagmins I and IV promote transmitter release independently of Ca2+ binding in the C2A domain. Nature 2002, 418, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-T.; Lu, J.-C.; Bai, J.; Chang, P.Y.; Martin, T.F.J.; Chapman, E.R.; Jackson, M.B. Different domains of synaptotagmin control the choice between kiss-and-run and full fusion. Nature 2003, 424, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, S.; Han, W.; Butz, S.; Liu, X.; Fernández-Chacón, R.; Lao, Y.; Südhof, T.C. Synaptotagmin VII as a plasma membrane Ca(2+) sensor in exocytosis. Neuron 2001, 30, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Haydon, P.G. Physiological astrocytic calcium levels stimulate glutamate release to modulate adjacent neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8629–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reyes, R.C.; Parpura, V. Mitochondria modulate Ca2+-dependent glutamate release from rat cortical astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9682–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Malarkey, E.B.; Sunjara, V.; Rosenwald, S.E.; Li, W.; Parpura, V. Ca2+-dependent glutamate release involves two classes of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 76, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, D.H.; Han, K.-S.; Shim, J.W.; Yoon, B.-E.; Kim, E.; Bae, J.Y.; Oh, S.-J.; Hwang, E.M.; Marmorstein, A.D.; Bae, Y.C.; et al. TREK-1 and Best1 Channels Mediate Fast and Slow Glutamate Release in Astrocytes upon GPCR Activation. Cell 2012, 151, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, K.-S.; Woo, J.; Park, H.; Yoon, B.-J.; Choi, S.; Lee, C.J. Channel-mediated astrocytic glutamate release via Bestrophin-1 targets synaptic NMDARs. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Q.; Prussia, A.; Yu, K.; Cui, Y.; Hartzell, H.C. Regulation of Bestrophin Cl Channels by Calcium: Role of the C Terminus. J. Gen. Physiol. 2008, 132, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virginio, C.; MacKenzie, A.; Rassendren, F.A.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Anderson, C.M.; Keung, E.C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Swanson, R.A. P2X7 receptor-mediated release of excitatory amino acids from astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, O.; Takahashi, M.; Attwell, D. Modulation of extracellular glutamate concentration in rat brain slices by cystine-glutamate exchange. J. Physiol. 1999, 514 Pt 3, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, D.A.; Xi, Z.-X.; Shen, H.; Swanson, C.J.; Kalivas, P.W. The origin and neuronal function of in vivo nonsynaptic glutamate. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9134–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.M.; McFarland, K.; Melendez, R.I.; Kalivas, P.W.; Seamans, J.K. Cystine/glutamate exchange regulates metabotropic glutamate receptor presynaptic inhibition of excitatory transmission and vulnerability to cocaine seeking. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6389–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Domercq, M.; Brambilla, L.; Galli, R.; Schols, D.; De Clercq, E.; Vescovi, A.; Bagetta, G.; Kollias, G.; Meldolesi, J.; et al. CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNFα: Amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.J.; Oshima, T.; Attwell, D. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 2000, 403, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-C.; Wyeth, M.S.; Baltan-Tekkok, S.; Ransom, B.R. Functional hemichannels in astrocytes: A novel mechanism of glutamate release. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3588–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.J.; Macvicar, B.A. Connexin and pannexin hemichannels of neurons and astrocytes. Channels (Austin) 2008, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimelberg, H.K.; Goderie, S.K.; Higman, S.; Pang, S.; Waniewski, R.A. Swelling-induced release of glutamate, aspartate, and taurine from astrocyte cultures. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seki, Y.; Feustel, P.J.; Keller, R.W.; Tranmer, B.I.; Kimelberg, H.K. Inhibition of ischemia-induced glutamate release in rat striatum by dihydrokinate and an anion channel blocker. Stroke 1999, 30, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, E.R.; Kimelberg, H.K. Role of calcium in astrocyte volume regulation and in the release of ions and amino acids. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mongin, A.A.; Kimelberg, H.K. ATP regulates anion channel-mediated organic osmolyte release from cultured rat astrocytes via multiple Ca2+-sensitive mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2005, 288, C204–C213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Kang, J.; Jaiswal, J.K.; Simon, S.M.; Lin, J.H.-C.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Dienel, G.; Zielke, H.R.; et al. Receptor-mediated glutamate release from volume sensitive channels in astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16466–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiacco, T.A.; McCarthy, K.D. Multiple Lines of Evidence Indicate That Gliotransmission Does Not Occur under Physiological Conditions. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlender, D.A.; Savtchouk, I.; Volterra, A. What do we know about gliotransmitter release from astrocytes? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramham, C.R.; Torp, R.; Zhang, N.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Ottersen, O.P. Distribution of glutamate-like immunoreactivity in excitatory hippocampal pathways: A semiquantitative electron microscopic study in rats. Neuroscience 1990, 39, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A. The Mystery and Magic of Glia: A Perspective on Their Roles in Health and Disease. Neuron 2008, 60, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Landeghem, F.K.H.; Weiss, T.; Oehmichen, M.; Deimling, A. Von Decreased Expression of Glutamate Transporters in Astrocytes after Human Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2006, 23, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesce, S.; Bezzi, P.; Rossi, D.; Meldolesi, J.; Volterra, A. HIV-1 gp120 glycoprotein affects the astrocyte control of extracellular glutamate by both inhibiting the uptake and stimulating the release of the amino acid. FEBS Lett. 1997, 411, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldon, A.L.; Robinson, M.B. The role of glutamate transporters in neurodegenerative diseases and potential opportunities for intervention. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Van Kammen, M.; Levey, A.I.; Martin, L.J.; Kuncl, R.W. Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Patel, S.; Regan, M.R.; Haenggeli, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Jin, L.; Dykes Hoberg, M.; Vidensky, S.; Chung, D.S.; et al. β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 2005, 433, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Foster, J.B.; Lin, C.L.G. Glutamate transporter EAAT2: Regulation, function, and potential as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, D.; Werner, P.; Raine, C.S. Glutamate excitotoxicity in a model of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, P.; Pitt, D.; Raine, C.S. Multiple sclerosis: Altered glutamate homeostasis in lesions correlates with oligodendrocyte and axonal damage. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waubant, E.; Maghzi, A.-H.; Revirajan, N.; Spain, R.; Julian, L.; Mowry, E.M.; Marcus, J.; Liu, S.; Jin, C.; Green, A.; et al. A randomized controlled phase II trial of riluzole in early multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillis, J.W.; O’Regan, M.H. Mechanisms of glutamate and aspartate release in the ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1996, 730, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewer, C.; Gameiro, A.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, Z.; Braams, S.; Rauen, T. Glutamate forward and reverse transport: From molecular mechanism to transporter-mediated release after ischemia. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, T.; Kafitz, K.W.; Roderigo, C.; Rose, C.R. Ammonium-evoked alterations in intracellular sodium and pH reduce glial glutamate transport activity. Glia 2009, 57, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtholt-Gompf, A.J.; Walther, H.V.; Adams, M.A.; Carlezon, W.A.; Ongür, D.; Cohen, B.M.; Cohen, B.M. Blockade of astrocytic glutamate uptake in rats induces signs of anhedonia and impaired spatial memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, Glutamate and Glia: A Trio of Trouble in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanacora, G.; Kendell, S.F.; Levin, Y.; Simen, A.A.; Fenton, L.R.; Coric, V.; Krystal, J.H. Preliminary Evidence of Riluzole Efficacy in Antidepressant-Treated Patients with Residual Depressive Symptoms. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarate, C.A.; Payne, J.L.; Quiroz, J.; Sporn, J.; Denicoff, K.K.; Luckenbaugh, D.; Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. An Open-Label Trial of Riluzole in Patients With Treatment-Resistant Major Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of excitotoxic neuronal death. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. The NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as a symptomatological and neuroprotective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: Preclinical evidence. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2003, 18, S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndountse, L.T.; Chan, H.M. Role of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in polychlorinated biphenyl mediated neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 184, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAN, M.; RAYMOND, L. N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor function and excitotoxicity in Huntington’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, P.; Bogaert, E.; Dewil, M.; Hersmus, N.; Kiraly, D.; Scheveneels, W.; Bockx, I.; Braeken, D.; Verpoorten, N.; Verhoeven, K.; et al. Astrocytes regulate GluR2 expression in motor neurons and their vulnerability to excitotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14825–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Liang, Z.-Q.; Wu, J.-C.; Zhang, X.-D.; Gu, Z.-L.; Qin, Z.-H. An autophagic mechanism is involved in apoptotic death of rat striatal neurons induced by the non-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor agonist kainic acid. Autophagy 2008, 4, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.-L.; Cao, Y.; Liang, Z.-Q.; Han, R.; Bennett, M.C.; Qin, Z.-H. Lysosomal enzyme cathepsin B is involved in kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity in rat striatum. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.K. CALCIUM: A Role for Neuroproduction and Sustained Adaptation. Mol. Interv. 2006, 6, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.G.; Pathan, N.; Ethell, I.M.; Krajewski, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Shibasaki, F.; McKeon, F.; Bobo, T.; Franke, T.F.; Reed, J.C. Ca2+-induced apoptosis through calcineurin dephosphorylation of BAD. Science 1999, 284, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, R.A. A “protease activation cascade” in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 924, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.K. Calpain and caspase: Can you tell the difference? Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Lenart, B.; Kintner, D.B.; Sun, D. Na-K-Cl cotransporter contributes to glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Olney, J.W.; Lukasiewicz, P.D.; Almli, T.; Romano, C. Ca2+-independent excitotoxic neurodegeneration in isolated retina, an intact neural net: A role for Cl− and inhibitory transmitters. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, D.G. Mitochondrial dysfunction and glutamate excitotoxicity studied in primary neuronal cultures. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, T.; Farooqui, A.A. Aging: An important factor for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, S.A.; Choi, Y.-B.; Pan, Z.-H.; Lei, S.Z.; Chen, H.-S.V.; Sucher, N.J.; Loscalzo, J.; Singel, D.J.; Stamler, J.S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 1993, 364, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, M.; Omote, K.; Ninomiya, T. Direct evidence for the role of nitric oxide on the glutamate-induced neuronal death in cultured cortical neurons. Brain Res. 1998, 780, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchen, M.R. Roles of mitochondria in health and disease. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. 1), S96–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrenius, S. Mitochondrial regulation of apoptotic cell death. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 149, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izrael, M.; Slutsky, S.G.; Admoni, T.; Cohen, L.; Granit, A.; Hasson, A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Krush Paker, L.; Kuperstein, G.; Lavon, N.; et al. Safety and efficacy of human embryonic stem cell-derived astrocytes following intrathecal transplantation in SOD1G93A and NSG animal models. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbeito, L. Astrocyte-based cell therapy: New hope for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, S.; Gharagozloo, M.; Simard, C.; Gris, D. Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells 2019, 8, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
Mahmoud S, Gharagozloo M, Simard C, Gris D. Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells. 2019; 8(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Shaimaa, Marjan Gharagozloo, Camille Simard, and Denis Gris. 2019. "Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release" Cells 8, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
APA StyleMahmoud, S., Gharagozloo, M., Simard, C., & Gris, D. (2019). Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells, 8(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184